GitHub Deployment
Introduction
GitHub integration is intended to improve the CI/CD experience on Hasura Cloud. With GitHub integration, you can link a GitHub repository and a branch to a Hasura Cloud project and automatically deploy Metadata and Migrations in a given directory to the linked project.
Check out our Starter Kit to see a few example workflows.
Deployment modes
Automatic Deployment Mode
With the Automatic deployment mode, Hasura Cloud automatically triggers a deployment for every commit pushed to the
GitHub repository from the given branch and directory.
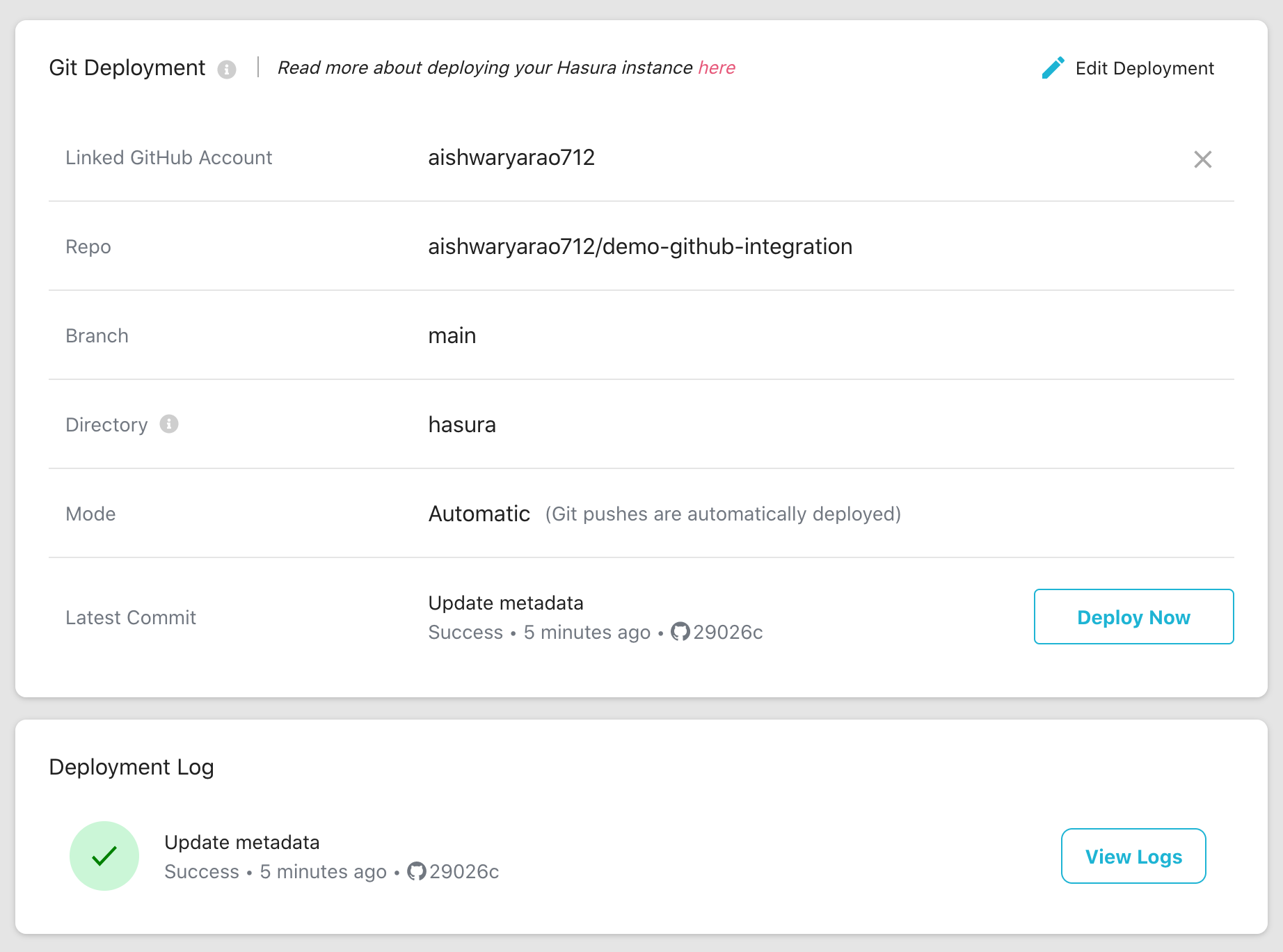
The Automatic deployment mode also has the Deploy Now button which allows the user to retry deploying the latest
commit.
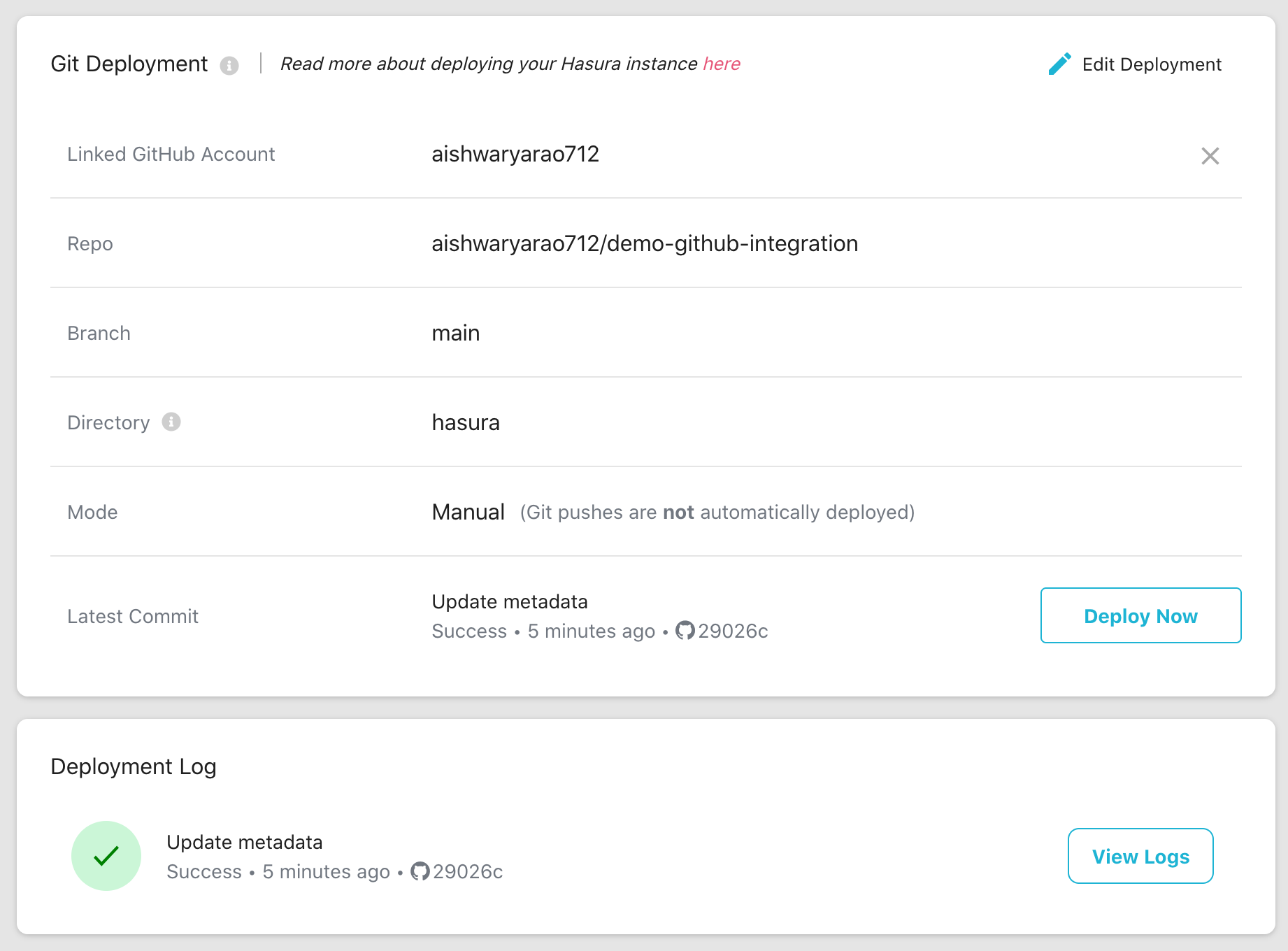
Manual Deployment Mode
With Manual deployment mode, Hasura Cloud does not automatically deploy the commits pushed to the configured branch.
The deployment of the latest commit in that branch can be triggered manually by clicking the Deploy Now button.
Initial setup
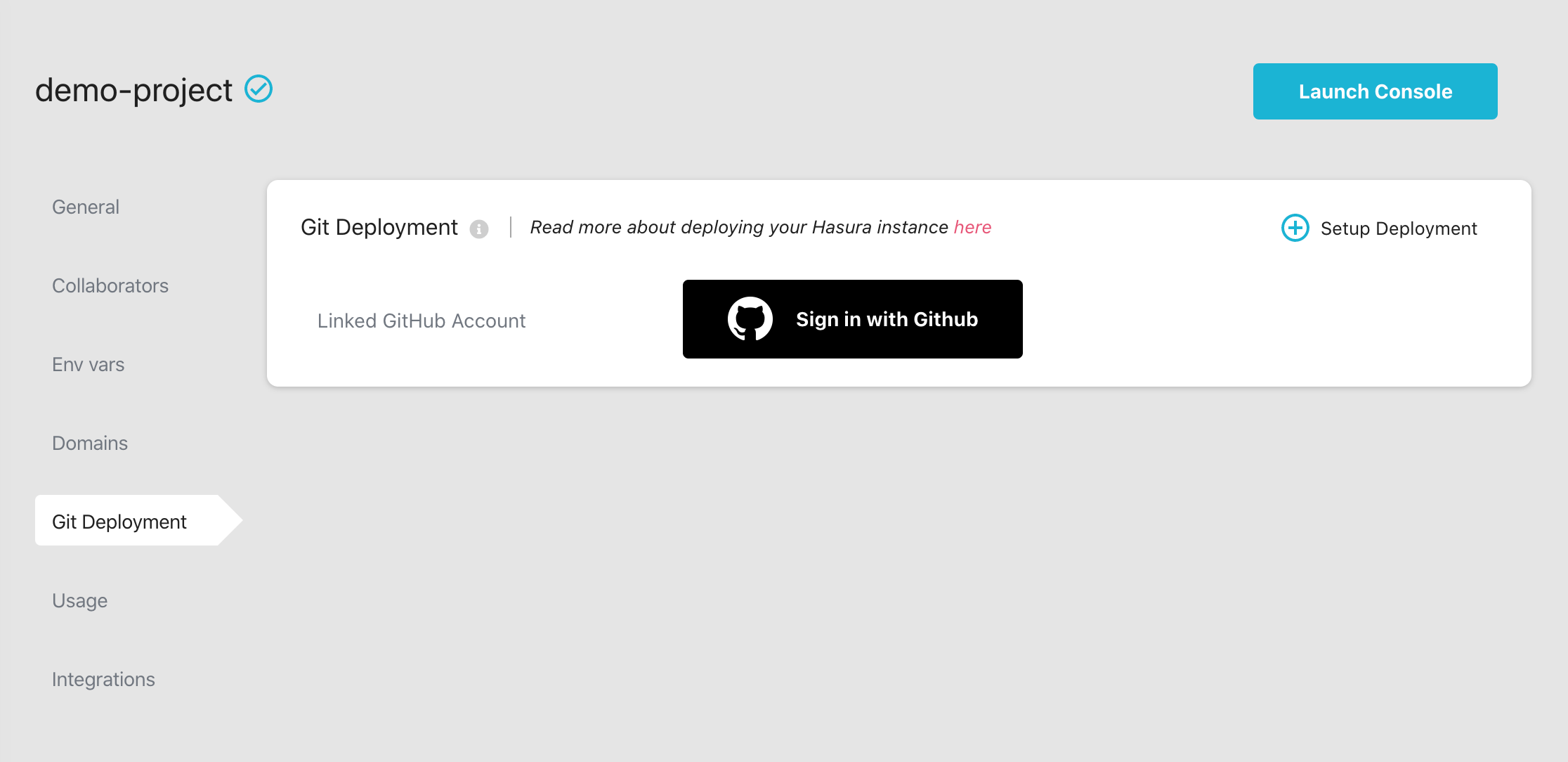
Link GitHub account to a Hasura Cloud project
To link a GitHub account, click on the Sign in with GitHub button in the Git Deployment section of the project
details.
When you link a new GitHub account, Hasura Cloud installs the Hasura Cloud GitHub App on your GitHub account. While authenticating, you can choose to grant access to all repositories or to specific repositories only.
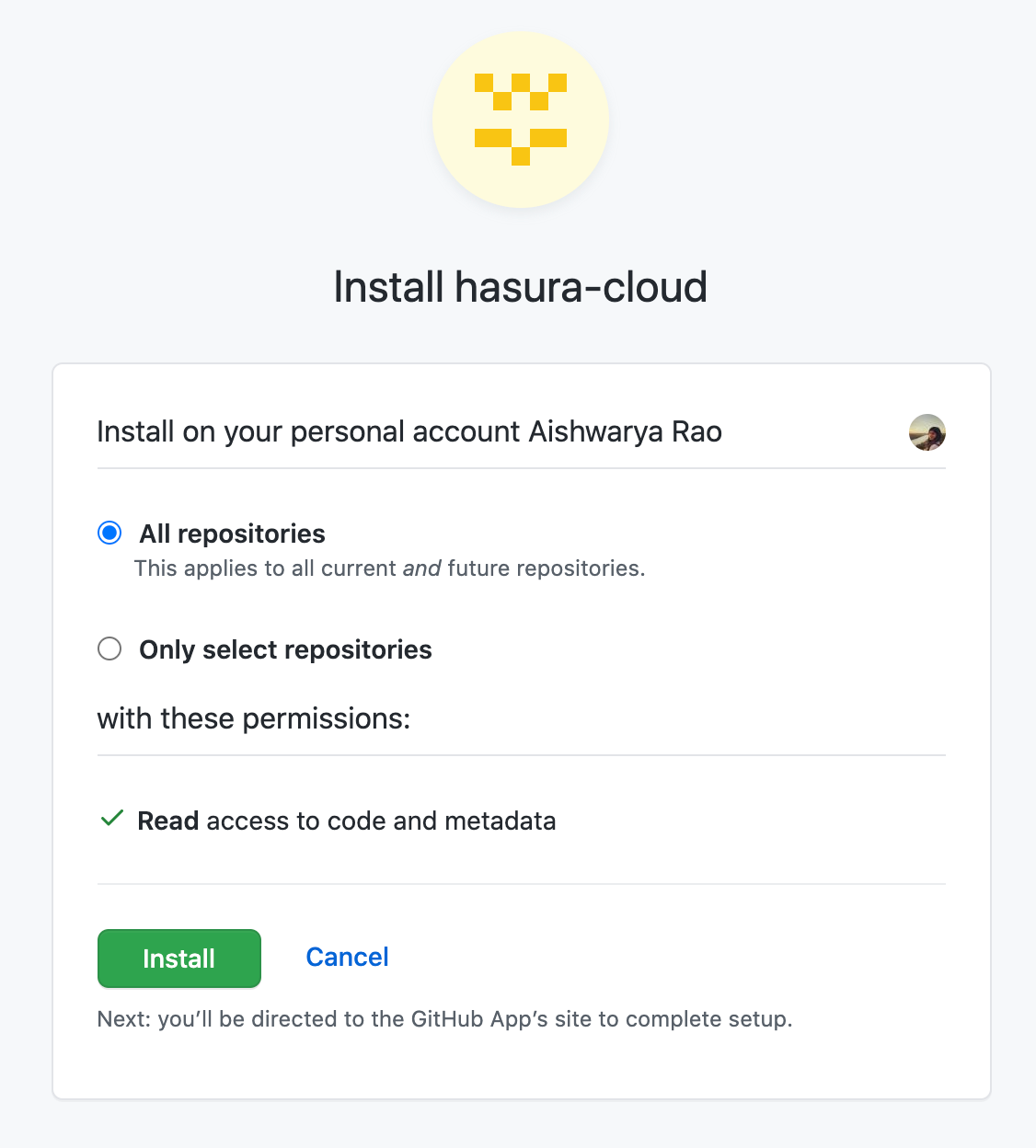
The permissions requested by Hasura Cloud can be viewed in the GitHub app settings once you install the app.
