Connecting Hasura to an Azure Postgres Database
Introduction
This guide explains how to connect a new or existing Azure Postgres database to a Hasura instance, either on Hasura Cloud or via one of our self-hosted solutions. If you're exploring Azure Postgres and are interested in migrating an existing Postgres database - such as from Heroku - check out their docs before continuing below.
If you plan on using Hasura Cloud, which we recommend, follow steps 1 and 2 below. If you're self-hosting a Hasura instance and already have a project running, skip to step 3.
Step 1: Sign up or log in to Hasura Cloud
Navigate to Hasura Cloud and sign up or log in.
Step 2: Create a Hasura Cloud project
On the Hasura Cloud dashboard, create a new project:
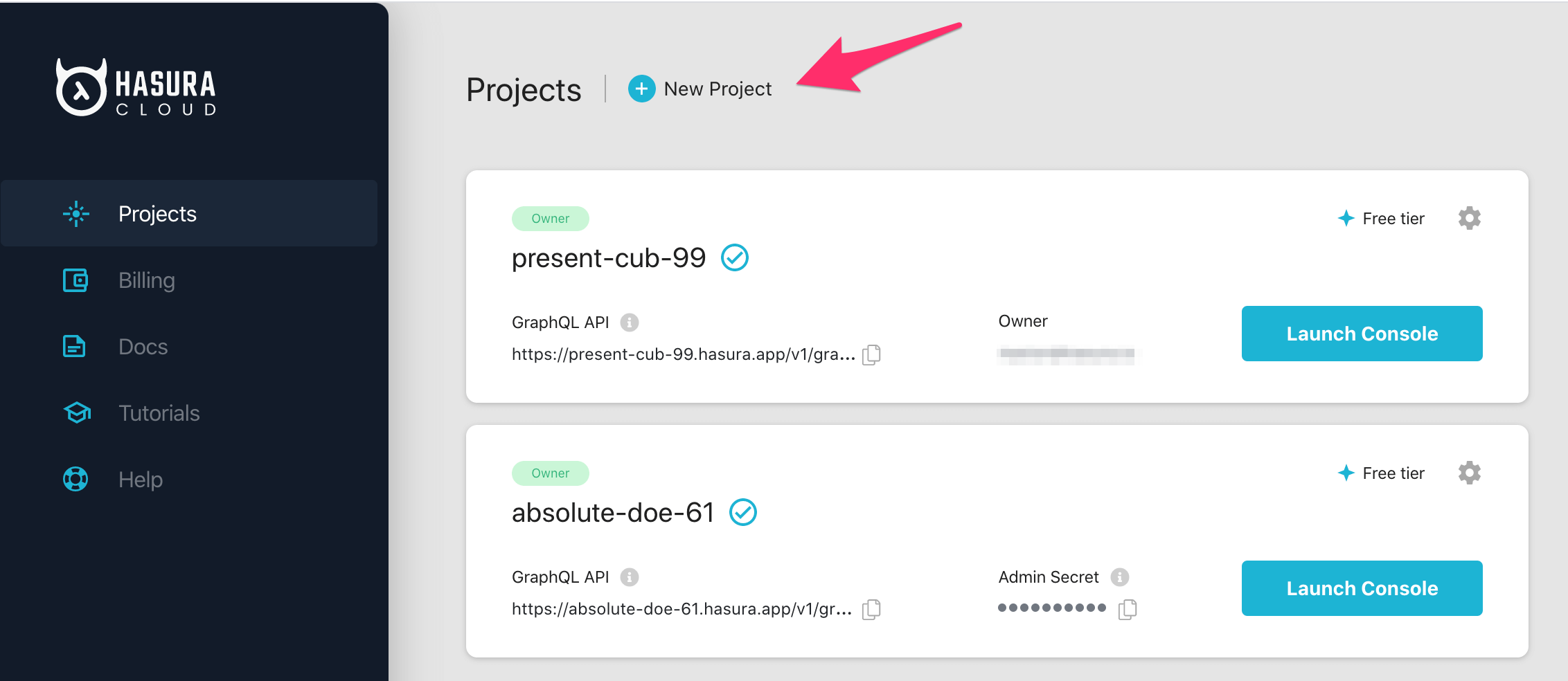
After the project is initialized successfully, click on Launch Console to open the Hasura Console in your browser.
