Logical Models
Introduction
Full support for Logical Models on MongoDB are supported from v2.31.0 onwards.
Logical Models are a GraphQL representation of database data. They provide an abstraction over the underlying database.
Logical Models are currently used by MongoDB as the primary method for defining a Collection or View's schema which will be used to generate the GraphQL API. Since NoSQL databases don't inherently have a schema present for the Documents present, we need to define one for our Collections as they are added in Hasura.
You can find examples of how to use Logical Models in the Cloud or Docker Getting Started guides for MongoDB. For a more detailed explanation of Logical Models themselves, read on.
Tracking a Collection with a Logical Model
Each Collection needs to have a Logical Model in order to specify its GraphQL schema.
A Logical model if optional
if a Collection has a database
validation schema
present, it will be used as the default.
- Console
- CLI
- API
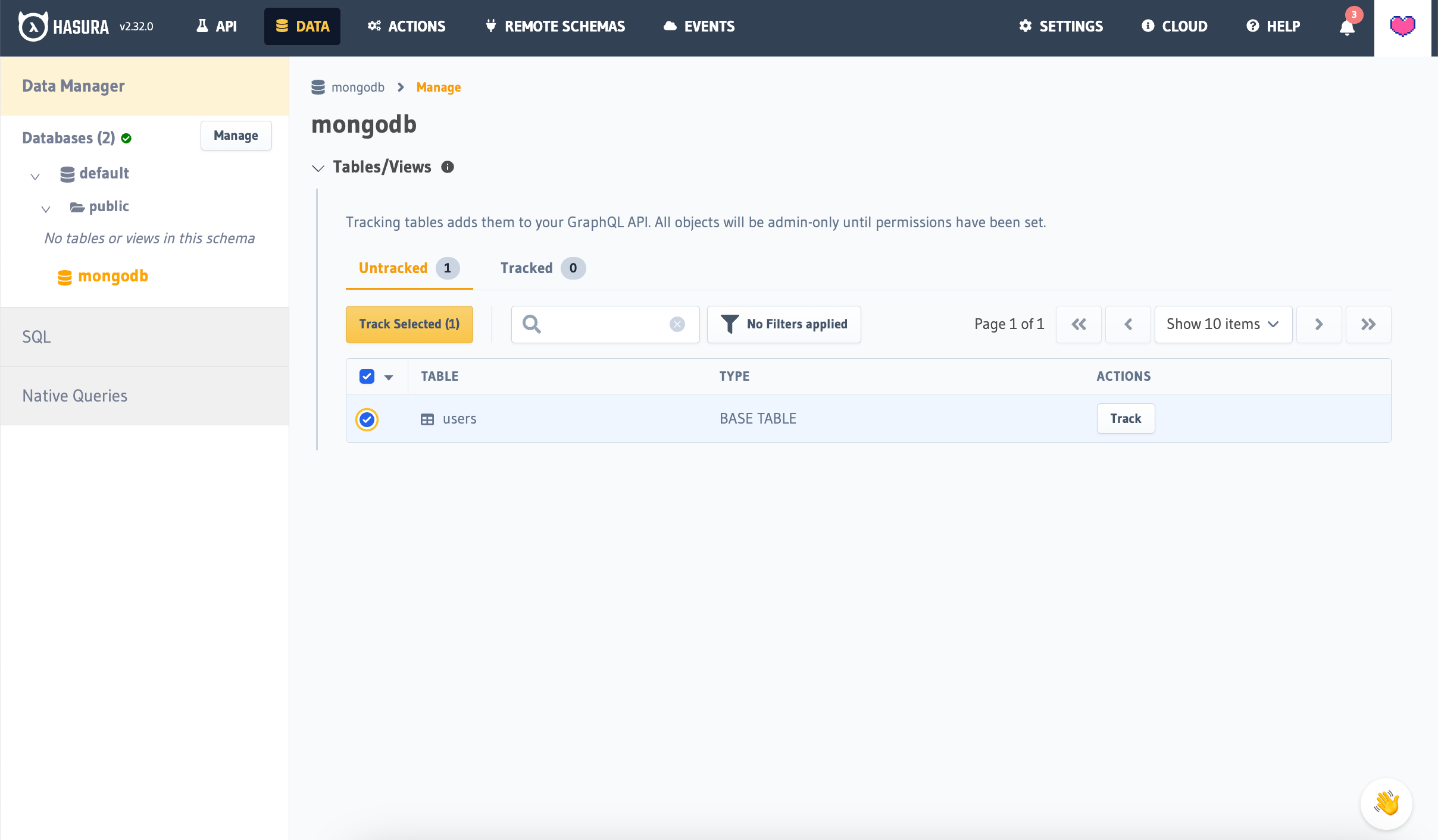
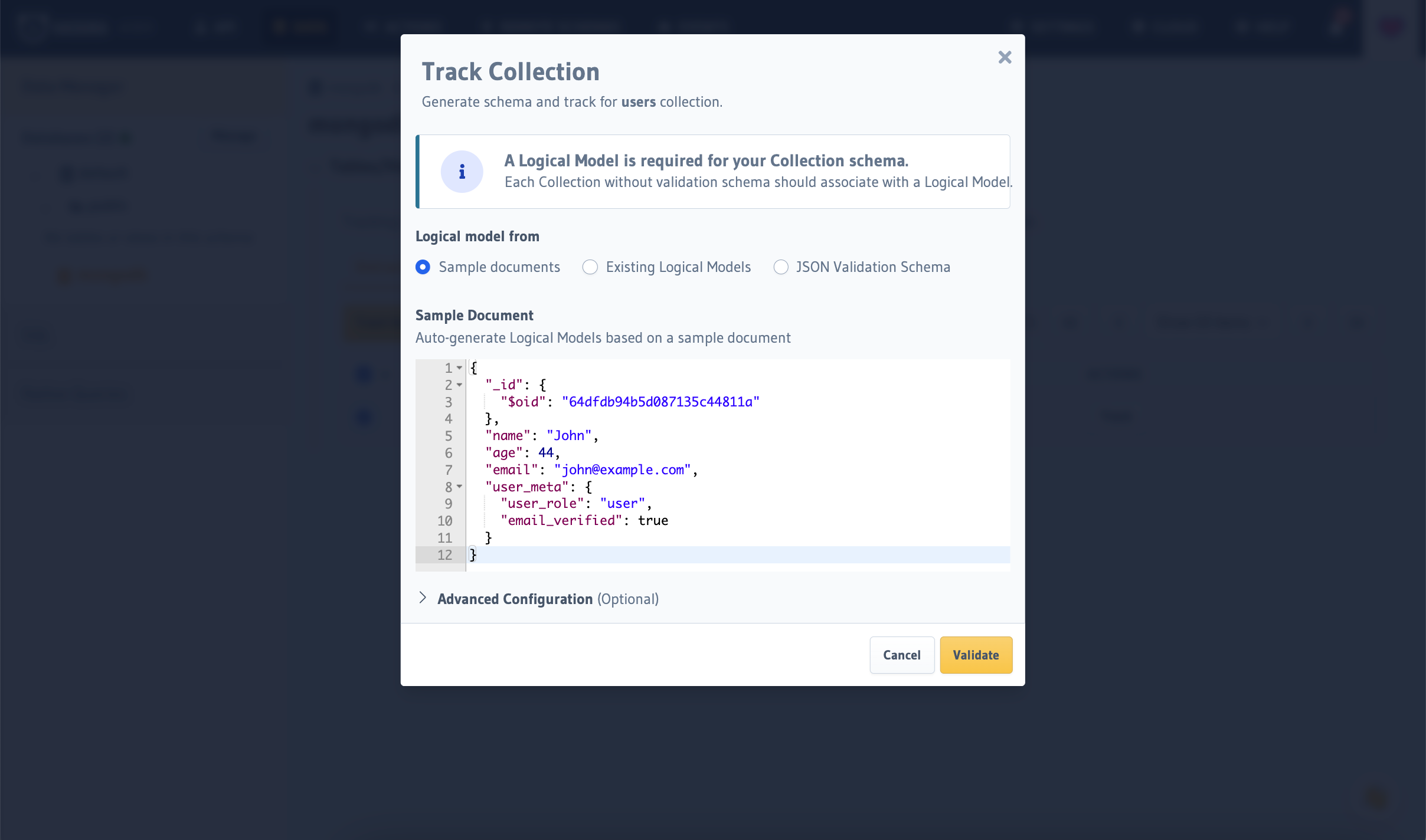
You can create a logical model by adding it to the appropriate database definition in the
metadata > databases > databases.yaml file:
logical_models:
- name: "<name>"
fields:
"<field name>":
type: "<MongoDB field type>"
nullable: false | true
description: "<optional field description>"
...
