Relationships Connect Data
Introduction
Relationships allow you to connect data, enabling you to query data across multiple entities.
Examples include:
- Querying a
Customerand at the same time getting theirOrdersand eachProductitem in those orders. (Model to Model) - Querying a
Customerand also getting the analytics of their app usage from another data source. (Model to Model in another subgraph or data connector) - Querying an
Orderand also getting a live currency conversion for the value of the order enabled with a lambda data connector with a connection to a currency exchange API. (Model to Command)
Relationships can be added between any kind of semantically related models and/or commands. They do not need to be related in the data source by, for example, a foreign key. They also do not need to be backed by the same data source or be in the same subgraph.
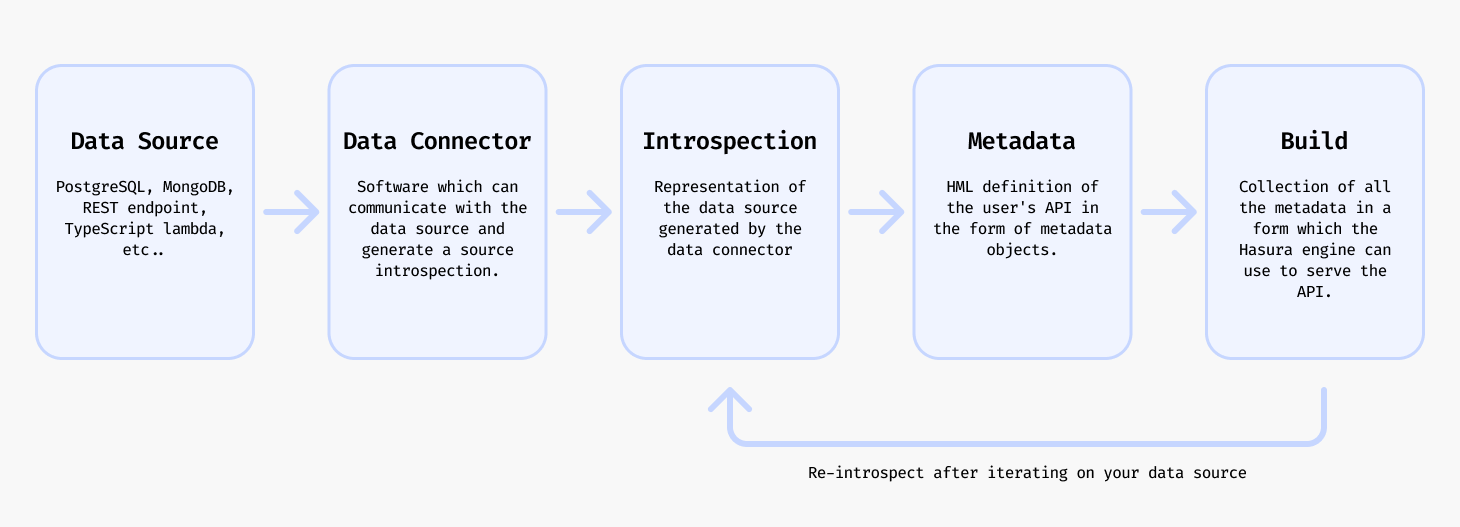
Lifecycle
Many relationships can be created automatically by the DDN CLI from detected underlying connections such as foreign keys. In such cases the lifecycle in creating a relationship in your metadata is as follows:
- Introspect your data source using the DDN CLI with the relevant data connector to fetch the entity resources.
- Add the detected relationships to your metadata with the DDN CLI.
- Create a build of your supergraph API with the DDN CLI.
- Serve your build as your API with the Hasura engine either locally or in the cloud.
- Iterate on your API by repeating this process or by editing your metadata manually as needed.
If the relationship cannot be detected automatically, you can easily manually create a relationship in your metadata and then perform lifecycle steps 3-5 from above as needed.
Create a relationship
Relationships are defined in metadata from an object type, to a model or command. But since models and commands are also defined with object types, you can think of relationships as being between models and/or commands.
The target command can be enabled with a a custom piece of business logic on a lambda data connector, or a native mutation operation.