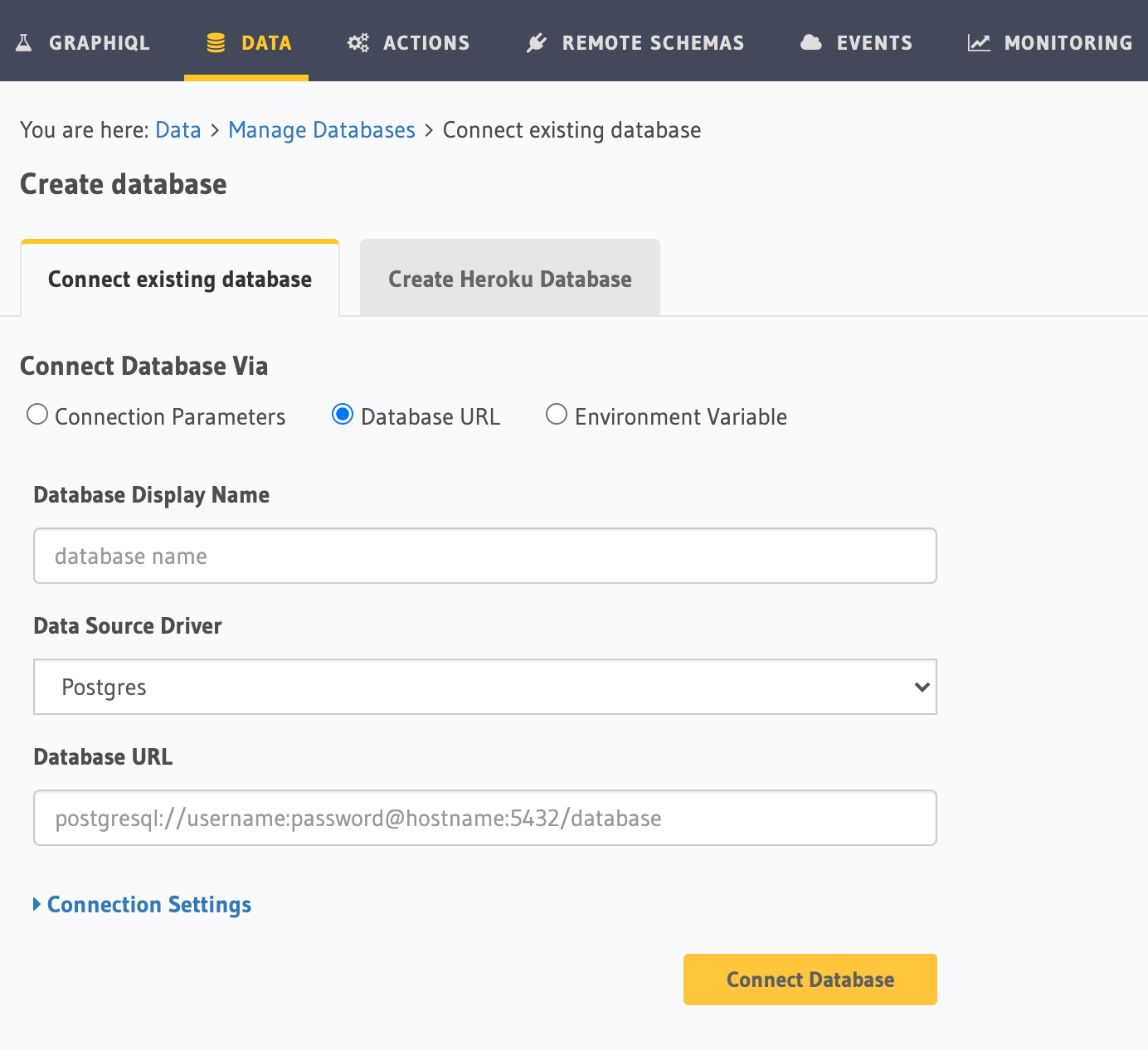
On the Hasura Console, navigate to the Data tab and choose Connect Existing Database. Hasura will prompt you for a
Postgres Database URL. We'll create this in the next step and then come back here.