And the track the Collection with its associated logical model by adding the definition to
metadata > databases > tables > <collection_name>.yaml.
table:
- <collection_name>
logical_model: <logical_model_name>
There will also be an associated includes statement in the metadata > databases > tables > tables.yaml file.
- '!include <table_name>.yaml'
You create a logical model through the metadata API:
POST /v1/metadata HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "mongo_track_tables",
"resource_version": 1,
"args": {
"allow_warnings": true,
"tables": [
{
"source": "default",
"table": [
"<collection_name>"
],
"logical_model": "<logical_model_name>"
}
]
}
}
Tracking a Logical Model
- Console
- CLI
- API
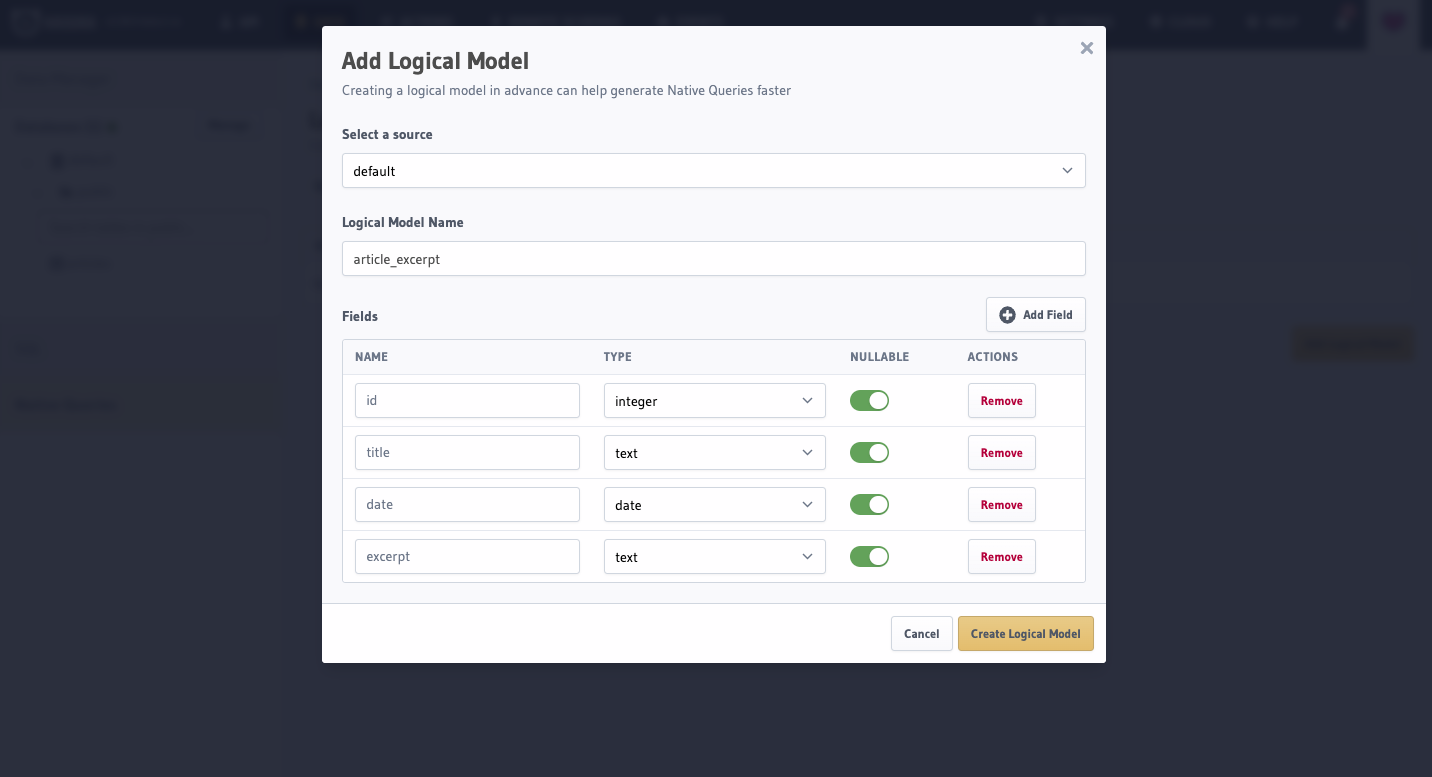
You can create a logical model by adding it to the appropriate model definition, under the database in the
metadata > databases > databases.yaml file:
logical_models:
- name: "<name>"
fields:
"<field name>":
type: "<MongoDB field type>"
nullable: false | true
description: "<optional field description>"
...
You create a logical model through the metadata API:
POST /v1/metadata HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "mongo_track_logical_model",
"args": {
"source": "default",
"name": "<name>",
"fields": [
{
"name": "<field name>",
"type": "<MongoDB field type>",
"nullable": false | true,
"description": "<optional field description>"
},
...
]
}
}
and then track an associated Collection, referencing the associated logical model using:
POST /v1/metadata HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "mongo_track_tables",
"args": {
"allow_warnings": true,
"tables": [
{
"table": [ <collection_name> ],
"source": <database_name>,
"logical_model": <logical_model_name>
}
]
}
}
The type of each field can be either a MongoDB data type or references to other Logical Models, and each field can be marked as nullable or not, see LogicalModelType.
For example, we could track a representation of an article as follows:
- Console
- CLI
- API

Add the following to the default database definition in the metadata > databases > databases.yaml file:
logical_models:
- name: article
fields:
id:
type: integer
nullable: false
title:
type: text
nullable: false
contents:
type: text
nullable: false
published_date:
type: date
nullable: true
is_published:
type: bit
nullable: false
POST /v1/metadata HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "mongo_track_logical_model",
"args": {
"source": "default",
"name": "article",
"fields": [
{
"name": "id",
"type":
{
"scalar": "int"
}
},
{
"name": "title",
"type":
{
"scalar": "text"
}
},
{
"name": "contents",
"type":
{
"scalar": "text"
}
},
{
"name": "published_date",
"type":
{
"scalar": "date",
"nullable": true
},
},
{
"name": "is_published",
"type":
{
"scalar": "bit"
}
}
]
}
}
Untracking a Logical Model
- Console
- CLI
- API
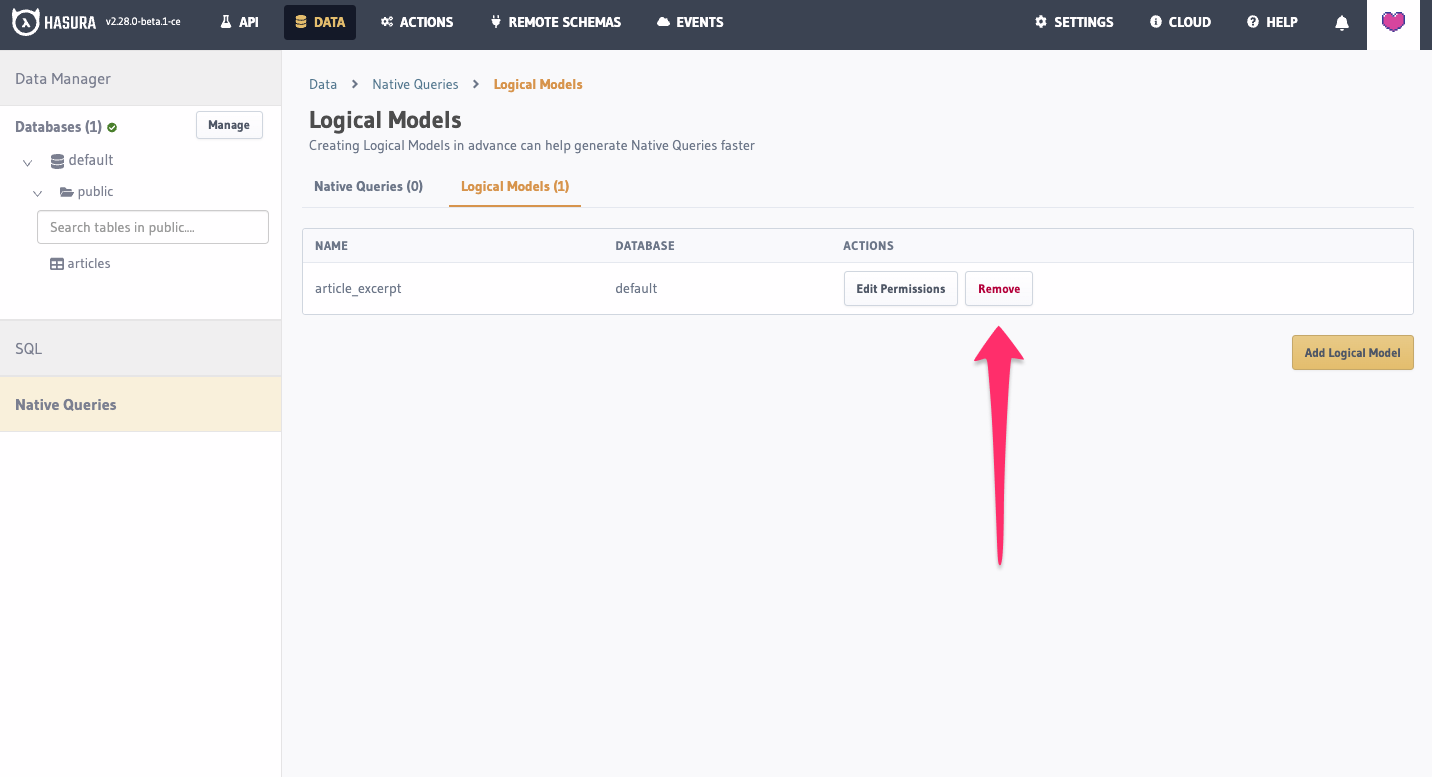
You can remove a Logical Model by removing it from the metadata > databases > databases.yaml file.
You can remove a Logical Model the same way:
POST /v1/metadata HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "mongo_untrack_logical_model",
"args": {
"source": "default",
"name": "<name>"
}
}
