MS SQL Server: Database to Remote Schema Relationships
Introduction
Database to Remote Schema relationships extend the concept of joining data across tables, to joining across tables and remote GraphQL sources. Once you create relationships between types from your database and types created from remote schemas, you can then "join" them by running GraphQL queries.
These APIs can be custom GraphQL servers you write, third party SaaS APIs, or even other Hasura instances.
Because Hasura is meant to be a GraphQL server that you can expose directly to your apps, Hasura also handles security and authorization while providing remote joins.
To see example use cases, check out this blog post.
Remote Schema relationships from MS SQL Server are supported from versions v2.6.0 and above.
Create Remote Schema relationships
Step 1: Add a Remote Schema and a database
Add a Remote Schema and a database as described here and here, if not already added.
Step 2: Define and create the relationship
The following fields can be defined for a Remote Schema relationship:
- Name: Define a name for the relationship.
- Remote Schema: Select a Remote Schema among all the ones you've created.
- Configuration: Set up the join configuration, to inject values as input arguments of the Remote Schema field.
- From column: Input injected from table column values.
- From static value: Input injected from a static value of your choice.
For example, let's assume that our database has a table order(id int, user_id int) and we've added a Remote Schema
user-remote-schema.
- We name the relationship
user. - We select the
user-remote-schemathat we've added. - We set up the config to join the
idinput argument of our Remote Schema field to theuser_idcolumn of this table (in this case, theordertable).
- Console
- CLI
- API
Head to the
Data -> [table-name] -> Relationshipstab.Click the
Add Relationshipbutton to open the widget.Search for the remote schema by name in the
To Referenceinput box.Once selected, it will open the details section below to fill in the rest of the relationship definition.
Define the relationship details and hit
Create Relationship.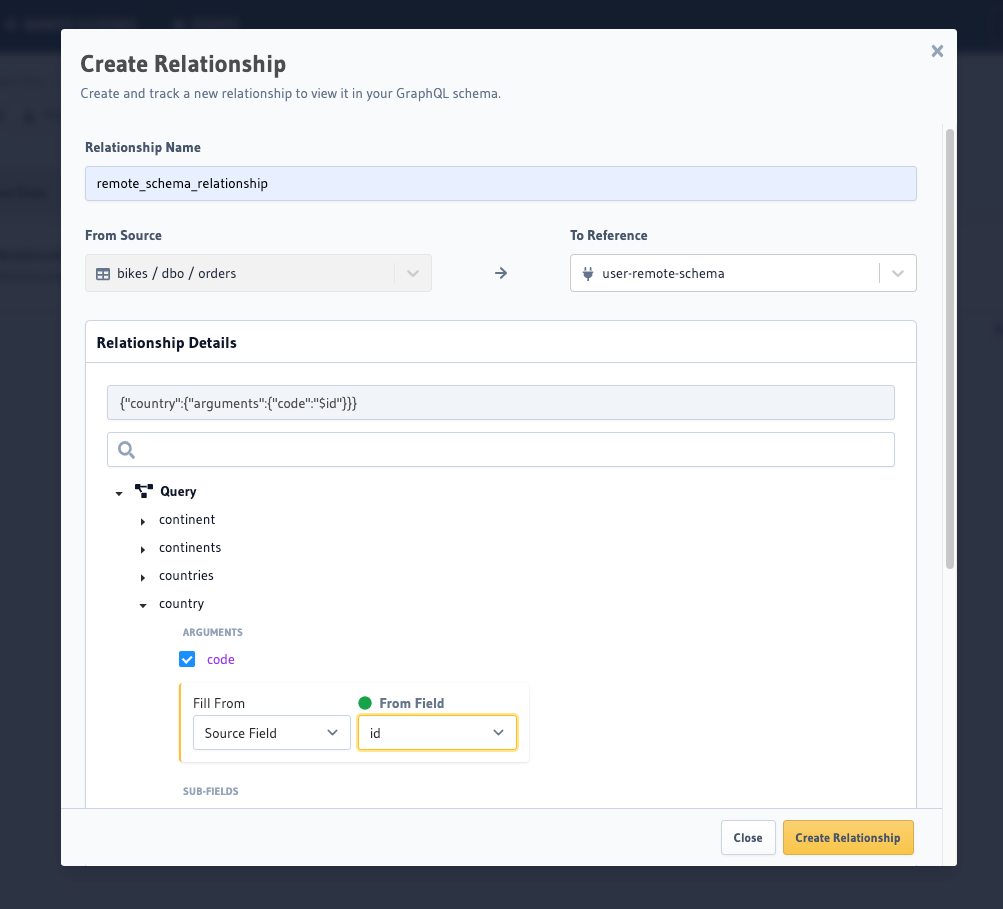
Update the databases > [database-name] > tables > [table-name].yaml file in the metadata directory:
- table:
schema: public
name: order
remote_relationships:
- name: user
definition:
remote_field:
user:
arguments:
id: $user_id
hasura_fields:
- user_id
remote_schema: user-remote-schema
Apply the Metadata by running:
hasura metadata apply
You can add a Remote Schema relationship by using the pg_create_remote_relationship Metadata API:
POST /v1/metadata HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type":"mssql_create_remote_relationship",
"args": {
"name": "user",
"source": "mssql1",
"table": { "name": "order", "schema": "dbo" },
"hasura_fields": ["user_id"],
"remote_schema": "user-remote-schema",
"remote_field": {
"user": {
"arguments": {
"id": "$user_id"
}
}
}
}
}
Step 3: Explore with GraphiQL
In the API tab, test out your Remote Schema relationship.
Remote Schema relationship permissions
Remote Schema relationship permissions are derived from the Remote Schema permissions defined for the role. When a remote relationship permission cannot be derived, the remote relationship field will not be added to the schema for the role.
Some cases in which a remote relationship permission cannot be derived are:
- There are no Remote Schema permissions defined for the role.
- The role doesn't have access to the field or types that are used by the remote relationship.
Remote relationship permissions apply only if Remote Schema permissions are enabled in GraphQL Engine.