Step 3: Create a Postgres DB on Azure
Log into the Azure portal.
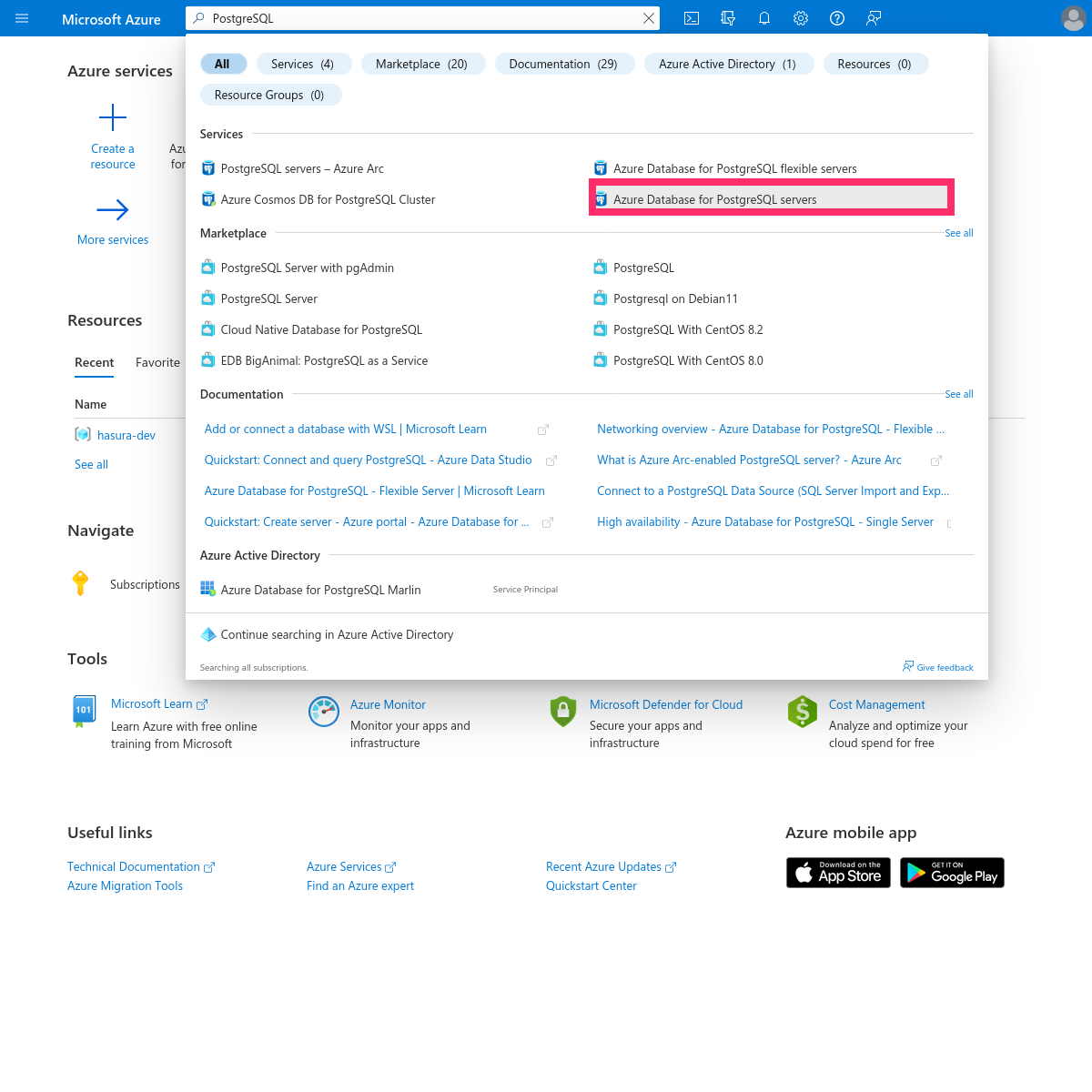
On the Azure portal, type "postgres" in the search window and choose Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers:
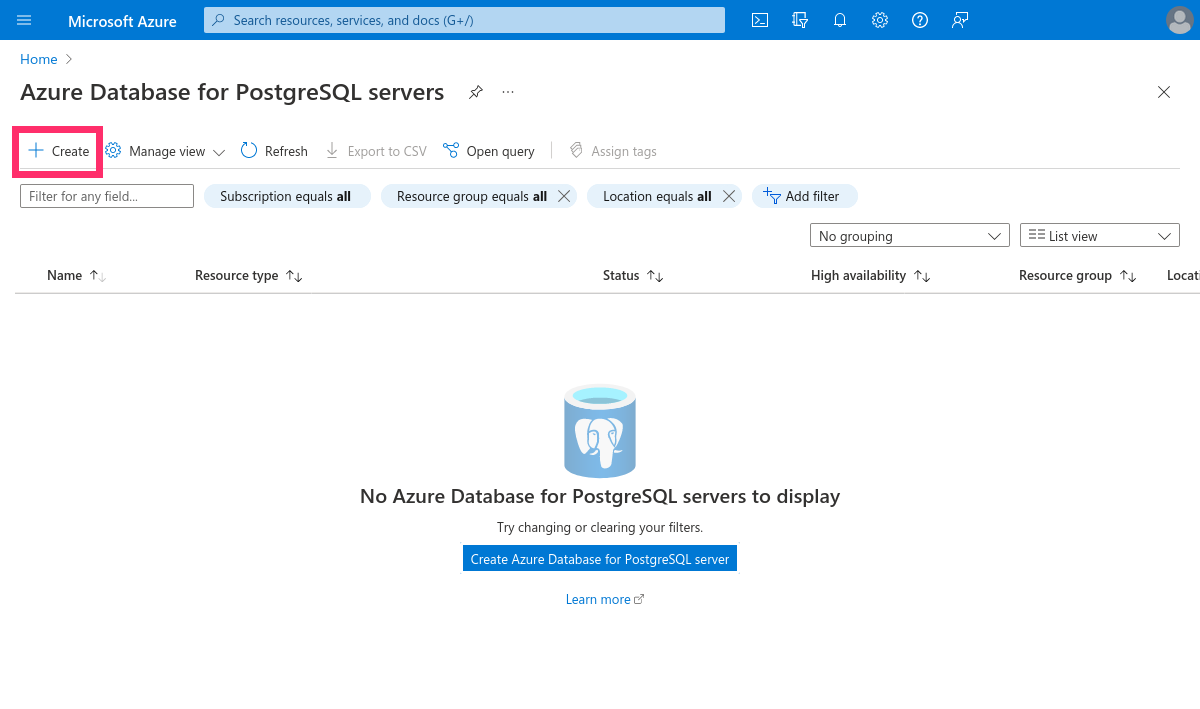
Click the + Create button to create a new Postgres database:
Choose the plan that fits your requirements. For this tutorial, we'll choose Flexible server:
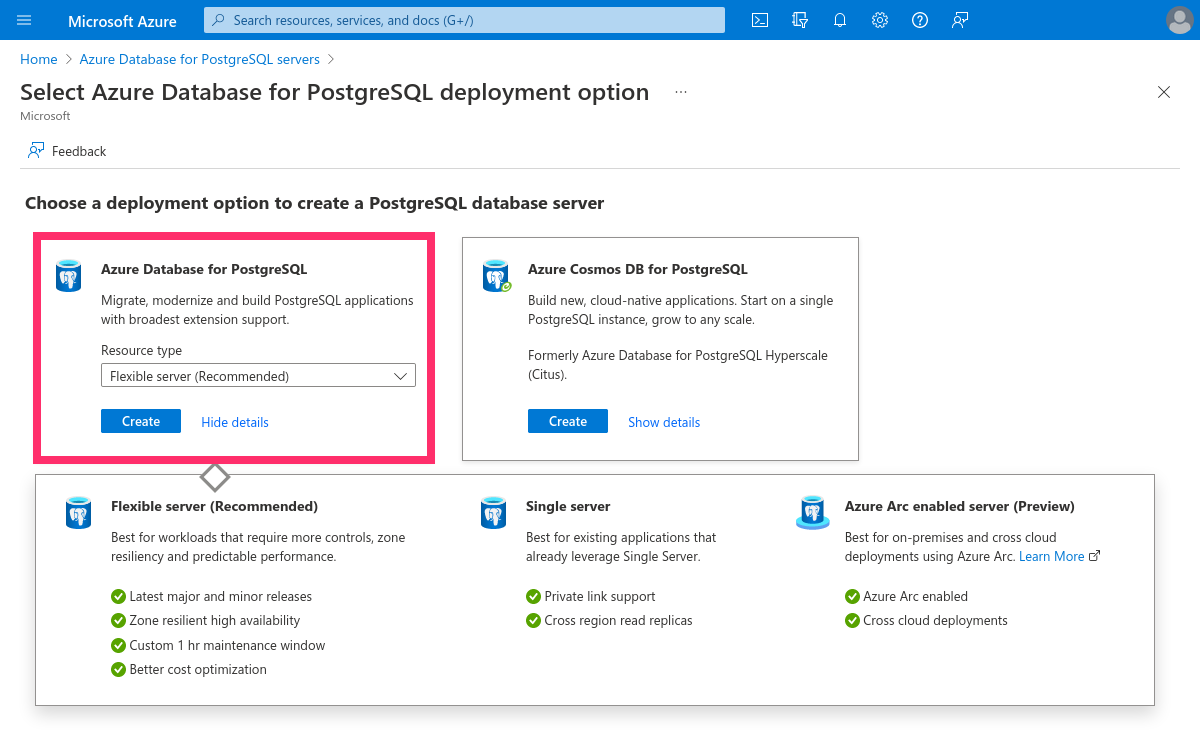
