Setting up Soft Deletes for Data
Introduction
For some projects you may require records to be "soft deleted", i.e. items should not actually be removed from the database, but should be marked with a timestamp to indicate when they were deleted.
A common approach is to add a column such as deleted_at to the table which is a nullable timestamp. When there is a
timestamp value present, the record should be treated as deleted.
For example: Let's imagine that we have a simple Todo application, our todos table would resemble the following:
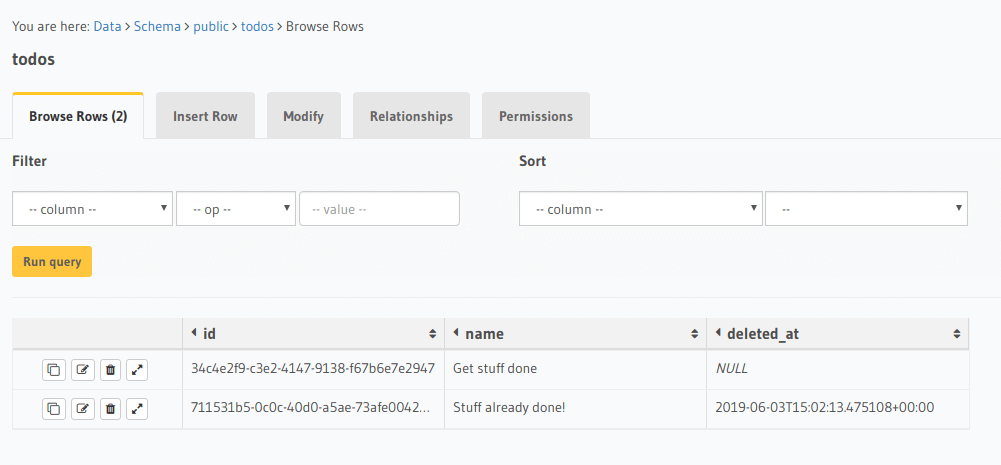
In this example we only have two todos, one has deleted_at with a timestamp value and the other contains a null
value. The todo with the timestamp value in deleted_at represents a deleted todo and was deleted at the set timestamp.
Follow the below steps to set up soft deletes for the todos table:
Step 1: Add a deleted_at column
Add a column with the following definition to the todos table:
deleted_at, type: timestamp, nullable, default: null
Step 2: Use update instead of delete mutations
After the previous step, we have a deleted_at column whose value will be null by default unless set explicitly.
Now in our application logic, instead of delete_todos mutations, use update_todos mutations to set the deleted_at
field to the current timestamp:
# Replace the delete mutations with this update mutation
mutation {
update_todos(where: { name: { _eq: "Stuff already done!" } }, _set: { deleted_at: "now()" }) {
returning {
id
name
deleted_at
}
}
}
Step 3: Set up appropriate insert/update/delete permissions
Now, we need to ensure that appropriate permissions are set to avoid actual deletes
from happening and allowing update of the deleted_at field.
Here are some typical rules we should set:
Delete permissions - remove all access
Insert permissions - remove access for inserting into deleted_at column
Update permissions - allow access for updating deleted_at column
Step 4: Restrict access to soft-deleted records
Now that we have set up the soft deleting pattern for records, we need to ensure that we restrict the "deleted" records from being accessed.
We can achieve this by setting appropriate permissions for roles which have access to
the todos table.
For example, let's say that a role user can only access non-deleted todos, we need to add the following permission
rule to ensure this:
Now the role user can only access non-deleted todos: