BigQuery: Tables Basics
Introduction
Adding tables allows you to define the GraphQL types of your schema including their corresponding fields.
Creating tables
Let's say we want to create two simple tables for articles and author schema:
authors (
`id` INT64,
`name` STRING
);
articles (
`id` INT64,
`title` STRING,
`body` STRING,
`author_id` INT64,
`is_published` BOOL,
`published_on` DATETIME,
`rating` INT64
);
- Console
- CLI
- API
Open the Hasura Console and head to the Data tab and click on the button on the left side bar to open up an interface
to create tables.
For example, here is the schema for the articles table in this interface:
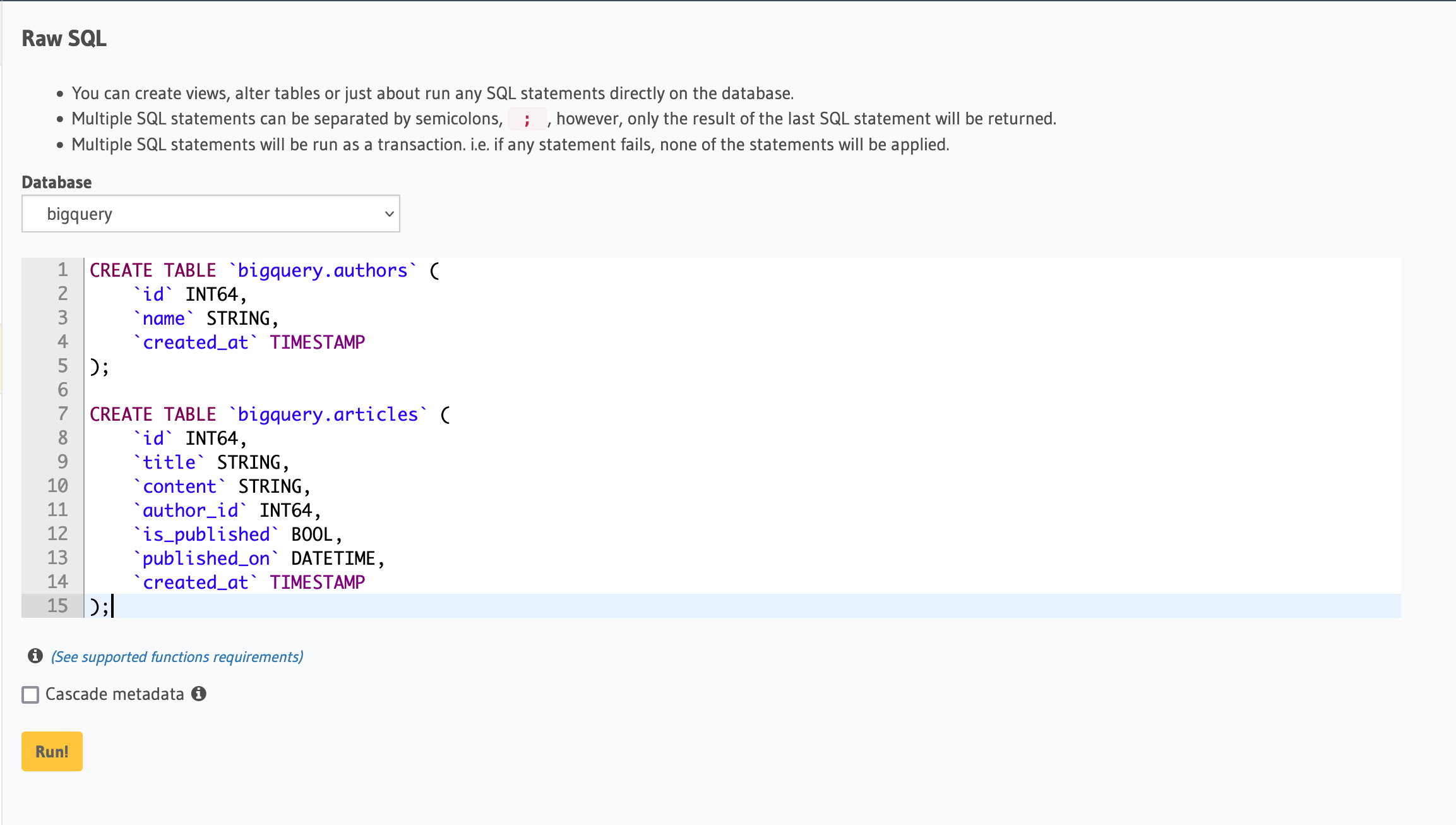
Create a migration manually and add the following SQL statement to the
up.sqlfile:CREATE TABLE `bigquery.authors` (
`id` INT64,
`name` STRING
);
CREATE TABLE `bigquery.articles` (
`id` INT64,
`title` STRING,
`body` STRING,
`author_id` INT64,
`is_published` BOOL,
`published_on` DATETIME,
`rating` INT64
);Add the following statement to the
down.sqlfile in case you need to roll back` the above statement:DROP TABLE `hasura.author`;
DROP TABLE `hasura.article`;Apply the migration by running:
hasura migrate apply
You can create a table by making an API call to the run_sql schema API:
POST /v2/query HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "bigquery_run_sql",
"args": {
"source": "<db_name>",
"sql": "CREATE TABLE `bigquery.author` (`id` INT64,`name` STRING);CREATE TABLE `bigquery.article` (`id` INT64,`title` STRING,`body` STRING,`author_id` INT64,`is_published` BOOL,`published_on` DATETIME,`rating` INT64);"
}
}
Tracking tables
Tables can be present in the underlying BigQuery database without being exposed over the GraphQL API. In order to expose a table over the GraphQL API, it needs to be tracked.
- Console
- CLI
- API
When a table is created via the Hasura Console, it gets tracked by default.
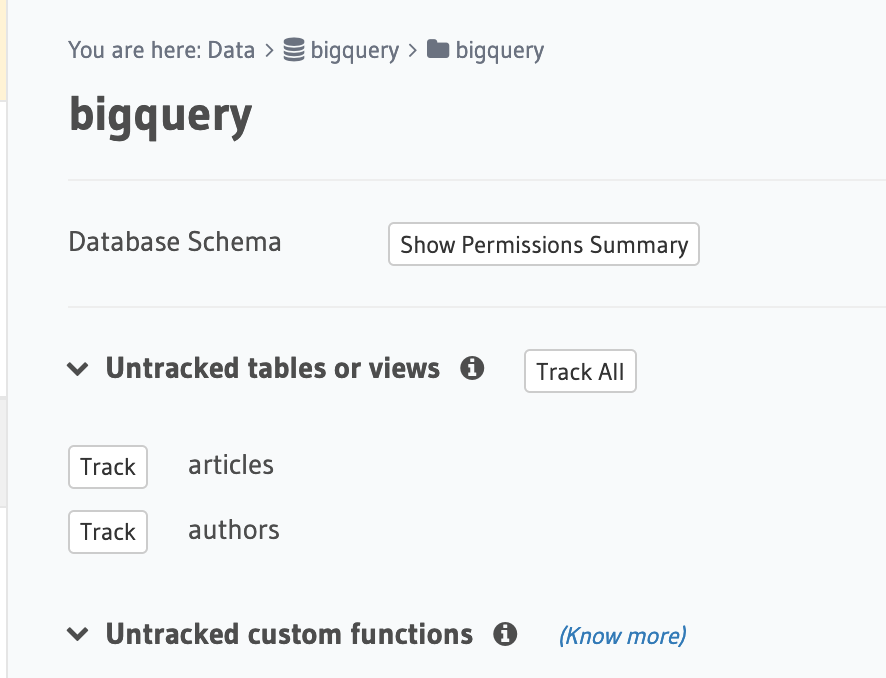
You can track any existing tables in your database from the Data -> Schema page:
To track the table and expose it over the GraphQL API, edit the
tables.yamlfile in themetadatadirectory as follows:- table:
dataset: bigquery
name: authors
- table:
dataset: bigquery
name: articlesApply the metadata by running:
hasura metadata apply
To track the table and expose it over the GraphQL API, make the following API call to the bigquery_track_table metadata API:
POST /v1/metadata HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "bigquery_track_table",
"args": {
"source": "<db_name>",
"table": {
"dataset": "bigquery",
"name": "articles"
}
}
}
Generated GraphQL schema types
As soon as a table is created and tracked, the corresponding GraphQL schema types and query/mutation fields will be automatically generated.
The following object type is generated for the articles table we just created and tracked:
# Object type
type Articles {
id: Int
title: String
body: String
author_id: Int
is_published: Boolean
published_on: Datetime
rating: Int
}
Let's analyze the above type:
Articlesis the name of the typeid,title,body, and so on are fields of theArticlestypeIntandString,BooleanandDatetimeare types that fields can have
The following query/mutation fields are generated for the articles table we just created and tracked:
# Query field: fetch data from the table: "bigquery.articles"
bigquery_articles(
distinct_on: [bigquery_articles_select_column!]
limit: Int
offset: Int
order_by: [bigquery_articles_order_by!]
where: bigquery_articles_bool_exp
): [bigquery_articles!]!
# Query field: fetch aggregated fields from the table: "bigquery.articles"
bigquery_articles_aggregate(
distinct_on: [bigquery_articles_select_column!]
limit: Int
offset: Int
order_by: [bigquery_articles_order_by!]
where: bigquery_articles_bool_exp
): bigquery_articles_aggregate!
These auto-generated fields will allow you to query data in the table.
See the query API reference for the full specifications.
GraphQL types documentation
Hasura automatically picks up any comments that might have been added to your tables and columns and adds them as GraphQL descriptions of the auto-generated types and fields.
Try out basic GraphQL requests
At this point, you should be able to try out basic GraphQL queries/mutations on the newly created tables from the API
tab in the Console. (You may want to add some sample data into the tables first)
Query all rows in the
articlestable:GraphiQLQuery VariablesRequest HeadersNo Schema Available