Configure your database with all required fields:
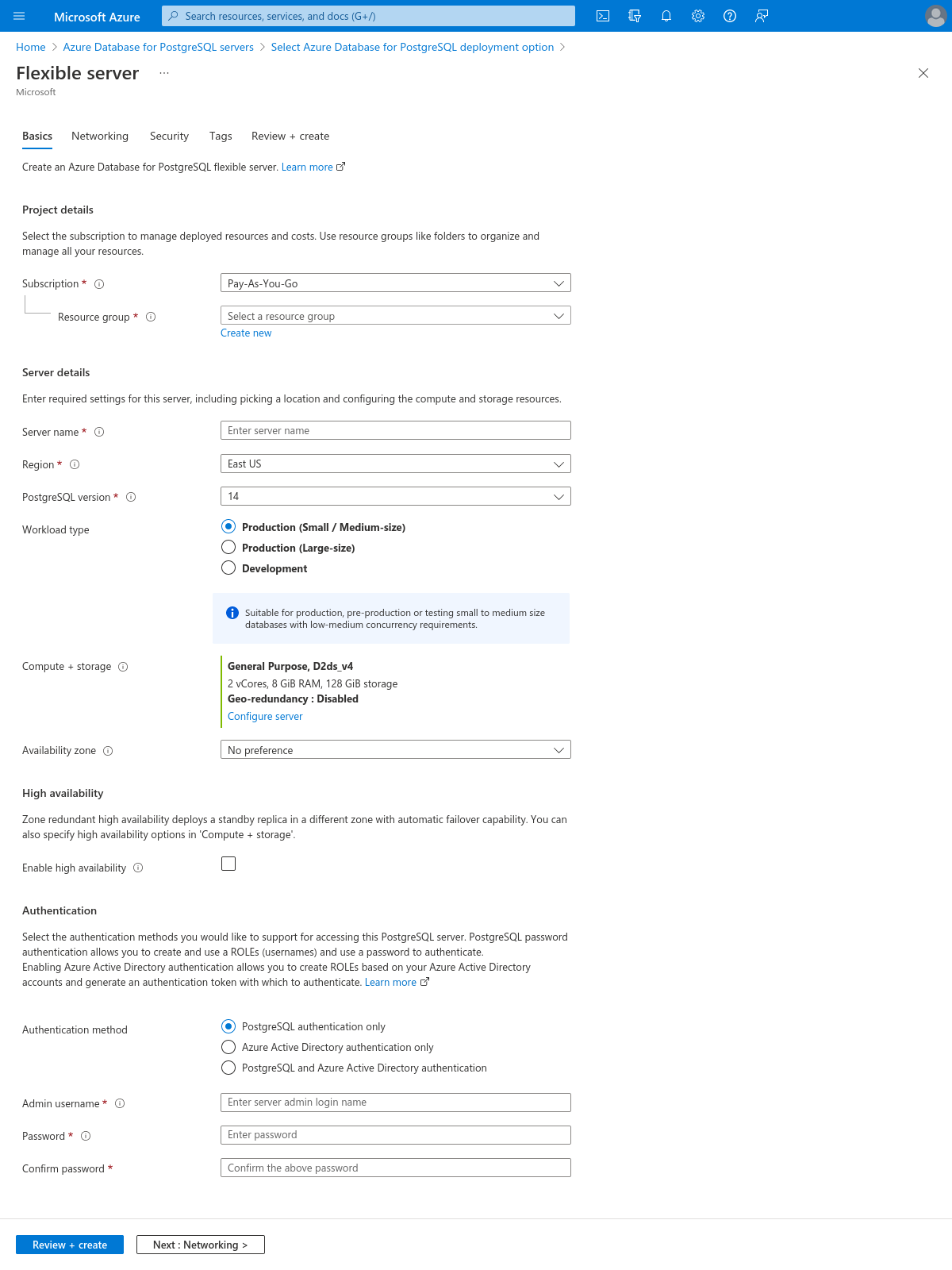
Then click Next : Networking >.
Step 4: Allow connections to your DB from Hasura
If you're using Hasura Cloud, you can quickly find your IP address from the Hasura Cloud IP field on the project's
details view:
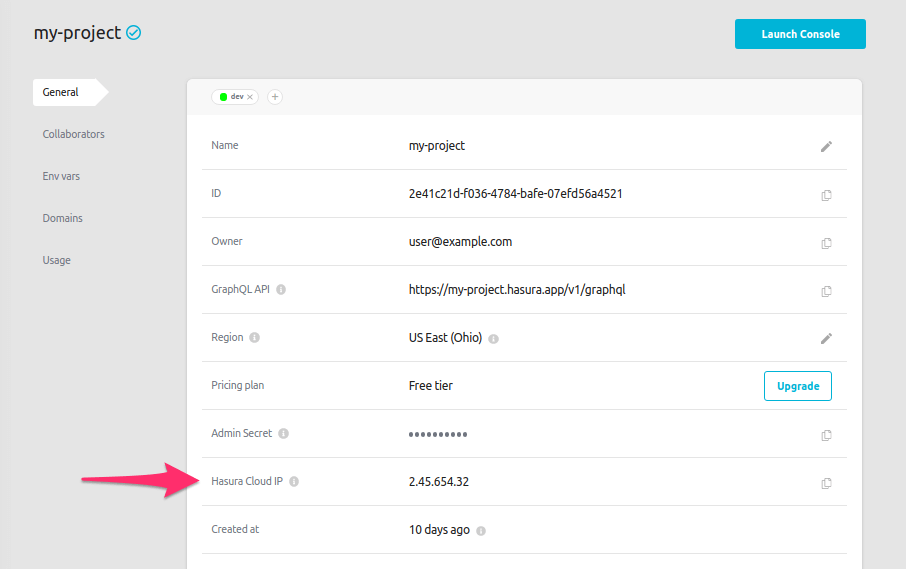
If you're using a self-hosted solution, you'll need to determine the IP address manually depending on your hosting service.