Once linked, the GitHub account with the granted scope becomes available to all the admins on the project as the session is used to manage the GitHub integration from the UI.
Setup GitHub repo with Hasura project Metadata
You'll need to set up a GitHub repository with the current Metadata of your Hasura project. This will become the starting point of the version control of the Metadata. If the repository is empty, the GitHub integration will result in loss of your existing Metadata on Hasura Cloud.
Within your local Hasura project's directory, if not already done, initialize a git repository. Then, run the following command via the Hasura CLI:
hasura metadata export --admin-secret <your-project-admin-secret> --endpoint <your-hasura-cloud-project-url>
This will export your project's Metadata to the metadata directory in your project directory in YAML format. Add and
commit these changes to git. Then, push the changes to your GitHub repository.
Once the GitHub integration is set-up, refrain from making changes in your Cloud project using Console. All the changes
to your project now should be executed by the version control process. If you have made a change directly in the Cloud
Console for any reason, please follow the metadata export command above and update your version control with the
latest Metadata. Otherwise, you may lose the manual changes in your project the next time GitHub integration runs.
You can learn more in our Metadata Best Practices guide.
Integrate GitHub repo with a Hasura Cloud project
Specify the GitHub repository, branch and the hasura-project directory in the form as shown below.
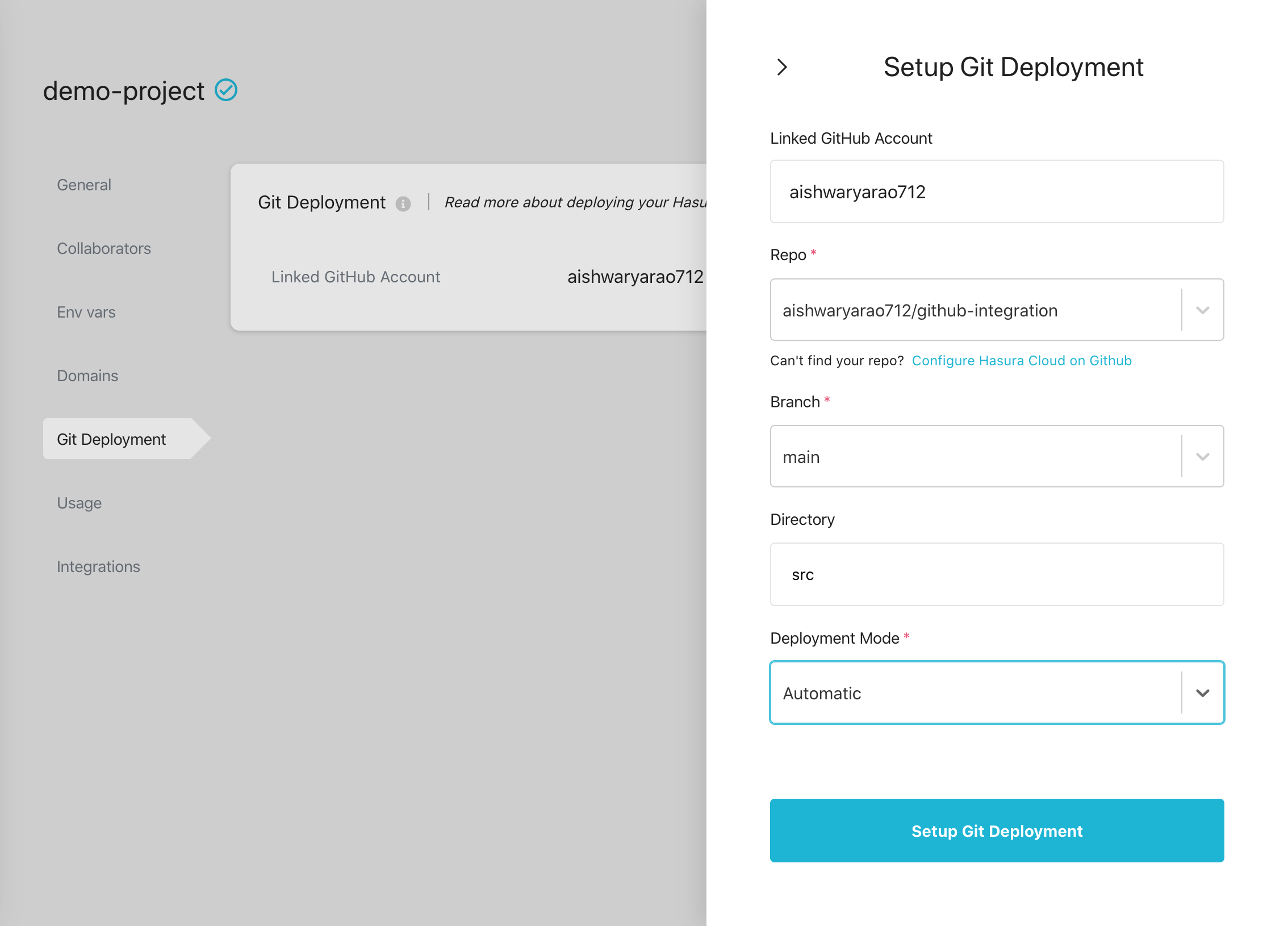
If the repository that you're looking for doesn't show up in the repository list, click
Configure Hasura Cloud on GitHub to grant access to the required repository.
