Quickstart with Hasura Cloud
Introduction
Hasura Cloud is a powerful tool that can work with a wide variety of databases. If you have a preferred database, check out our supported databases for details on how to connect.
If you're just getting started with Hasura, you can also try out our free Neon Postgres database. We'll walk you through the setup process in this guide, so you can get started quickly and easily.
If you're not sure what you want to build with Hasura, check out our sample use cases for inspiration, and we'll walk you through the setup step-by-step!
Step 1: Create an account
Navigate to cloud.hasura.io, and create a new Hasura Cloud account.
Step 2: Create a project
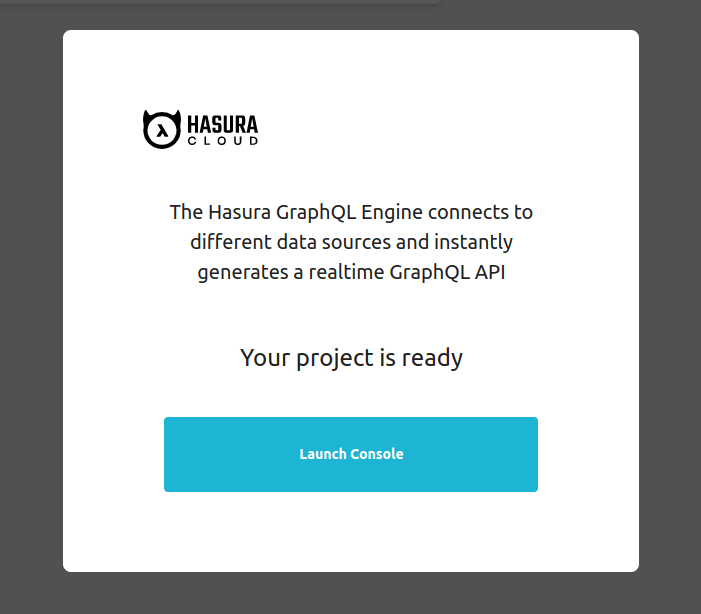
On creating a new account, Hasura Cloud automatically creates an initial project for you.
Click Launch Console to open the Hasura Console in your browser.
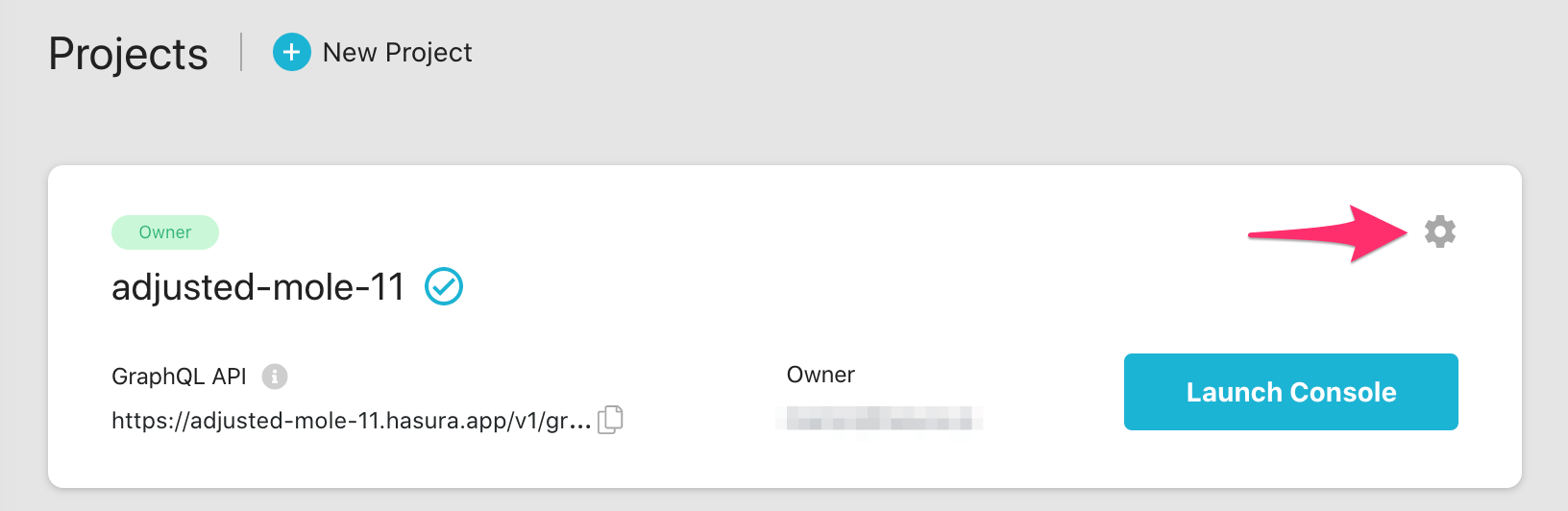
If you already have an account, you can create a new project by clicking the New Project link on the
Projects page.
