Resolving Metadata Inconsistencies
Introduction
Typically, when you have a metadata inconsistency, your Hasura metadata — which is the information describing the structure and configuration of your Hasura GraphQL API — is not aligned with the actual state of the underlying database or the Hasura configuration. This can happen for several reasons:
- Schema changes in a data source: If you make changes directly to the database schema (like adding, modifying, or dropping tables or columns) without updating the Hasura metadata, it can lead to inconsistencies. Hasura expects the database schema to accurately reflect the metadata it has on it.
- Manual changes to metadata: If you manually modify Hasura's metadata files (like
tables.yaml,relationships.yaml, etc.) and these changes don't correspond to the actual database schema or Hasura settings, it can result in inconsistencies. - Failed migrations or operations: Sometimes, failed migrations or incomplete operations (due to network issues, errors in execution, etc.) can leave the metadata in an inconsistent state.
- Conflicts in Remote Schemas: If you have Remote Schemas that are not properly configured, change without updating the metadata or conflict with existing configurations, it may lead to metadata inconsistencies.
Resolving metadata inconsistencies
You can use the CLI, Console or API to resolve metadata inconsistencies. Regardless of the method you choose, you'll have two options:
Reloading metadata: This action is used when you make changes to your database schema outside of the Hasura Console, such as adding a new table or modifying an existing one directly in your database. This ensures that Hasura's GraphQL engine is aware of the latest structure of your database and can accurately reflect these changes in the GraphQL API it generates. It does not modify or reset any existing metadata configurations but simply updates Hasura's understanding of the current database schema by introspecting it again and updating the metadata accordingly.
Resetting metadata: clears all the existing metadata configurations in Hasura. This includes relationships, permissions, and any manual configurations you've made using the Console. After resetting the metadata, you will need to reconfigure these settings. It's useful when you want to start fresh with Hasura's setup or if there are irreparable inconsistencies in your current metadata setup.
- CLI
- Console
- API
The status of Metadata inconsistency can be checked with the hasura metadata inconsistency command.
hasura metadata inconsistency status
The CLI will log:
INFO metadata is consistent
You can attempt to reload the metadata with the command:
hasura metadata reload
If there are inconsistent objects they can be listed with:
hasura metadata inconsistency list
For example, the CLI will log:
NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION REASON
author table {"name":"author","schema":"public"}... Inconsistent object: no such table/view exists in source: "author"
You can then manually address each of the inconsistencies or, if necessary, drop them all with the command:
hasura metadata inconsistency drop
CLI will log:
INFO all inconsistent objects removed from metadata
Click
Settingsin the top-right corner of any Console page: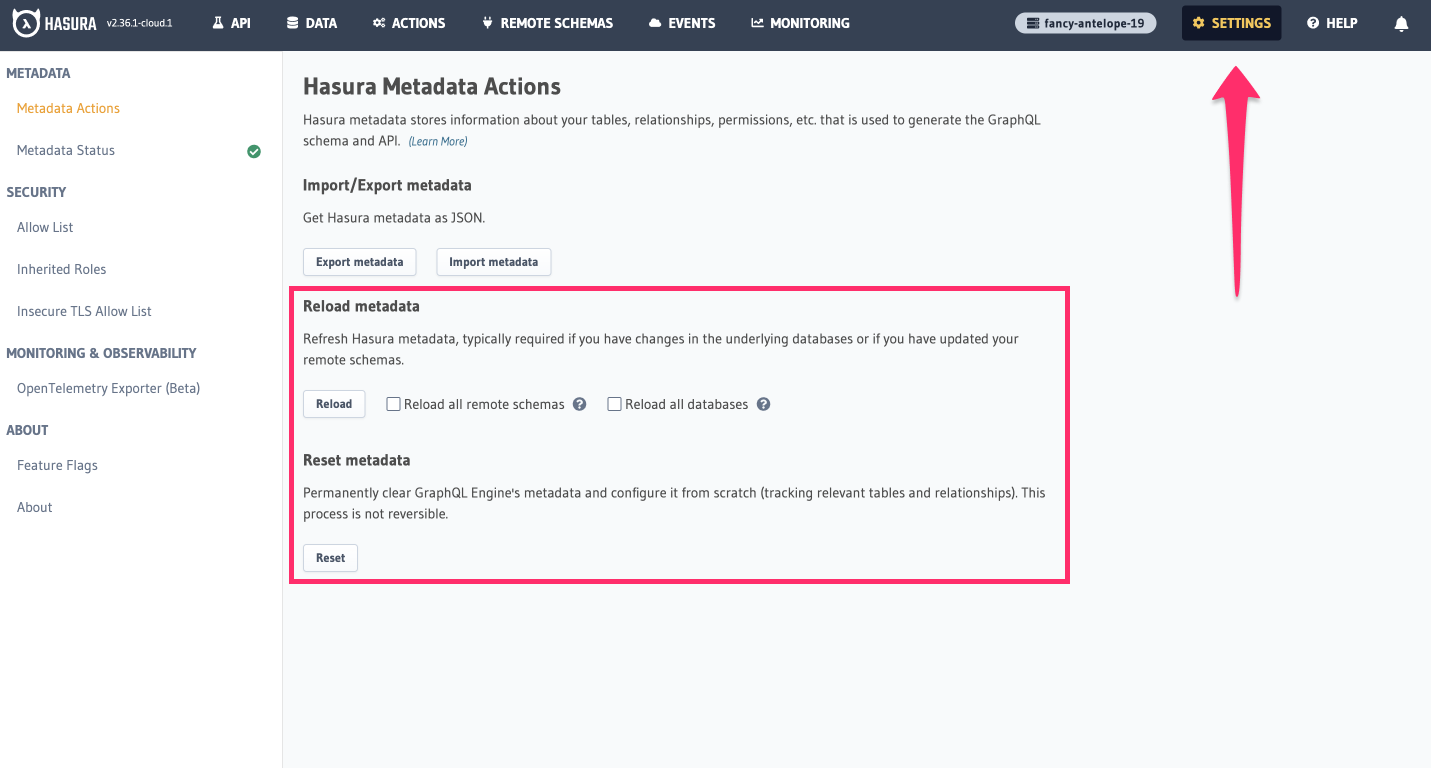
If you choose this option, an alert will pop up asking you to confirm your choice.
You can attempt to reload the metadata with the reload_metadata Metadata API:
POST /v1/metadata HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type" : "reload_metadata",
"args": {
"reload_remote_schemas": true,
"reload_sources": false,
"recreate_event_triggers": true
}
}
The clearing of Metadata can be done via the clear_metadata Metadata API:
curl -d'{"type": "clear_metadata", "args": {}}' http://localhost:8080/v1/metadata
If an admin secret is set, add -H 'X-Hasura-Admin-Secret: [your-admin-secret]' as the API is an admin-only API.
Next steps
A metadata inconsistency can be a frightening and frustrating thing to encounter. To ensure it doesn't happen again, consider using migrations to make changes to your database schema and Hasura metadata. Migrations are a safe and reliable way to make changes to your database schema and metadata.
If you're looking for an end-to-end example, check out our quickstart guide.