Using the DDN CLI
The DDN CLI and your data connectors will detect many relationships in your data sources automatically, for instance from foreign keys in a relational database, and once introspected, you can add them to your metadata.
ddn connector introspect <connector_name>
ddn connector show-resources <connector_name>
ddn relationship add <connector_link_name> <collection_name>
Or optionally add all relationships found for a connector at once:
ddn relationship add <connector_link_name> "*"
Note that the above CLI commands work without also adding the relevant subgraph to the command with the --subgraph
flag because this has been set in the CLI context. You can learn more about creating and switching contexts in the
CLI context section.
Manually creating a relationship
Relationships can also be manually added to your metadata.
The VS Code extension can help you to author relationships.
For example, you can configure a relationship so that you can also get Orders when querying a Customer.
---
kind: Relationship
version: v1
definition:
sourceType: Customers # The existing source object type which also defines the model
name: orders # A name we want to use when we query the Orders from the Customer
target:
model: # The target can be a model or a command
name: Orders # The existing model that we want to access when we query the Orders from the Customer
relationshipType: Array # The relationship type which can be Object or Array. Since a customer can have many orders, we use an Array.
mapping: # The mapping defines which field on the source object type maps to which field on the target model
- source:
fieldPath:
- fieldName: customerId # The existing field on the source object type that we want to map to the target model
target:
modelField:
- fieldName: customerId # The existing field on the target model that we want to map to the source object type
By defining this Relationship object, all other models or
commands whose output type is the source object type in the relationship
will now have a connection to the target model or command.
Learn more about the Relationship object.
Update a relationship
Your underlying data source may change over time. You can update your relationship to reflect these changes.
If you have an automatically detected relationship and a property on the source object type has changed, you can update the relationship to reflect this change.
First, update your connector configuration and models.
ddn connector introspect <connector_name>
ddn model update <connector_name> <model_name>
Now, you can either delete the existing Relationship object and use the DDN CLI to add it again:
ddn relationship add <connector_link_name> <collection_name>
Or you can update the Relationship object manually. Learn more about the
Relationship object.
Delete a relationship
If you no longer need a relationship, simply delete the Relationship metadata object manually. It is fully
self-contained.
Tutorials
These tutorials follow on from the tutorials in the How to Build with DDN section.
Creating a relationship
Between a model and a model
- PostgreSQL
- MongoDB
- ClickHouse
Following on from the PostgreSQL tutorial in the How to Build with DDN section, you can create a relationship between two models which already have a foreign key relationship defined in the database.
In the tutorial, we created a posts to users relationship. Let's now add the inverse, detected automatically by the
same foreign key as a relationship between the Users to Posts models.
ddn connector show-resources my_pg
Add the users realtionship which was found automatically due to the foreign key.
ddn relationship add my_pg users
Now, you can build your supergraph API, serve it, and query your data.
ddn supergraph build local
ddn run docker-start
Now you can query your data with your relationship in the console get users and their posts.
ddn console --local
query UsersWithPosts {
users {
id
posts {
title
}
name
}
}
{
"data": {
"users": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Alice"
"posts": [
{
"title": "My First Post"
},
{
"title": "Another Post"
}
],
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Bob"
"posts": [
{
"title": "Bob's Post"
}
],
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Charlie"
"posts": [
{
"title": "Hello World"
}
],
}
]
}
}
Following on from the MongoDB tutorial in the How to Build with DDN section, you can manually create a relationship between two models which have no foreign-key-like relationship defined in the database which the data connector would be able to detect.
In the tutorial, we created a posts to users relationship. Let's now add the inverse as a relationship from the
Users to Posts models.
---
kind: Relationship
version: v1
definition:
name: posts
sourceType: Users
target:
model:
name: Posts
relationshipType: Array
mapping:
- source:
fieldPath:
- fieldName: userId
target:
modelField:
- fieldName: userId
Now you can build your supergraph API, serve it, and query your data.
ddn supergraph build local
ddn run docker-start
Now you can query your data with your relationship in the console get users and their posts.
ddn console --local
query UsersWithPosts {
users {
name
age
posts {
id
content
title
}
}
}
{
"data": {
"users": [
{
"name": "Alice",
"age": 25,
"posts": [
{
"id": "67585252ee01950f5dfc0421",
"content": "This is Alice's first post.",
"title": "My First Post"
},
{
"id": "67585252ee01950f5dfc0422",
"content": "Alice writes again!",
"title": "Another Post"
}
]
},
{
"name": "Bob",
"age": 30,
"posts": [
{
"id": "67585252ee01950f5dfc0423",
"content": "Bob shares his thoughts.",
"title": "Bob's Post"
}
]
},
{
"name": "Charlie",
"age": 35,
"posts": [
{
"id": "67585252ee01950f5dfc0424",
"content": "Charlie joins the conversation.",
"title": "Hello World"
}
]
}
]
}
}
Following on from the ClickHouse tutorial in the How to Build with DDN section, you can manually create a relationship between two models which have no foreign-key-like relationship defined in the database which the data connector would be able to detect.
In the tutorial, we created a posts to users relationship. Let's now add the inverse as a relationship from the
Users to Posts models.
---
kind: Relationship
version: v1
definition:
name: posts
sourceType: Users
target:
model:
name: Posts
relationshipType: Array
mapping:
- source:
fieldPath:
- fieldName: userId
target:
modelField:
- fieldName: userId
Now you can build your supergraph API, serve it, and query your data.
ddn supergraph build local
ddn run docker-start
Now you can query your data with your relationship in the console get users and their posts.
ddn console --local
query UsersWithPosts {
users {
name
age
posts {
content
title
userId
}
}
}
{
"data": {
"users": [
{
"name": "Alice",
"age": 25,
"posts": [
{
"content": "This is Alice's first post.",
"title": "My First Post",
"userId": 1
},
{
"content": "Alice writes again!",
"title": "Another Post",
"userId": 1
}
]
},
{
"name": "Bob",
"age": 30,
"posts": [
{
"content": "Bob shares his thoughts.",
"title": "Bob's Post",
"userId": 2
}
]
},
{
"name": "Charlie",
"age": 35,
"posts": [
{
"content": "Charlie joins the conversation.",
"title": "Hello World",
"userId": 3
}
]
}
]
}
}
Between a model and a command
We will use a business logic function defined in a lambda data connector to build a model to command relationship for all connector types.
Create a custom function with the TypeScript lambda data connector to use in the tutorials
Initialize a new data connector with the TypeScript connector.
ddn connector init my_ts -i
- Select
hasura/nodejsfrom the list of connectors. - Accept the suggested port.
- Edit the
functions.tsfile in the connector directory with theshoutNamefunction.
export function shoutName(name: string) {
return `${name.toUpperCase()}`;
}
ddn connector introspect my_ts
Then, we can add the model made available from the introspection.
ddn command add my_ts shoutName
To create a relationship between the Users model and the shoutName function (see the drop-down above for how to
implement this function) we can create the following relationship. Using the
VS Code extension makes the authoring and
validation of the relationship easier.
---
kind: Relationship
version: v1
definition:
name: shoutName # Define a name to expose in the supergraph API
sourceType: Users # The existing source object type (which also defines the source model Users)
target:
command: # The target is a command
name: ShoutName # The name of the existing command we have defined in metadata
subgraph: app # The existing subgraph the command is defined in
mapping:
- source:
fieldPath:
- fieldName: name # The field on the source object type that we want to provide to the target command as an argument
target:
argument:
argumentName: name # The name of the argument on the target command that we want to map to the source field
ddn supergraph build local
ddn run docker-start
ddn console --local
We can now query the Users model and also return the result of the shoutName function with its default argument of
name.
query {
users {
name
shoutName
}
}
{
"data": {
"users": [
{
"name": "Alice",
"shoutName": "ALICE"
},
{
"name": "Bob",
"shoutName": "BOB"
},
{
"name": "Charlie",
"shoutName": "CHARLIE"
}
]
}
}
With relationships and custom commands we can transform or enrich any data.
Updating a relationship
Your underlying data source may change over time. You can update your relationship to reflect these changes.
If you have an automatically detected relationship and a property on the source object type has changed, you can update the relationship to reflect this change.
First, update your connector configuration and models.
ddn connector introspect <connector_name>
ddn model update <connector_name> <model_name>
Now, you can either delete the existing Relationship object and use the DDN CLI to add it again:
ddn relationship add <connector_link_name> <collection_name>
Or you can update the Relationship object manually. Learn more about the
Relationship object.
Deleting a relationship
If you no longer need a relationship, simply delete the Relationship metadata object manually. It is fully
self-contained.
Reference
You can learn more about relationships in the metadata reference docs.
