Authorization
Introduction
Authorization determines what a verified user can access.
Hasura supports role-based authorization where access control over data is achieved by creating permissions based on the user role and database operation on the table.
Every authenticated request to Hasura Engine should contain dynamic
session variables from your
authentication service of at least X-Hasura-Roleas well as any others you may
need to use in your authorization rules.
Authorization rules, or "Permissions", are defined by you in Hasura Engine. To control access to data, you create
permissions per role and table for each of the select, insert, update and delete database operations.
Permissions can also be defined for Actions and Remote Schemas.
Example
If we wanted to create a Permission which allowed users to only view their own data on the user table for a
select database operation, we would create a row select Permission for the table like this:
{
“id”: {
“_eq”: “X-Hasura-User-Id”
}
}
This would check that the X-Hasura-User-Id session variable matches the id value in the user table of the user
which is being selected. This is a simple yet effective example and many more complex rules can be created as per
your needs.
Hasura roles and permissions are implemented at the Hasura Engine layer. They have no relationship to database users and roles.
Easily test permissions
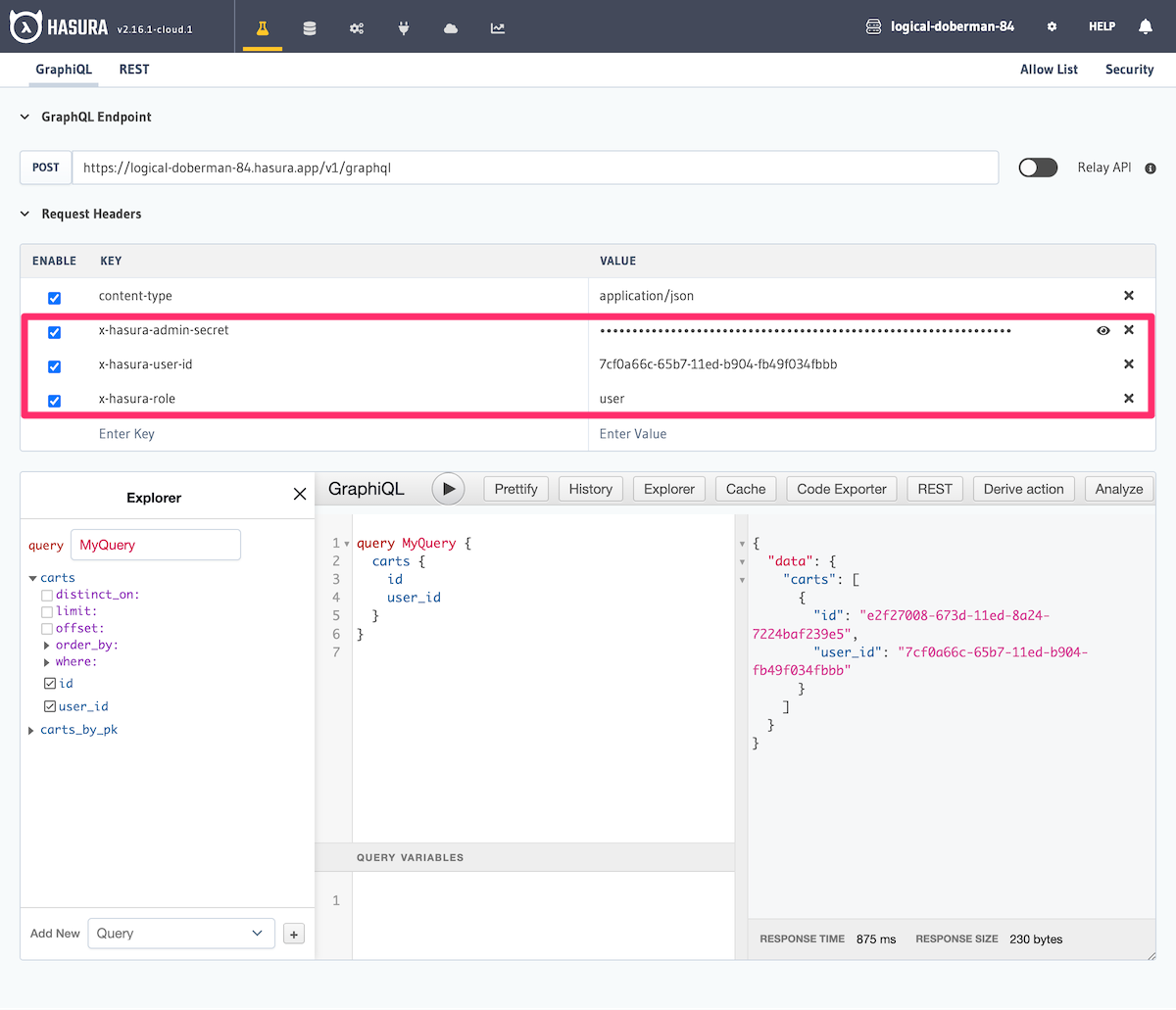
If you just want to see permissions in action, you don't need to first set up or integrate your auth service with GraphQL Engine. You can just do the following:
- Define permission rules for a table, role and operation. eg:
usertable,userrole andselectoperation. - Use the API GraphiQL interface in the Console to make a request and send the session variables as request headers
(send a
X-Hasura-Rolekey, with its value as the name of the role you've defined rules for). The data in the response will be restricted as per your configuration.
Additional access controls and API limits like maximum query depth are available in Hasura Cloud and Enterprise. See more at API limits with Hasura Cloud.
- Authorization Patterns with Hasura - Check out this tutorial.