Regardless of tier, you have the choice of either Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Google Cloud Platform (GCP) as hosting providers.
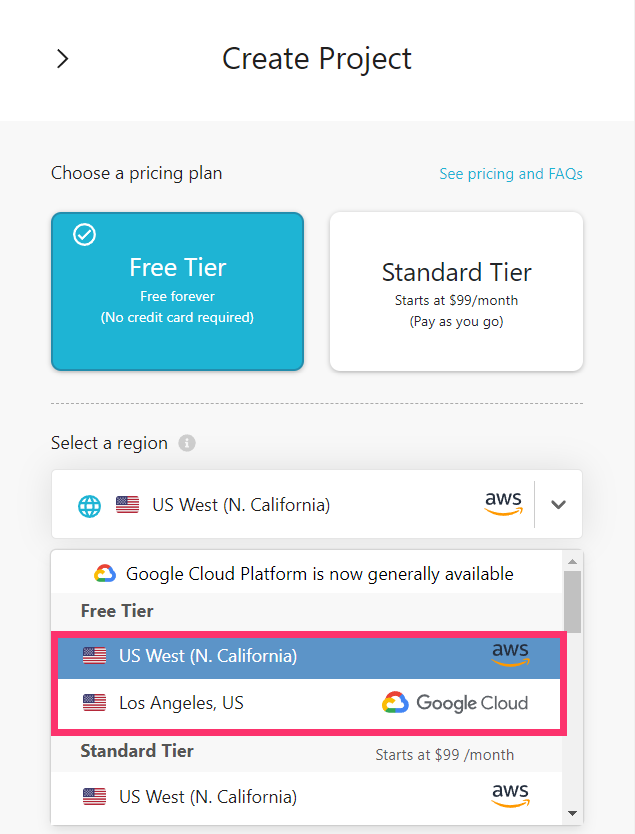
Make your selection and then click Create Free Project:
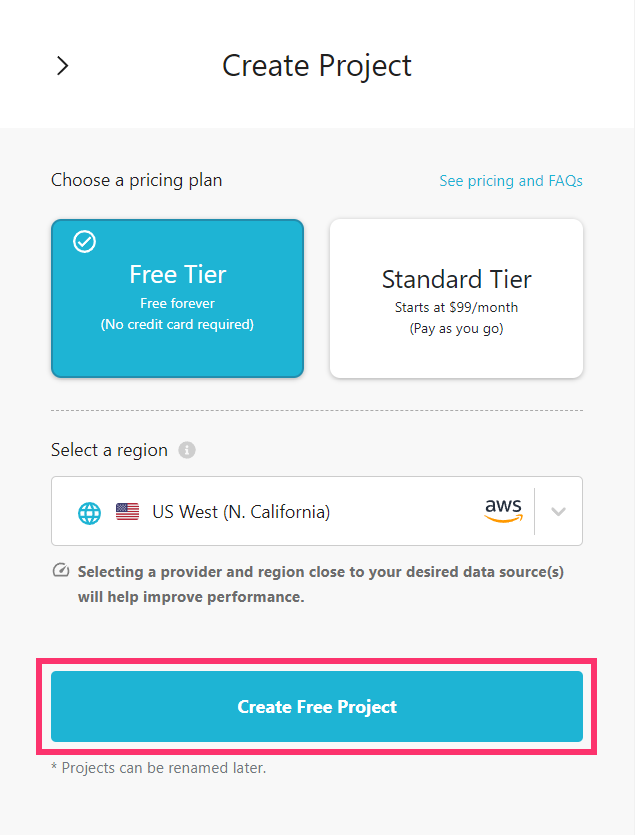
Step 3: Connect a database
Hit the Launch console button to open the Hasura Console and navigate to Data -> Manage -> Connect Database:
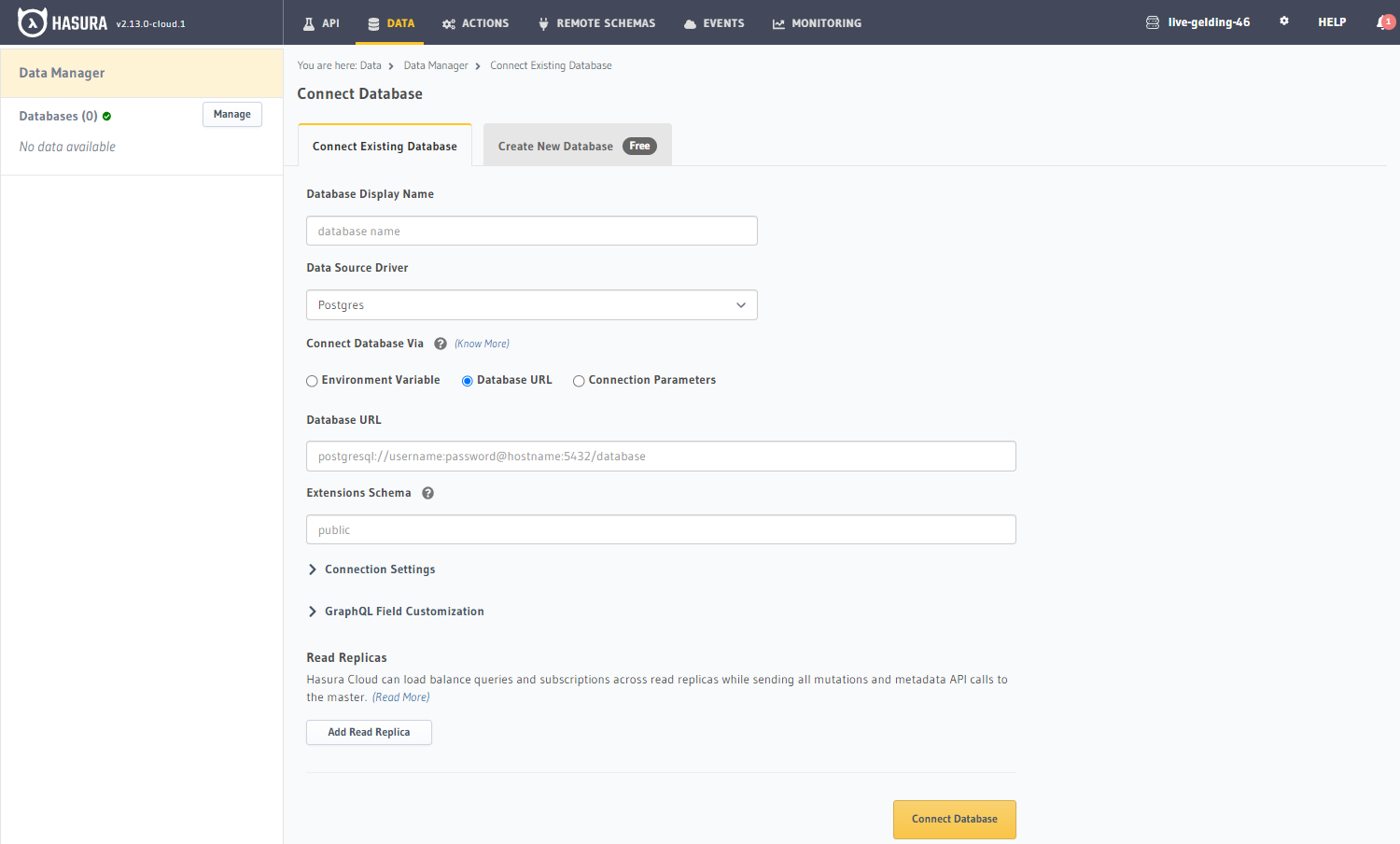
- To try out quickly with a new Postgres database, choose
Create New Database. - To use an existing database, choose
Connect existing database.
