Snowflake: Extend Schema with User-defined Functions
Snowflake UDFs are supported from v2.26.0.
What are user-defined functions?
Snowflake User-defined functions (UDFs) are custom functions that can be used to either encapsulate some custom business logic or extend the built-in SQL functions and operators.
Hasura GraphQL Engine lets you expose certain types of UDFs as top-level fields in the GraphQL API to allow querying them.
Supported functions
Currently, only functions which satisfy the following constraints can be exposed as top level fields in the GraphQL API:
- The function must return rows in the format of an existing tracked table in the schema.
Creating functions
Functions can be created the Snowflake UI. See the Snowflake docs for details.
Track functions
Functions can be present in the underlying Snowflake database without being exposed over the GraphQL API. In order to expose a function over the GraphQL API, it needs to be tracked.
- Console
- API
You can track any existing supported functions in your database from the Data -> Manage page.
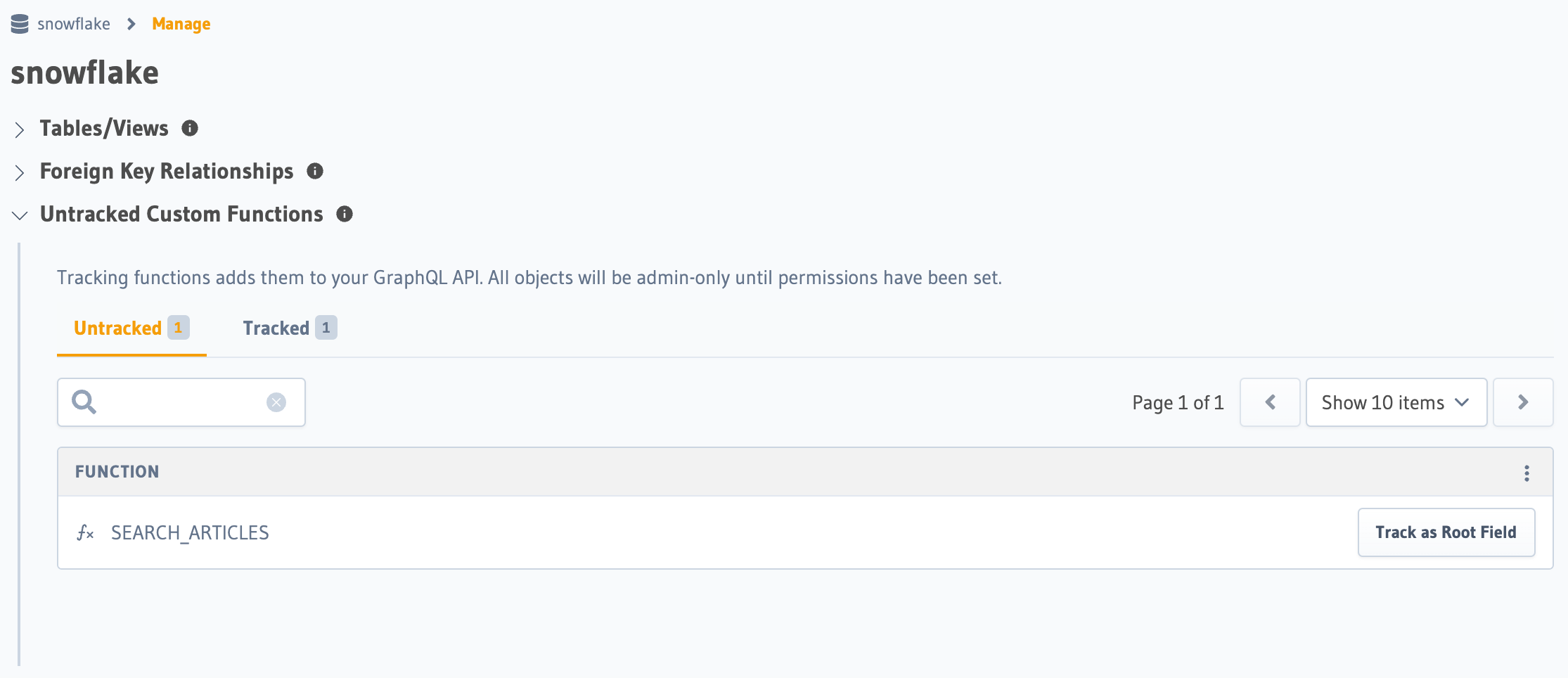
Click Track as Root Field and select the return table.
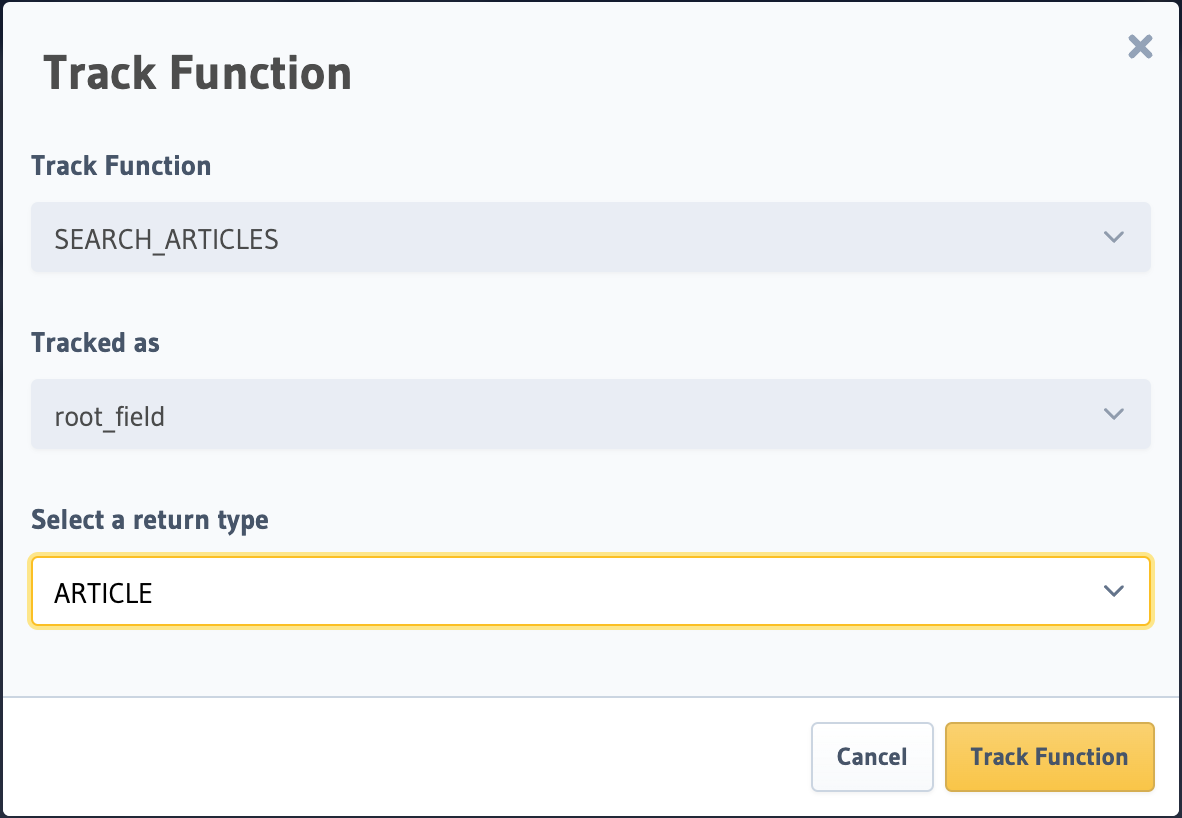
To track the function and expose it over the GraphQL API, make the following API call to the snowflake_track_function Metadata API:
POST /v1/metadata HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "snowflake_track_function",
"args": {
"source": "<db_name>",
"schema": "public",
"name": ["name", "of", "function"],
"configuration": {
"response": {"type": "table", "table": TABLE_NAME}
}
}
}
Snowflake doesn't currently support direct reference of tables in the return type of function definitions. To accomadate for this, Hasura currently requires that the response be specified in metadata.
Use cases
Custom functions are ideal solutions for retrieving some derived data based on some custom business logic that requires user input to be calculated based on inputs. If your custom logic does not require any user input, you can use views instead.
Querying custom functions using GraphQL queries
Using arguments with custom functions
As with tables, arguments like where, limit, order_by, offset, etc. are also available for use with
function-based queries.
For example, limit the number of articles returned by the function defined in the text-search example above:
query {
search_articles(args: { search: "hasura" }, limit: 5) {
id
title
content
}
}