Clicking on the Setup Git Deployment button integrates the specified GitHub repository, branch and directory with the
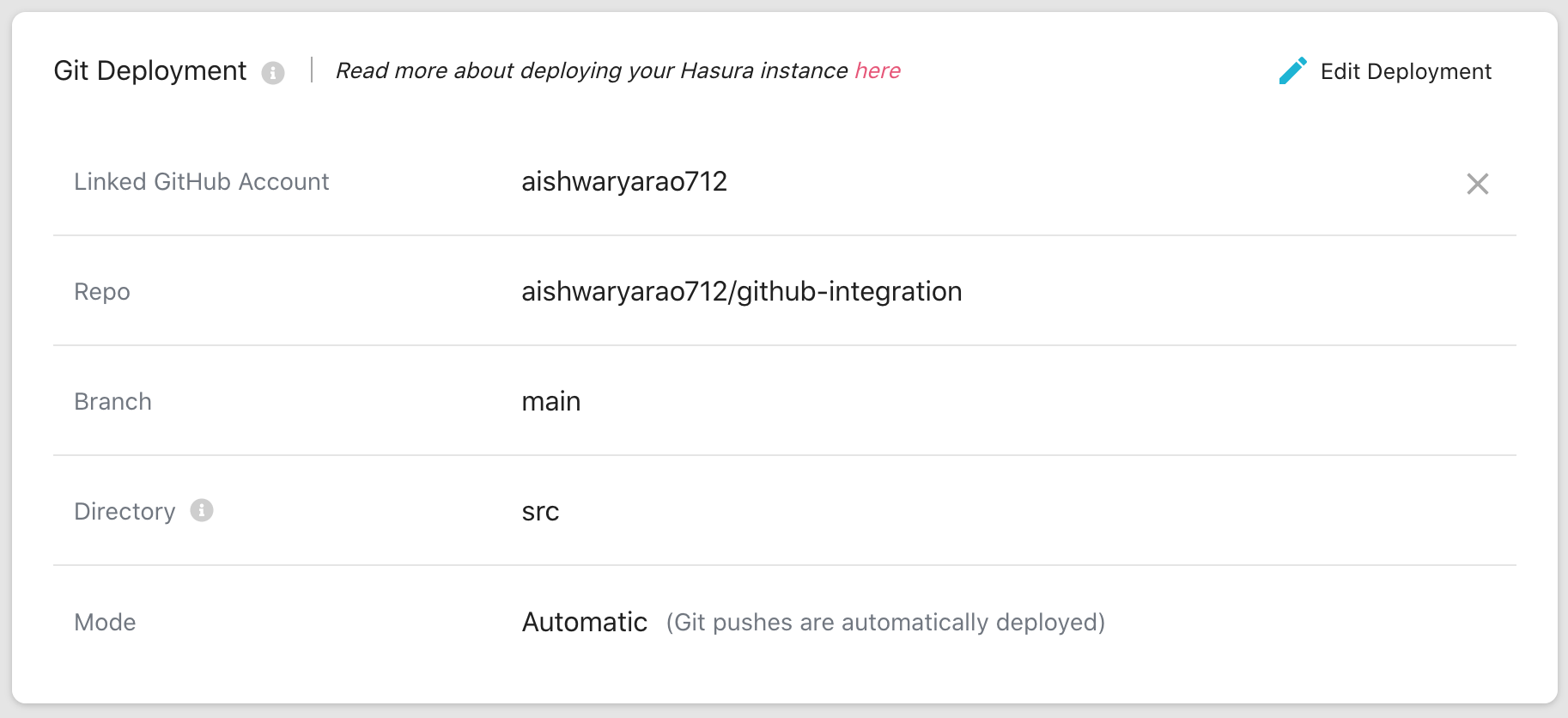
Hasura Cloud project. The details for the integration can be viewed in the Git Deployment section of project details.