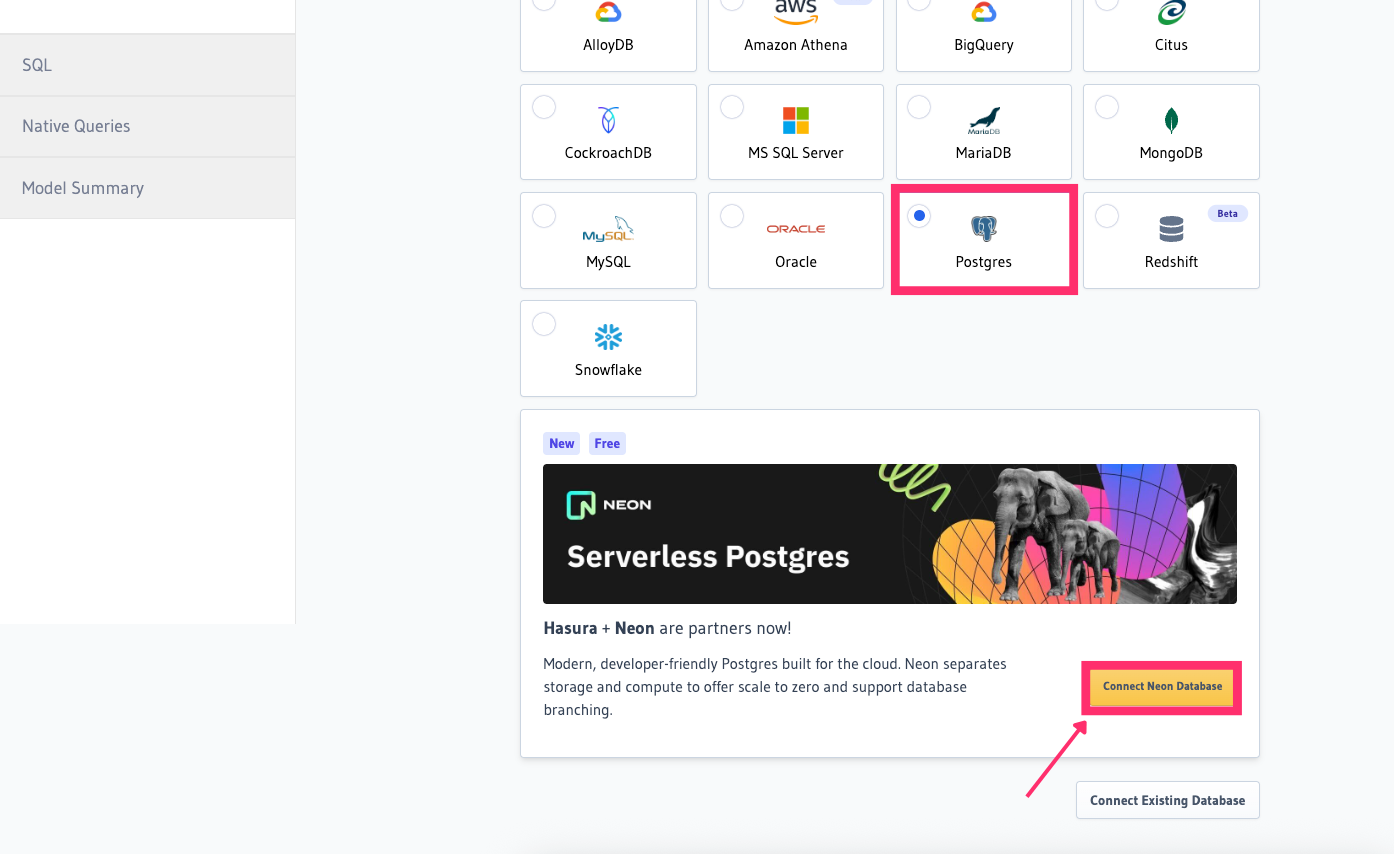
Option 3.1: Create and connect a new database
If you chose Create New Database:
Click on Connect Neon Database to create and connect a new Postgres database to your Hasura Project.
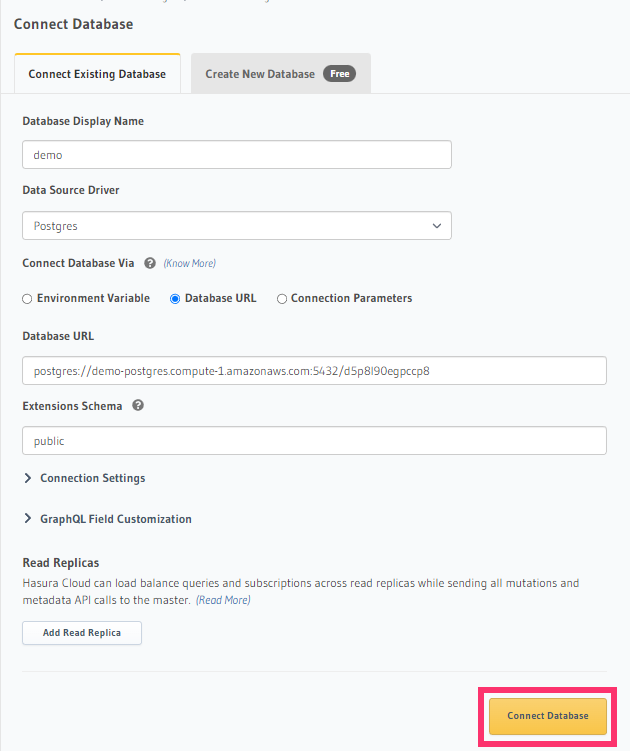
Option 3.2: Connect an existing database
If you chose Connect existing database:
- Give the database a name, say
default - Choose the database type from the list of supported databases
- Enter your database connection details
- Click
Connect Database.
Check out this section for other steps required to ensure connectivity to your database from Hasura Cloud if needed.
Step 4: Try out Hasura
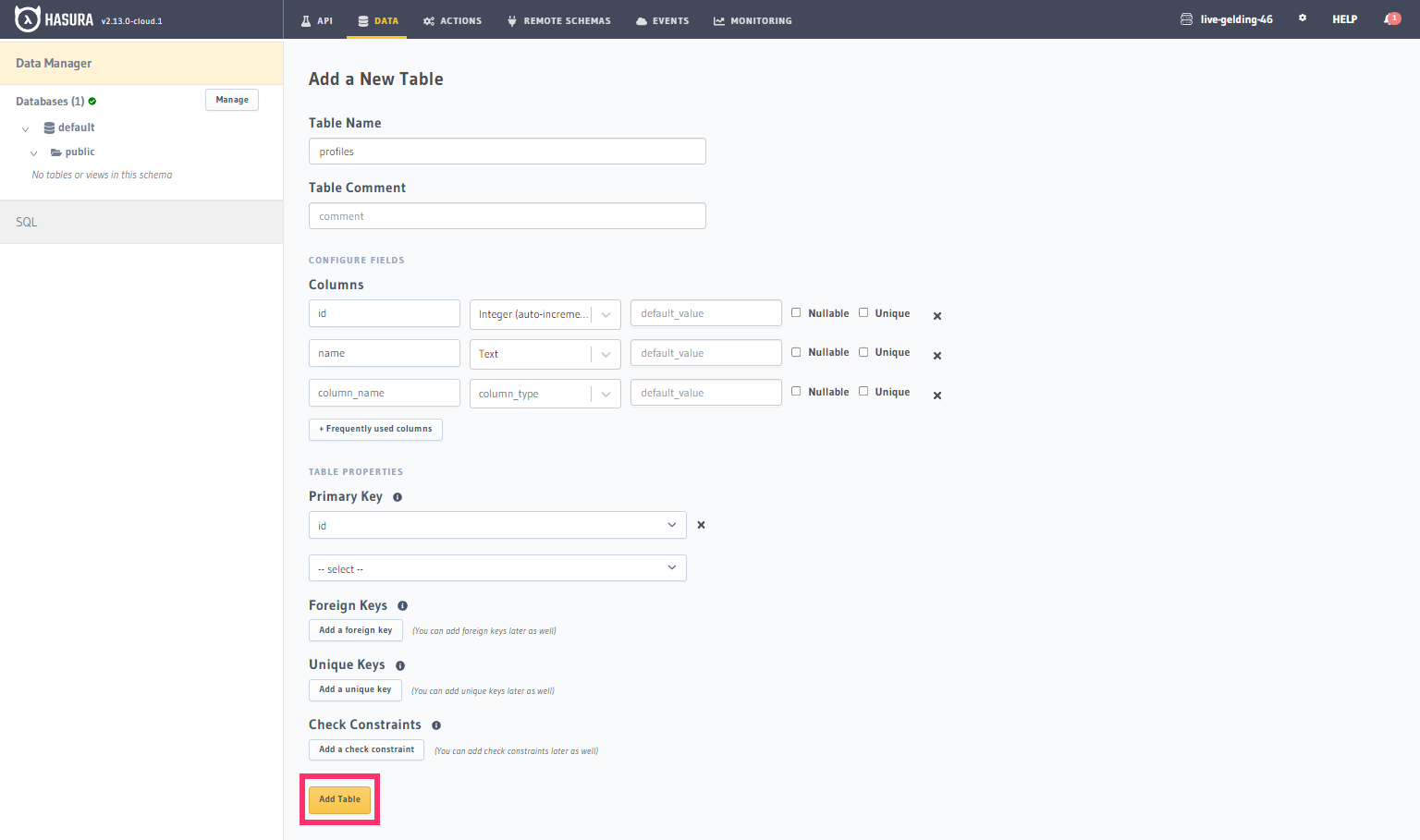
Create a table
On the Hasura Console, navigate to Data -> Create table and create a sample table called profiles with the following
columns:
profiles (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, -- serial -> auto-incrementing integer
name TEXT
)
Now, insert some sample data into the table using the Insert Row tab of the profiles table.
