Single Sign-on Configuration
Authorization Flow
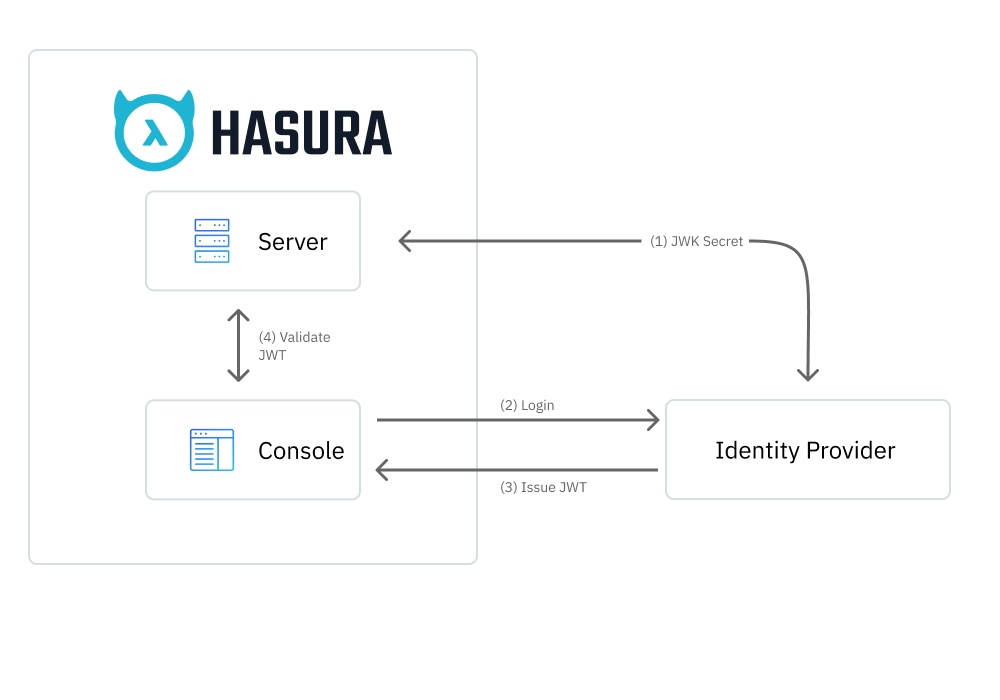
- First of all, the GraphQL Engine server needs to know the authentication context and verification secrets of the Identity Provider (IdP). If the JSON Web Key Sets (JWKS) are exposed on the remote URL, the server will fetch the JWT secret on start up.
- When clicking on the SSO login button, the Console initiates the Authorization Code flow with the IdP.
- On successful authorization, the IdP issues a JWT ID token to the Console with an
adminor equivalent role. - The Console then uses the JWT to execute Metadata and GraphQL API calls.
Configuration
Configuring the identity provider
Create a new service provider on your identity provider with the following configuration:
- Configure the allowed origin, CORS to be where the Hasura Console is hosted.
- Set the callback URL to
http(s)://<hasura-domain>/console/oauth2/callback. - Ensure the ID token option is enabled.
- Add
"x-hasura-allowed-roles": ["admin"]and"x-hasura-default-role": "admin"into the JWT custom claims. The JWT payload should follow the Hasura JWT spec.
Once created, note the client ID, login URL, request token URL, and JWT secret.
Configuring Hasura Enterprise
Set the --sso-providers argument
(HASURA_GRAPHQL_SSO_PROVIDERS) which takes a list of SSO provider objects.
[
{
"client_id": "<client-id-from-idp>",
"name": "<display-name>",
"scope": "openid",
"authorization_url": "<login-url>",
"request_token_url": "<request-token-url>",
"admin_roles": ["admin"],
"jwt_secret": {
"type": "RS256",
"jwk_url": "https://...",
"issuer": "myapp"
}
}
]
client_id: Client ID of the identity application.name: Display name of the SSO button in the login page of the Hasura Console.scope: The OAuth scope. It must containopenidso the identity provider can return the JWTid_tokenfrom the request token endpoint.authorization_url: The authorization URL that the browser redirects to from the Console.request_token_url: URL the Console uses to get the ID token using the authorization code.admin_roles: By default, the role should beadminin the token issued by IdP so that Console access is provided. But, if you have a configuration where theadminrole is used for something else, set this key to indicate which roles should be treated as admin. This is an array of strings.jwt_secret: JWT secret the server uses to verify the JWT signature. It follows the JWT secret configuration.
Other protocols
You can use any OpenID Connect compliant middleware service such as Dex that acts as a portal to other identity providers. Hasura talks to the middleware to authorize and verify signatures without caring about how the middleware handles external providers. Dex supports SAML 2.0, LDAP protocols, as well as identity providers like GitHub, Google, and Active Directory.
The authorization flow is similar to the OAuth / OpenID Connect flow, with an extra step to authenticate the IdP through middleware.
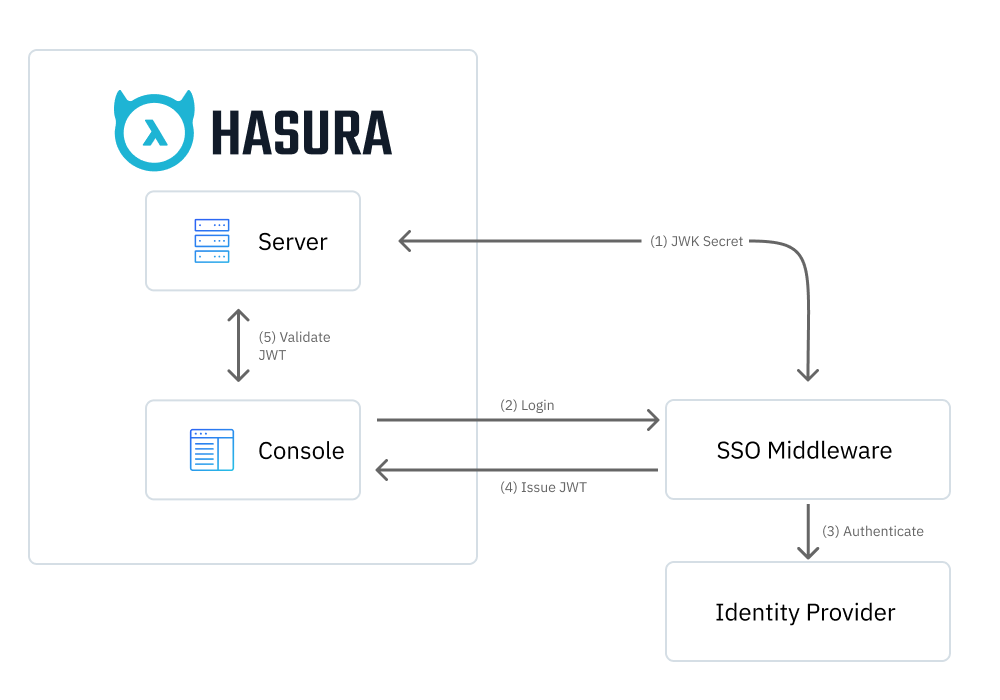
- Configure GraphQL Engine with the JWT Secret and Login URL of the middleware.
- When clicking on the SSO login button, the Console initiates the Authorization Code flow with the middleware.
- The middleware handles the authorization with the IdP.
- On successful authorization, the middleware converts the profile of the IdP to a JWT ID token and issues it to the Console.
- The Console then uses the JWT to execute Metadata and GraphQL API calls.
SAML configuration
Configuring the identity provider
Create a new service provider on your SAML identity provider with the following configuration:
- Configure the callback URL to be
http(s)://<dex-url>/callback. - Note the sign-on endpoint, entity ID, and issuer.
- Download the CA certificate.
- Note the XML attribute paths of username, email, and roles so Dex can map those attributes to JWT custom claims. You can find them in the Federation metadata document.
Configuring Dex
Create a config file with a static client and a SAML connector.
# The default Dex base URL is http://localhost:5556/dex
# However the /dex path is removed in the helm chart
issuer: http(s)://<dex-url>
storage:
type: memory
# Configuration for the HTTP endpoints.
web:
http: 0.0.0.0:5556
allowedOrigins: ['*']
staticClients:
- id: hasura-app
redirectURIs:
- 'http(s)://<hasura-url>/console/oauth2/callback'
name: 'Hasura App'
public: true
connectors:
- type: saml
id: saml
name: SAML
config:
ssoURL: <SAML sign-on endpoint>
# CA to use when validating the signature of the SAML response.
ca: /path/to/saml-ca.pem
# CA's can also be provided inline as a base64'd blob.
#
# caData: ( RAW base64'd PEM encoded CA )
# To skip signature validation, uncomment the following field. This should
# only be used during testing and may be removed in the future.
#
# insecureSkipSignatureValidation: true
redirectURI: http(s)://<dex-url>/callback
# Name of attributes in the returned assertions to map to ID token claims.
usernameAttr: name
emailAttr: email
# groups are required to be mapped with x-hasura-allowed-roles
groupsAttr: groups
# Optional: Manually specify dex's Issuer value.
#
# When provided dex will include this as the Issuer value during AuthnRequest.
# It will also override the redirectURI as the required audience when evaluating
# AudienceRestriction elements in the response.
entityIssuer: http(s)://<dex-url>/callback
# Optional: Issuer value expected in the SAML response.
# ssoIssuer: https://login.microsoftonline.com/4bc01d1d-5a16-4d79-b651-5a5b592aeb57/v2.0
Configuring Hasura Enterprise
Set the environment variable HASURA_GRAPHQL_SSO_PROVIDERS to talk to Dex.
[
{
"client_id": "hasura-app",
"name": "SAML Login",
"scope": "openid offline_access groups",
"authorization_url": "http(s)://<dex-url>/auth",
"request_token_url": "http(s)://<dex-url>/token",
"admin_roles": ["admin"],
"jwt_secret": {
"type": "RS256",
"jwk_url": "http(s)://<dex-url>/keys",
"issuer": "http(s)://<dex-url>",
"claims_map": {
"x-hasura-allowed-roles": { "path": "$.groups" },
"x-hasura-default-role": { "path": "$.groups[0]" }
}
}
}
]
The groups scope is required to enable the groups field in the JWT claims. You also need to set the claims_map to
map the groups field to x-hasura-allowed-roles and x-hasura-default-role.