Postgres: Database to Remote Database Relationships
Introduction
Remote database relationships (a.k.a remote source relationships) extend the concept of joining data between tables within a single database to joining data across tables between separate databases.
After you've established relationships between types in your source database and types in your target database, you can "join" them with GraphQL queries.
Because Hasura is meant to be a GraphQL server that you can expose directly to your apps, Hasura also handles security and authorization while providing remote joins.
Remote database relationships for Postgres are supported from versions v2.1.0 and above.
Create remote database relationships
Step 1: Add two database sources
Add a source database as described here and track the required tables. Then, repeat the process to add your target database.
Step 2: Define and create the relationship
A remote database relationship is defined alongside the source database table (that is, the source side of the join).
The following fields can be defined for a Remote Schema relationship:
- Relationship type: Either
objectorarray- similar to normal relationships. Hasura supports both many-to-one (object) and one-to-many (array) relationships. - Relationship Name: A name for the relationship.
- Reference Source: The name of the target database (that is, the target side of the join).
- Reference Table: The table in the target database source that should be joined with the source table
- Field Mapping: A mapping between fields in the source table and their corresponding fields in the target table, just as a foreign key relationship would be defined by such mapping within a single database.
For example, say we have a table orders(id int, user_id int) in the source database and a table
user(id int, name text) in the target database.
We can create an object remote database relationship user joining the orders table to the user table using the
orders.user_id and user.id fields.
- Console
- CLI
- API
Head to the
Data > [database] > [orders] > Relationshipstab. Click onAdd Relationshipsto open the widget.Search for the remote database table in the "To Reference" input box
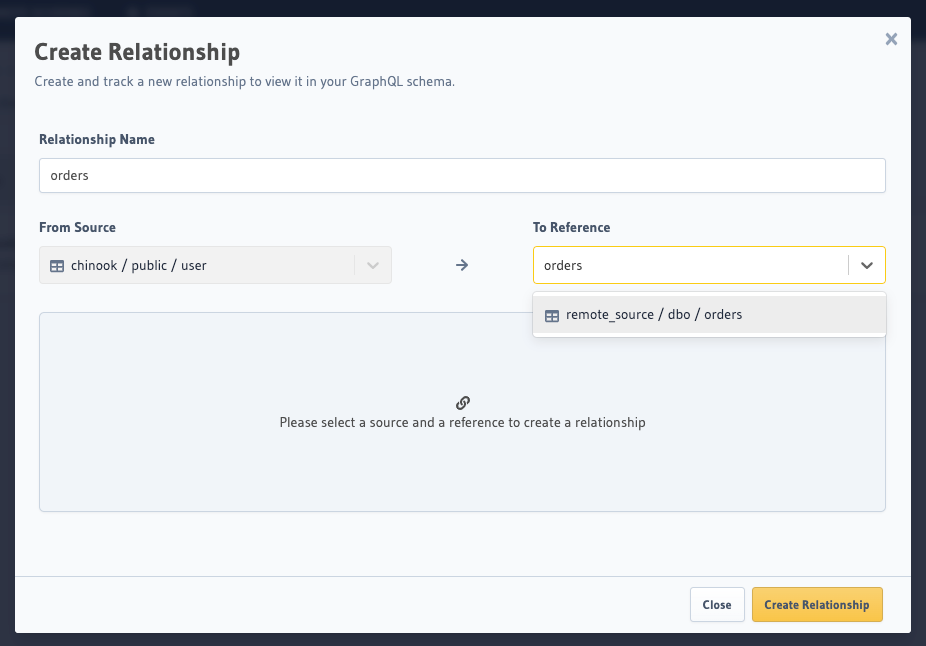
- Fill in the relationships details - type of the relationship & column mapping.
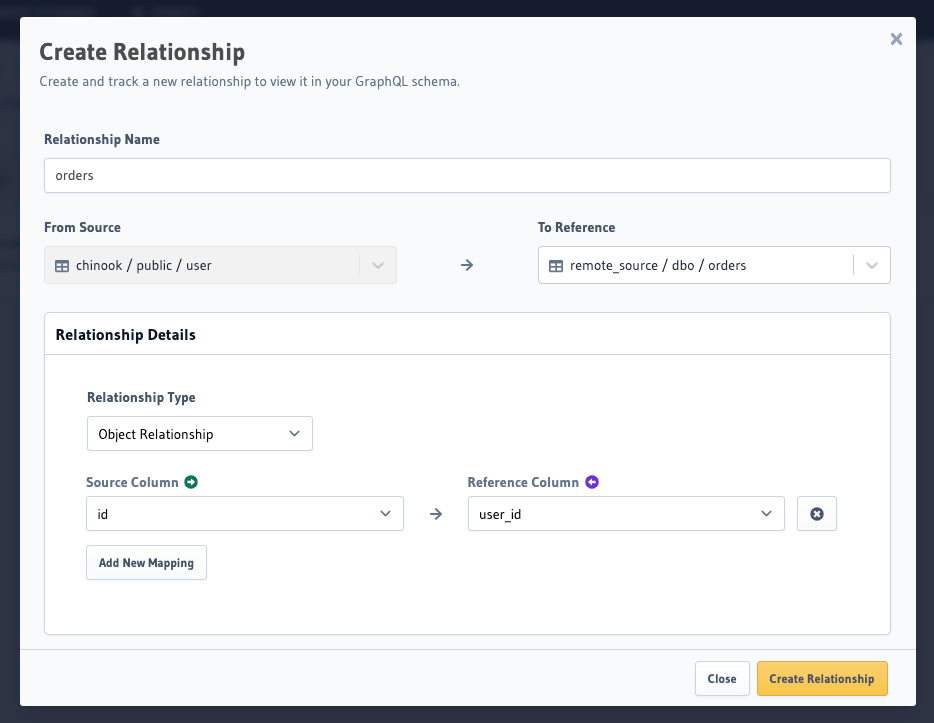
- Hit
Create Relationshipto track the remote relationship.
Update the metadata > databases > [db-name] > tables > [public_orders].yaml file:
table:
name: order
schema: public
remote_relationships:
- name: user
definition:
to_source:
relationship_type: object
source: pg2
table:
name: user
schema: public
field_mapping:
user_id: id
Apply the metadata:
hasura metadata apply
You can add a remote database relationship by using the
pg_create_remote_relationship
or
pg_update_remote_relationship
Metadata APIs with the to_source field.
POST /v1/metadata HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "pg_create_remote_relationship",
"args": {
"name": "user",
"source": "pg1",
"table": {
"name": "order",
"schema": "public"
},
"definition": {
"to_source": {
"relationship_type": "object",
"source": "pg2",
"table": {
"name": "user",
"schema": "public"
},
"field_mapping": {
"user_id": "id"
}
}
}
}
}
Step 3: Explore with GraphiQL
Run the following query in the GraphiQL editor to test your remote database relationship across the two connected databases: