Setting default values for fields using Postgres defaults¶
Table of contents
Introduction¶
You can set values of certain fields automatically when not explicitly passed to a fixed value, e.g. true for a boolean field, or output of a simple SQL function, e.g. now() for a timestamp field, by setting column default values in the table definition.
Note
The Postgres default value is ignored when a value is explicitly set to the field.
Example: Say we have a field created_at in a table article which we want to be set to the current
timestamp whenever a new row is added to the table:
Step 1: Modify the table¶
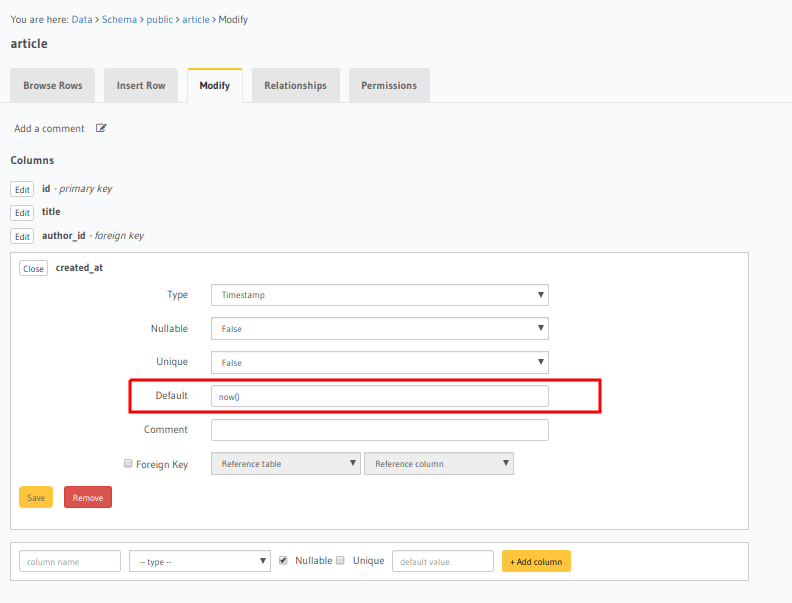
Edit the created_at field and set its default value as the SQL function now().
Open the console and head to Data -> [article] -> Modify.
Click the Edit button next to the created_at field and add now() as a default value.
Create a migration manually and add the following SQL statement to the up.sql file:
ALTER TABLE ONLY "public"."article" ALTER COLUMN "created_at" SET DEFAULT now();
Add the following statement to the down.sql file in case you need to roll back the above statement:
ALTER TABLE article ALTER COLUMN created_at DROP DEFAULT;
Apply the migration by running:
hasura migrate apply
You can add a default value by using the run_sql metadata API:
POST /v1/query HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "run_sql",
"args": {
"sql": "ALTER TABLE article ALTER COLUMN created_at SET DEFAULT now();"
}
}
To set an auto-incrementing default value
To set a default value as an auto-incrementing integer you first need to set up a sequence which will be the
source of our default value.
Let’s say we have a field called roll_number which we would like to be set by default as an auto-incremented
integer.
Run the following SQL command to create a new sequence.
CREATE SEQUENCE roll_number_seq;
Now set the default value of the roll_number field as nextval('roll_number_seq').
Step 2: Run an insert mutation¶
Now if you do not pass the created_at field value while running an insert mutation on the article table, its
value will be set automatically by Postgres.
mutation {
insert_article(
objects: [
{
title: "GraphQL manual",
author_id: 11
}
]) {
returning {
id
title
created_at
}
}
}