Add the Hasura IP address that you copied:
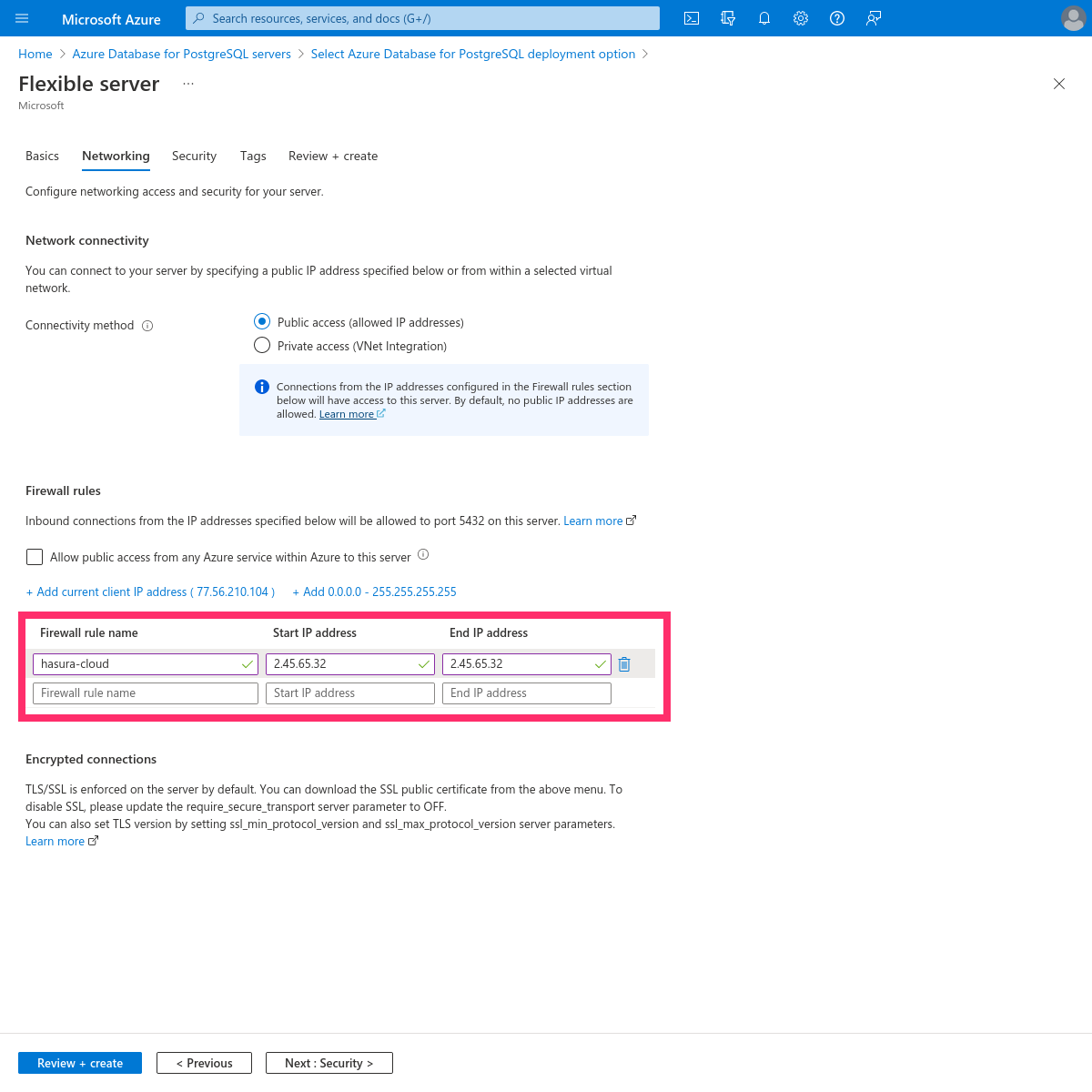
Then click Save on the top left.
Optionally, select Allow public access from any Azure service within Azure to this server, if you require intra-Azure
connectivity.
Finally, click Review + create to review your settings, and if you're happy, create the database.
If you're using a database user other than the default one, make sure to give it the right Postgres permissions.
For Azure flexible server, Hasura v1.x does not work with
JIT turned on. JIT can be turned off from Azure
console. Hasura v2.x works fine with JIT enabled.
Step 5: Construct the database connection URL
The structure of the database connection URL looks as follows:
postgresql://<user-name>:<password>@<public-ip>:<postgres-port>/<db>
On the database dashboard, click on Overview:
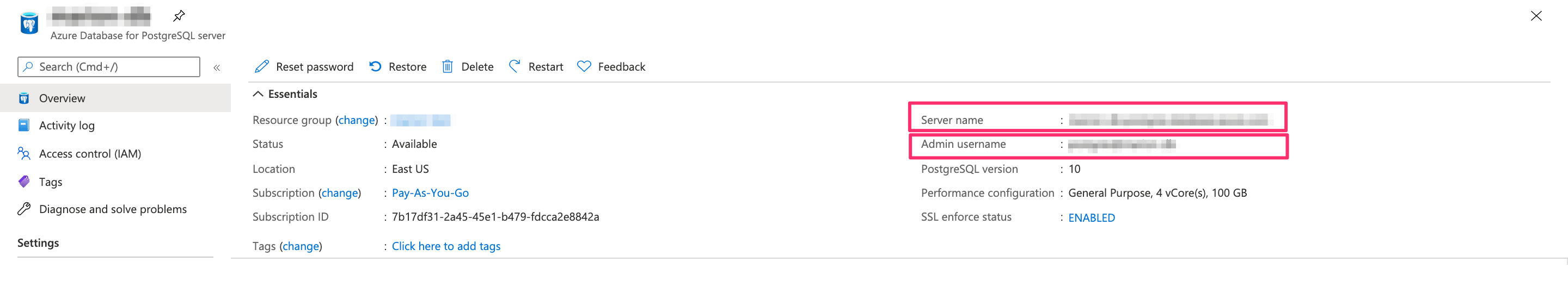
user-name: If you have a separate database user, the user name will be their name. If you didn't specify a user, use theAdmin username(see screenshot above). Note: you need to escape the@. Replace it with%40.password: If you have a separate database user, use their password. Otherwise, use the password that you chose when creating the database.public-ip: On the screenshot above, theServer nameis the public IP.postgres-port: The default port for Postgres is5432.db: The DB ispostgresby default unless otherwise specified.
Step 6: Finish connecting the database
Back on the Hasura Console, enter the database URL that we retrieved in step 5:
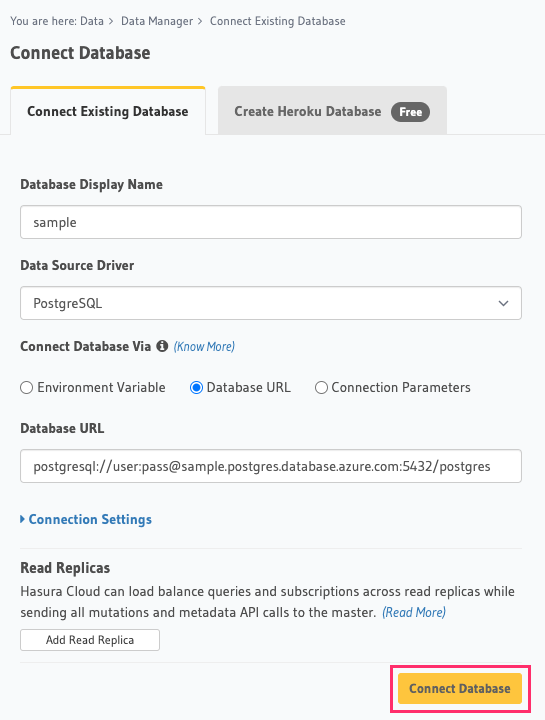
Then click Connect Database.
For security reasons, it is recommended to set database URLs as env vars and using the env vars to connect to the databases in place of the raw database URLs.
Voilà. You are ready to start developing.
Next steps
You can check out our 30-Minute Hasura Basics Course and other GraphQL & Hasura Courses for a more detailed introduction to Hasura.
If using Hasura Cloud, you can also click the gear icon to manage your Hasura Cloud project. (e.g. add collaborators, env vars or custom domains).
For more information on which Postgres features we support, check out this page.