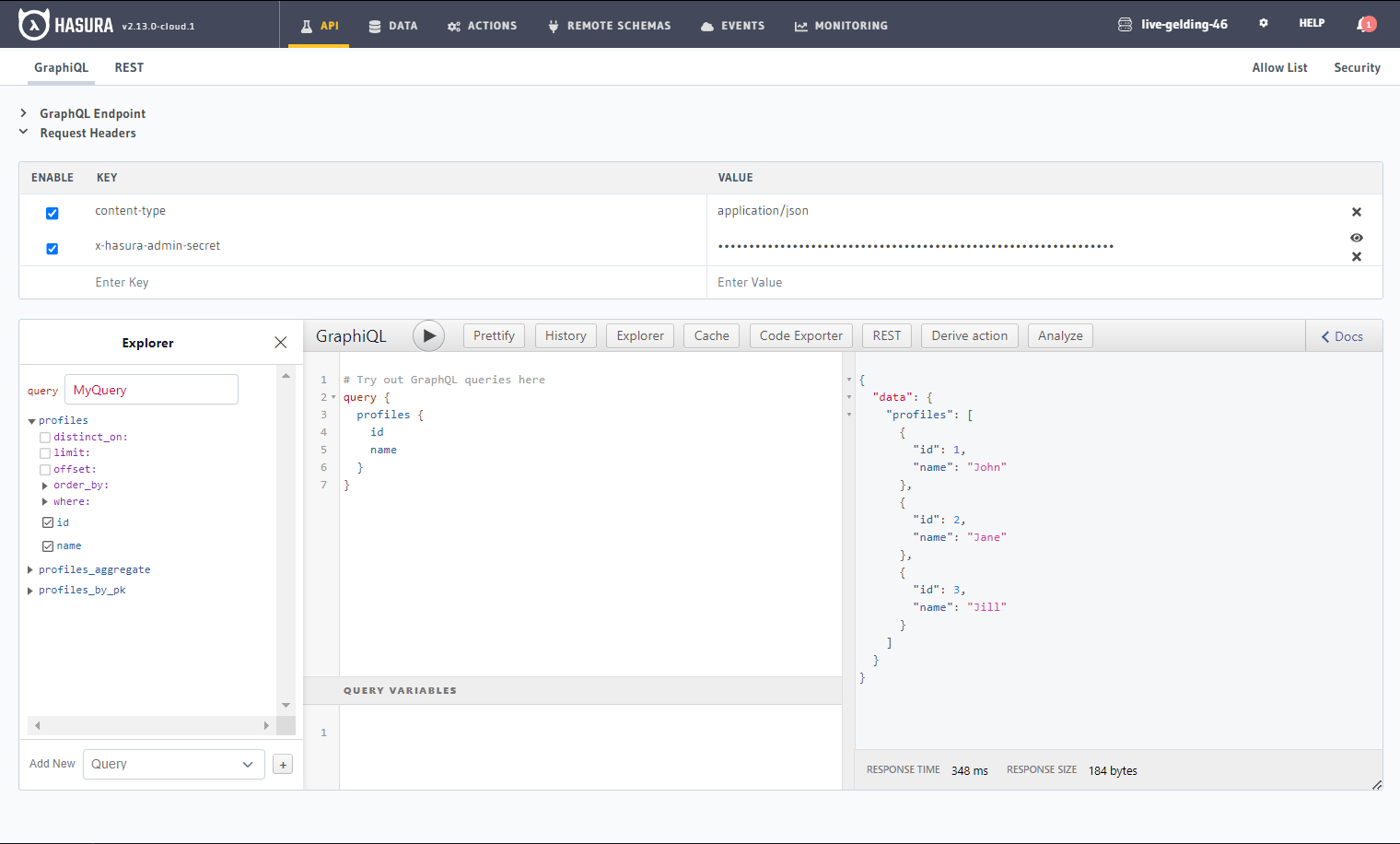
Try out a query
Head to the API tab in the Console and try running the following query:
query {
profiles {
id
name
}
}
You'll see that you get all the inserted data!
Next steps
Learn tutorial
For a full hands-on tour of Hasura, check out our 30-Minute Hasura Basics Tutorial.
Database operations
- Databases overview
- Database modeling: Learn how to model your database schema, as well as how to extend it.
- Querying data: Use GraphQL queries to query data from your GraphQL API.
- Inserting data: Use GraphQL mutations to insert data into your GraphQL API.
- Postgres permissions
Business logic
There are several options for the implementation of business logic, depending on your use case.
- Actions: Actions can be used if you'd like to extend your GraphQL schema by integrating with a REST endpoint.
- Remote Schemas: If you have an existing GraphQL server or if you're comfortable with implementing one, you can use Remote Schemas.
- Event Triggers: To trigger a serverless function based on a database event, use event triggers.
- Scheduled Triggers: Scheduled Triggers are used to execute custom business logic at specific points in time.
Manage Hasura Cloud project
You can click the gear icon in the Hasura Cloud dashboard to manage your Hasura Cloud project (e.g. add collaborators, env vars or custom domains).