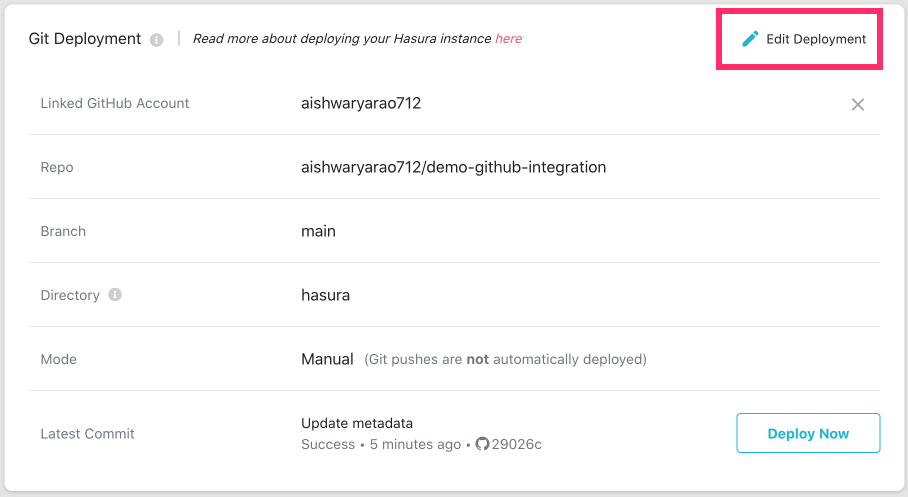
Edit GitHub Integration
Click on the Edit Deployment button in the GitHub Deployment section to edit the GitHub
repository/branch/directory/deployment mode for the GitHub integration.
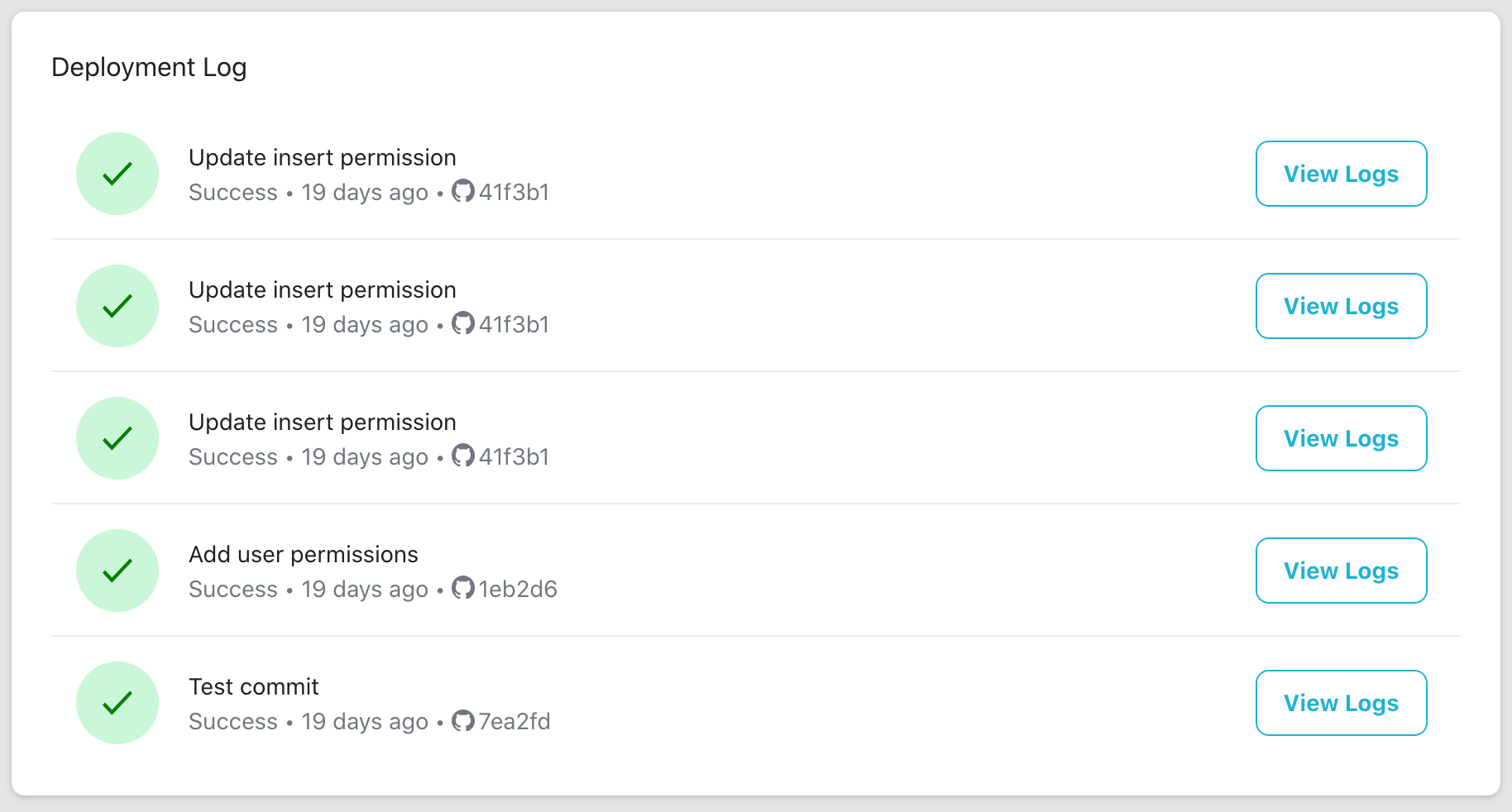
Deployment Log
User can view the deployed commits and their deployment status in the Deployment Log section of Git Deployment.
Deployment Process
Once a commit deployment is triggered, the progress for a commit can be tracked by clicking on the View Logs button in
the Deployment Log section.
Refer to the following task wise breakdown of the deployment job to understand what the job will be doing.
Check the troubleshooting section below and do reach out to support if you observe any issues with the deployment process or run into any other problems post the deployment.
Deployment sub-tasks
The following is a task wise breakdown of the commit deployment job.
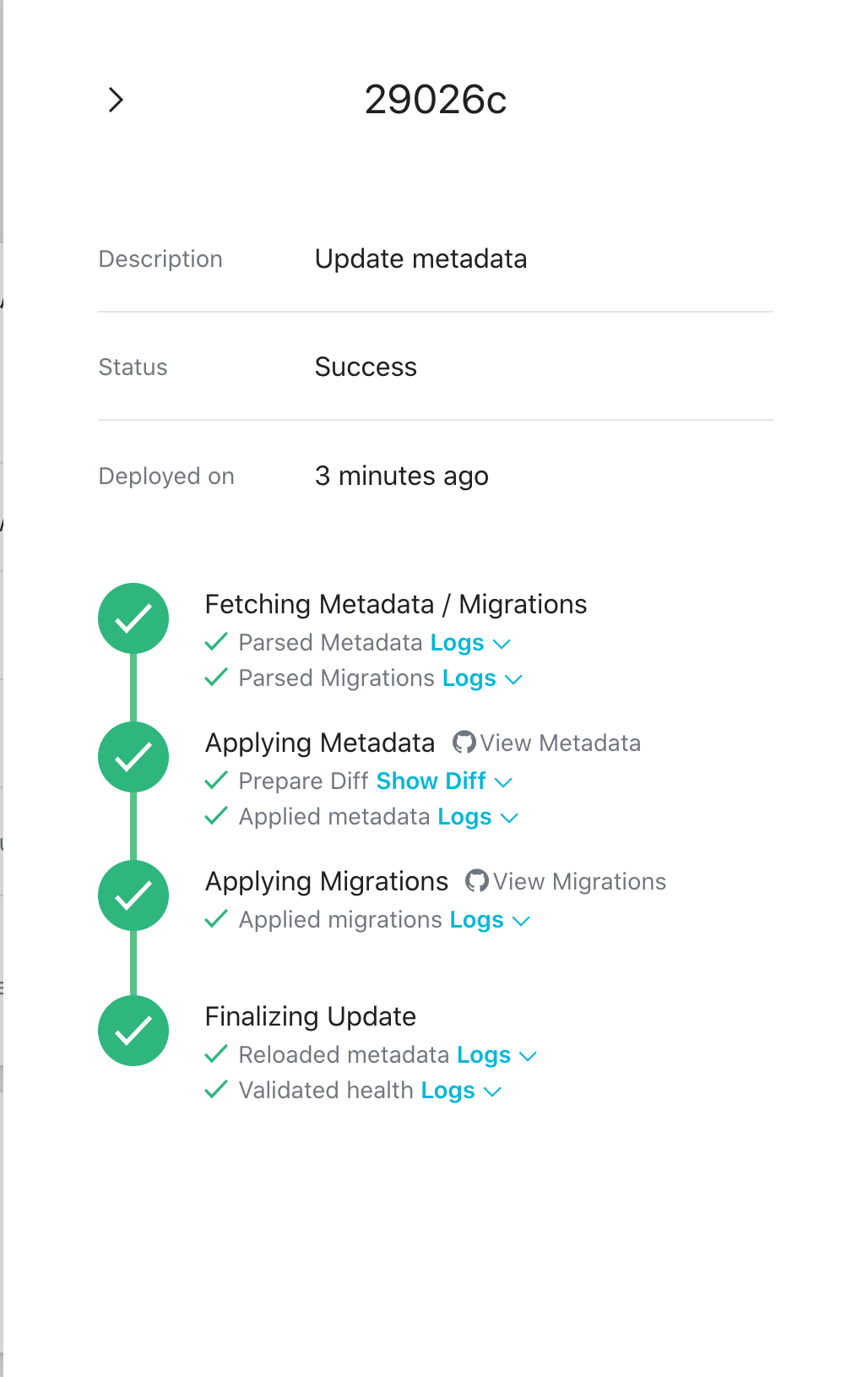
Each task in the deployment has realtime logs and can be viewed by clicking on the Logs option for each
successful/failed step.
Step 1: Fetching Metadata / Migrations
The Metadata and Migrations are fetched from the GitHub repository and validated.
Step 2: Applying Metadata
The Metadata in the GitHub repository is applied to the server.
Step 3: Applying Migrations
The Migrations in the GitHub repository are applied to your data sources.
Step 4: Finalizing Update
The Metadata on the server is reloaded and project health is verified before finalizing the update.
Things to check before running your first deployment
You need to ensure the your Cloud project has been appropriately set up to execute the deployment.
- Ensure all the required Hasura config related and any other custom ENV vars that might be used in the Metadata are added to your Cloud project as well.
- Ensure that you have connected the required database(s) with the right name and connection params as you have in the Metadata to the Cloud project.
- Follow the steps in our Metadata Best Practices guide to ensure that your Metadata is in the right format and structure.
Troubleshooting failures
If a deployment fails, depending on the kind of error, you can fix it by retrying the deployment by either updating your Metadata and Migrations with a fix and pushing a commit to deploy again or by just redeploying the failed commit after making any required fixes to your project.
The following are some troubleshooting steps to fix some possible errors in the deployment sub-tasks:
Error parsing Metadata
- Nothing has been modified on your project yet so there will be no service impact.
- Typically happens due to some issue with the Metadata directory structure or the format of the Metadata files.
- Check the reported error message and fix the issues in the Metadata. See Metadata format.
- Push the fix to GitHub to redeploy.
Error parsing Migrations
- Nothing has been modified on your project yet so there will be no service impact.
- Typically happens due to some issue with the Migration directory structure or the format of the Migration files.
- Check the reported error message and fix the issues in the Migrations. See Migrations format.
- Push the fix to GitHub to redeploy.
Error applying Metadata
- Nothing has been modified on your project yet so there will be no service impact.
- Typically happens due to some invalid Metadata (e.g. due to type mismatches, missing required keys, etc.) trying to be applied.
- Check the reported error message and fix the issues in the Metadata. See Metadata format.
- Push the fix to GitHub to redeploy.
Error applying Migrations
As your Metadata has already been applied but applying your Migrations have failed, your project might be in an unhealthy state. If your Migrations and Metadata had only incremental changes, i.e. no existing objects were modified, you likely won’t have any service impact because existing parts of your Metadata are likely to be still valid and your existing functionality will be working as it were.
Look at the underlying database error. Make the appropriate fix depending on the error and redeploy.
Some common errors:
source with name “default” is inconsistent
In this situation, most likely either the target project doesn't have the required database connected or the ENV VARS or the database name used to connect the database is not matching in your source and target projects.
To fix this, use the same ENV VARS and connect the database with the same name in both your projects.
“relation '<some-object>' already exists”In such situations when you get errors of tables or other objects already existing, this might be because the Migration might have been already applied on the database and the project was not yet aware of it.
To fix this, use the Hasura CLI command
hasura migrate apply --skip-execution --version <migration_version> --endpoint "<cloud_project_endpoint>"to mark the Migration as already applied on the project. Then redeploy the failed commit to continue with further steps.version check: failed to get version from serverIn such situations, the project has inconsistent Metadata and has issues connecting to the server.
To fix this, try reloading the Metadata and confirming all required ENV VARS for the project are available. If the issue persists, please contact the Hasura Help Center.
Error code: 520If you encounter an error code of
520after attempting to apply migrations, this is likely due to a long-running process. This issue can arise in various database systems when certain actions require exclusive access to data structures, such as tables or rows.For example, in PostgreSQL, operations that require an
ACCESS EXCLUSIVElock can lead to this error. Such locks are commonly needed when performing actions like adding columns. More about PostgreSQL’s explicit locking can be found in their documentation on explicit locking.In these cases, it's helpful to create a new table with any new columns / changed column types, insert your data to the new table, and then drop the old table and rename the new one to match the now deprecated table.
Inconsistent Metadata after finalizing update
- It is possible your project might be in an unhealthy state depending on which Metadata objects are inconsistent and what Migrations were applied. If your Metadata and Migrations had only incremental changes, i.e. no existing objects were modified, you likely won’t have any service impact because existing parts of your Metadata are likely to be still valid and your existing functionality will be working as it was.
- Check the logs under
Applying MigrationsandFinalizing Update. - In the situation that the applied Metadata applied was indeed incorrect, fix the Metadata and push a new commit to redeploy.
- If objects depending on upstream services are inconsistent, e.g. Remote Schemas, the upstream service might be unavailable or inconsistent. In this case please fix them and redeploy the commit.
- If database objects are inconsistent with errors such as Inconsistent object: no such table/view exists in source:
<table-name>, it could be because:- a Migration might have been skipped as the project believes its already been applied though its not the case. To fix
it, mark the Migration as unapplied using the following Hasura CLI command
hasura migrate delete --version <migration_version> --server --database-name <database-name> --endpoint <cloud_project_endpoint>and redeploy the commit. - a Migration to create the database objects might be missing completely. To fix this create a new Migration for creation of the missing objects and push a new commit to redeploy.
- a Migration might have been skipped as the project believes its already been applied though its not the case. To fix
it, mark the Migration as unapplied using the following Hasura CLI command
- A rollback can be done to the previous functioning state of Metadata by reverting your Metadata changes on your branch and then pushing to redeploy.