MS SQL Server: Setting Default Values for Fields Using MS SQL Server Defaults
Introduction
You can set values of certain fields automatically when not explicitly passed to a fixed value, e.g. true for a boolean field, or output of a simple SQL function, e.g. GETDATE() for a timestamp field, by setting column default values in the table definition.
The MS SQL Server default value is ignored when a value is explicitly set to the field.
Example: Say we have a field created_at in a table article which we want to be set to the current timestamp
whenever a new row is added to the table:
Step 1: Modify the table
Edit the created_at field and set its default value as the SQL function GETDATE().
- Console
- API
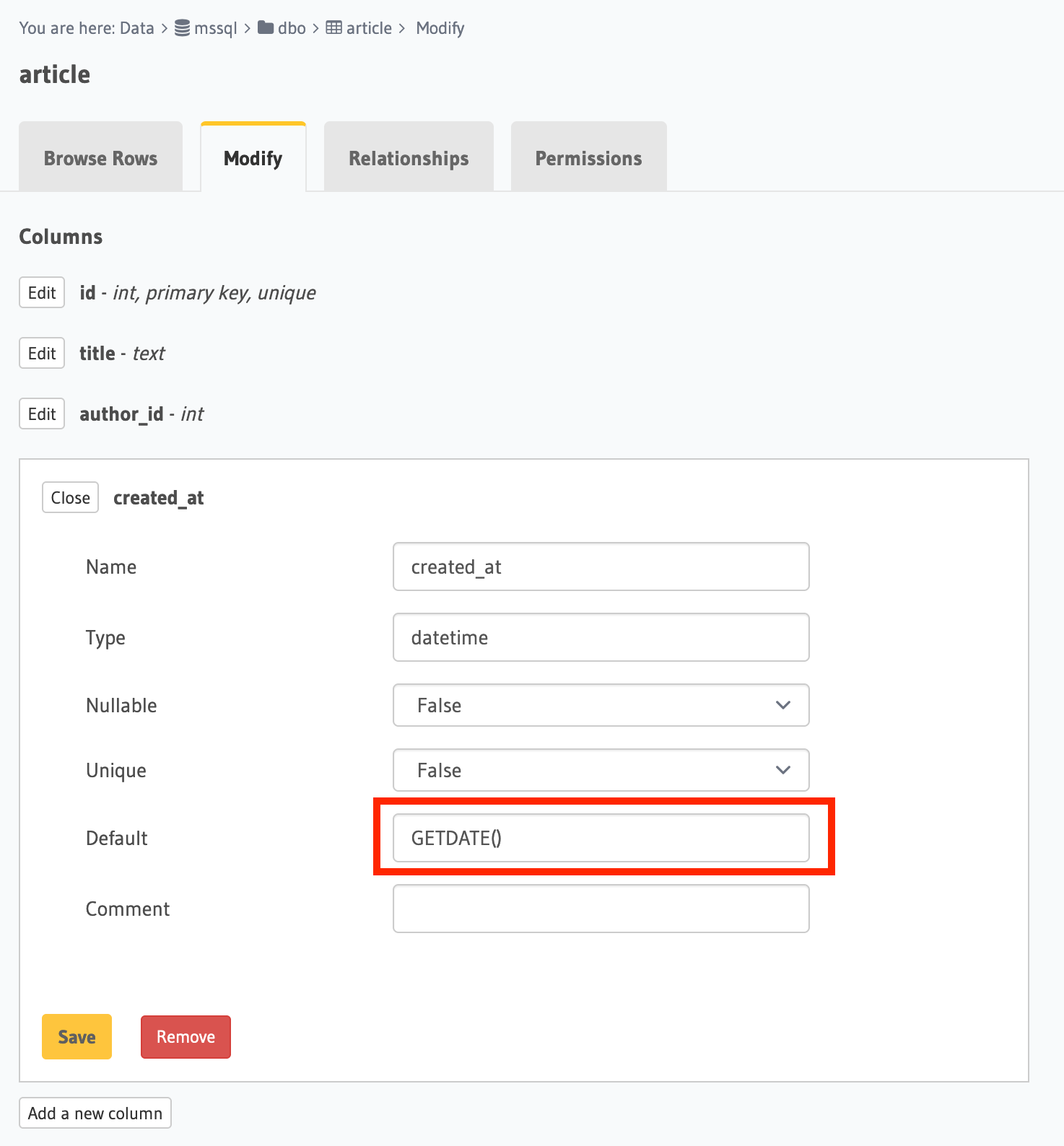
Open the Console and head to Data -> [article] -> Modify.
Click the Edit button next to the created_at field and add GETDATE() as a default value.
You can add a default value by using the mssql_run_sql schema API:
POST /v2/query HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "mssql_run_sql",
"args": {
"source": "<db_name>",
"sql": "ALTER TABLE article ADD CONSTRAINT DF_article DEFAULT GETDATE() FOR created_at;"
}
}
To set a default value as an auto-incrementing integer you first need to set up a sequence which will be the source of
our default value.
Let's say we have a field called roll_number which we would like to be set by default as an auto-incremented integer.
Run the following SQL command to create a new sequence.
CREATE SEQUENCE roll_number_seq AS INT START WITH 0 INCREMENT BY 1;
Now set the default value of the roll_number field as DEFAULT (NEXT VALUE FOR roll_number_seq).
Step 2: Run an insert mutation
Now if you do not pass the created_at field value while running an insert mutation on the article table, its value
will be set automatically by MS SQL Server.