Note that you can only remove an unused Logical Model; if the model is attached to a Native Query, this operation will fail. You must remove the Native Query first.
To untrack the above article Logical Model, we would run the following:
- Console
- CLI
- API

Remove the above metadata from the metadata > databases > databases.yaml file.
POST /v1/metadata HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "mongo_untrack_logical_model",
"args": {
"source": "default",
"name": "article"
}
}
Referencing other Logical Models
Logical Model fields are allowed to refer to other Logical Models, even recursively, allowing nested data types.
Object or array relationships between Native Queries are an example use of this.
To elaborate on the article example above, we can include authors in the data model:
- API
POST /v1/metadata HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "bulk_atomic",
"args":
[
{
"type": "mongo_track_logical_model",
"args": {
"source": "default",
"name": "article",
"fields": [
{
"name": "id",
"type":
{
"scalar": "integer"
}
},
{
"name": "title",
"type":
{
"scalar": "text"
}
},
{
"name": "contents",
"type":
{
"scalar": "text"
}
},
{
"name": "author_id",
"type":
{
"scalar": "integer"
}
},
{
"name": "author",
"type":
{
"logical_model": "author",
},
}
]
}
},
{
"type": "mongo_track_logical_model",
"args": {
"source": "default",
"name": "author",
"fields": [
{
"name": "id",
"type":
{
"scalar": "integer"
}
},
{
"name": "name",
"type":
{
"scalar": "text"
}
},
{
"name": "articles",
"type":
{
"array":
{
"logical_model": "article"
}
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
bulk_atomicTracking the Logical Models one-by-one would fail, since article refers to author, which is not yet defined.
Tracking the Logical Models in one atomic operation postpones coherency checks until all models are tracked, which allows for mutual references.
Permissions
By default, a model has no permissions, and only the admin account will be able to use it. You can enable the model by adding permissions for a given role.
As Logical Models are currently only used for read-only purposes, you can only add select permissions.
The permissions consist of a list of columns that the role can access, and a filter that specifies which rows the role can receive.
- Console
- CLI
- API
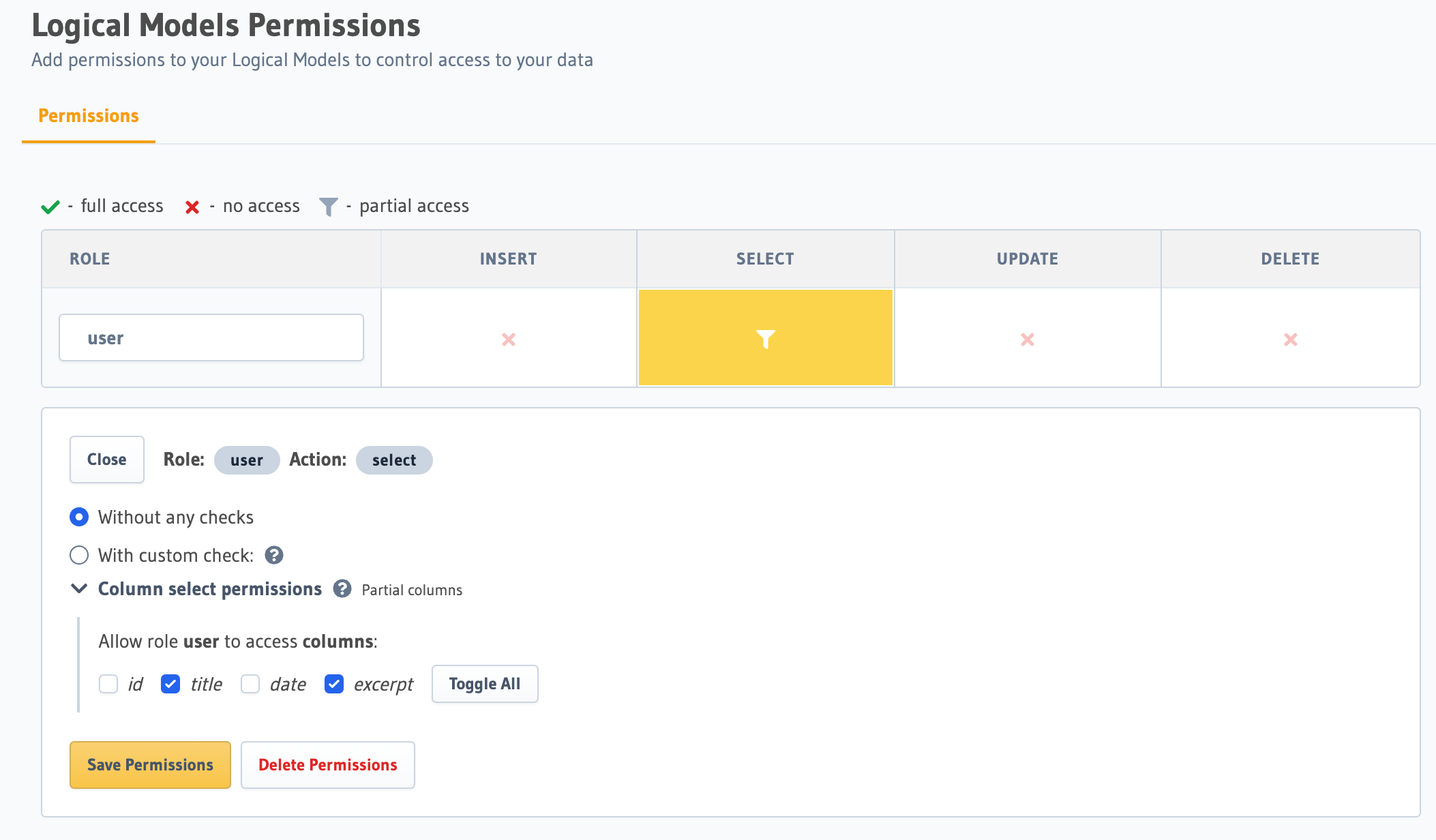
Columns must be specified, though you can use "*" to specify that you want to allow all columns.
The filter is the same boolean expression syntax as query filters. To allow
all rows to be passed through to the response, you can specify an empty filter, {}.
Add the required permissions to the relevant logical model in metadata > databases > databases.yaml:
logical_models:
- name: "<name>"
fields:
...
select_permissions:
- role: "<role name>"
permission:
columns: "*" | [
"column 1",
"column 2",
...
]
filter: "<boolean expression>"
- ...
Columns must be specified, though you can use "*" to specify that you want to allow all columns.
The filter is the same boolean expression syntax as query filters. To allow
all rows to be passed through to the response, you can specify an empty filter, {}.
POST /v1/metadata HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "mongo_create_logical_model_select_permission",
"args": {
"source": "default",
"name": "<logical model name>",
"role": "<role name>",
"permission": {
"columns": "*" | [
"column 1",
"column 2",
...
],
"filter": <boolean expression>
}
}
}
For example, to allow access to the article Logical Model for the reader role, but only for published articles, we
could use the following permission to limit the accessible rows to those where is_published is true, and then hide
that column from the list (by specifying all other columns).
- Console
- CLI
- API
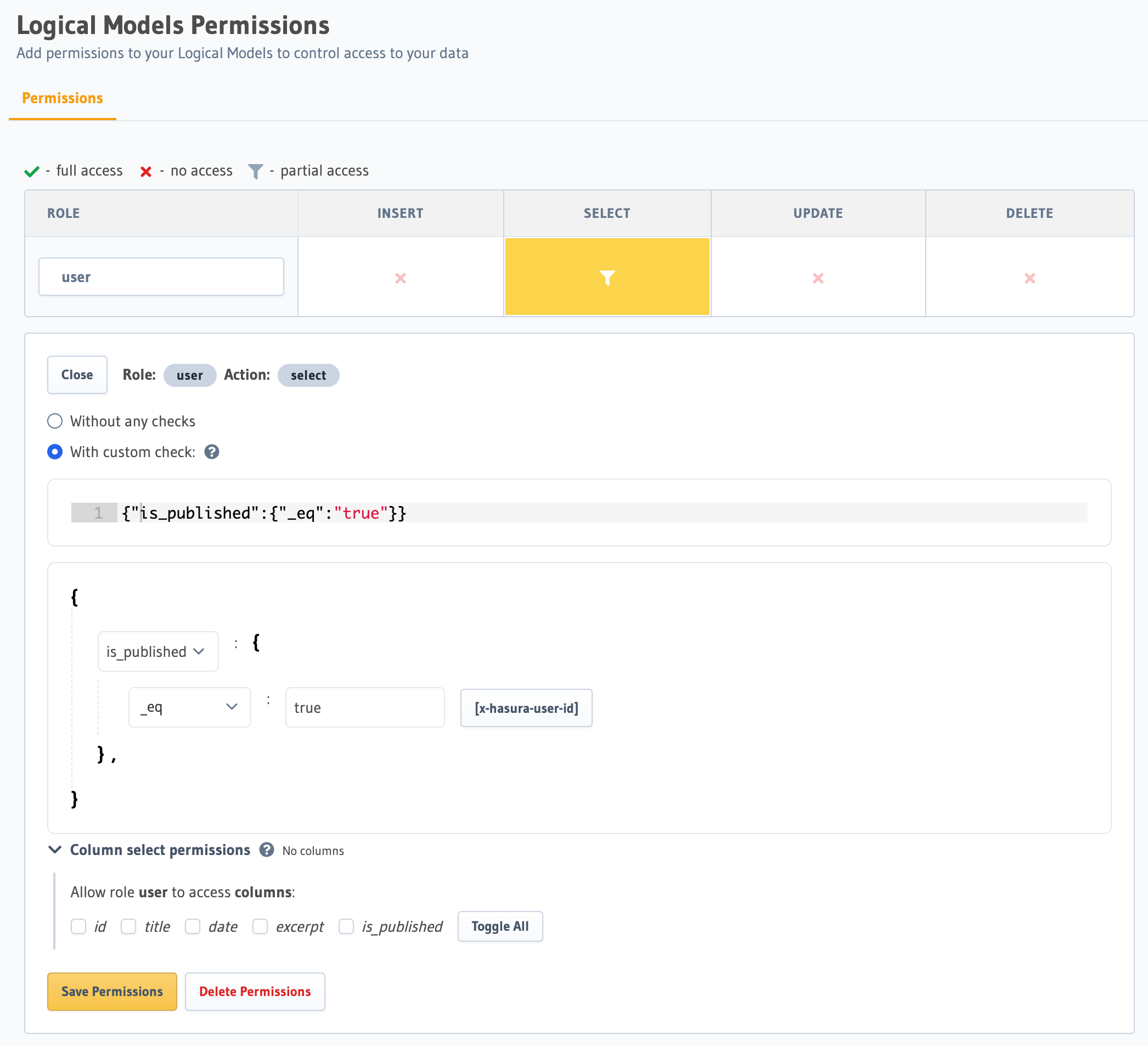
Add the required permissions to the relevant logical model in metadata > databases > databases.yaml:
logical_models:
- name: '<name>'
fields: ...
select_permissions:
- role: reader
permission:
columns:
- id
- title
- contents
- date
filter:
is_published:
_eq: true
- ...
POST /v1/metadata HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "mongo_create_logical_model_select_permission",
"args": {
"source": "default",
"name": "article",
"role": "reader",
"permission": {
"columns": [
"id",
"title",
"contents",
"date"
],
"filter": {
"is_published": {"_eq": true}
}
}
}
}
You can also drop permissions:
- Console
- CLI
- API
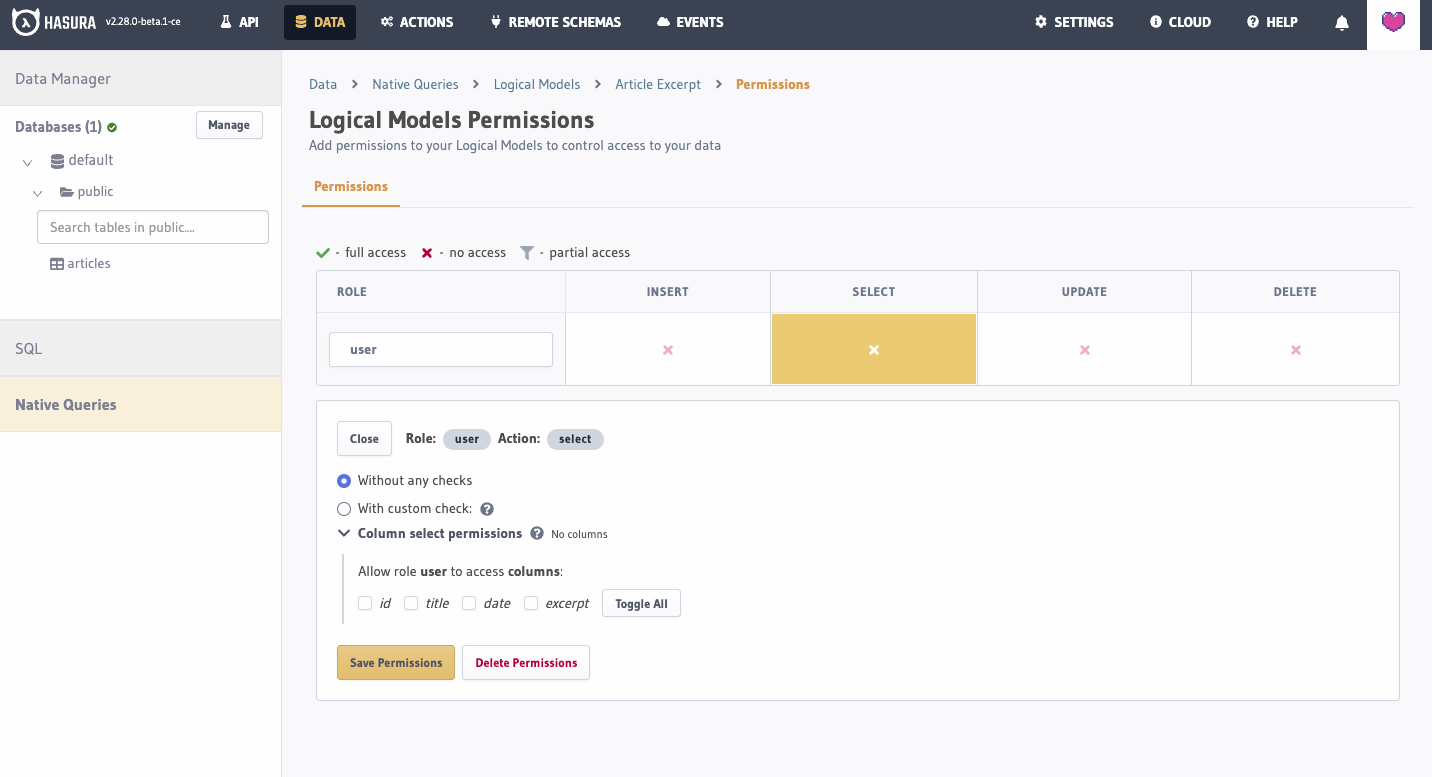
Remove the relevant permission from metadata > databases > databases.yaml.
POST /v1/metadata HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "mongo_drop_logical_model_select_permission",
"args": {
"source": "default",
"name": "<logical model name>",
"role": "<role name>"
}
}