Query Data with GraphQL
After loading the sample database to YugabyteDB, you can benefit from the GraphQL API layer provided by Hasura. In this and the following final sections, you will use GraphQL queries and mutations to process the data stored in the YugabyteDB cluster.
Expose Tables to GraphQL Layer
Even though Hasura automatically detects structural changes on the database side, you still need to specify explicitly what tables can be queried with GraphQL APIs.
Expose the Users and Todos tables to the GraphQL layer:
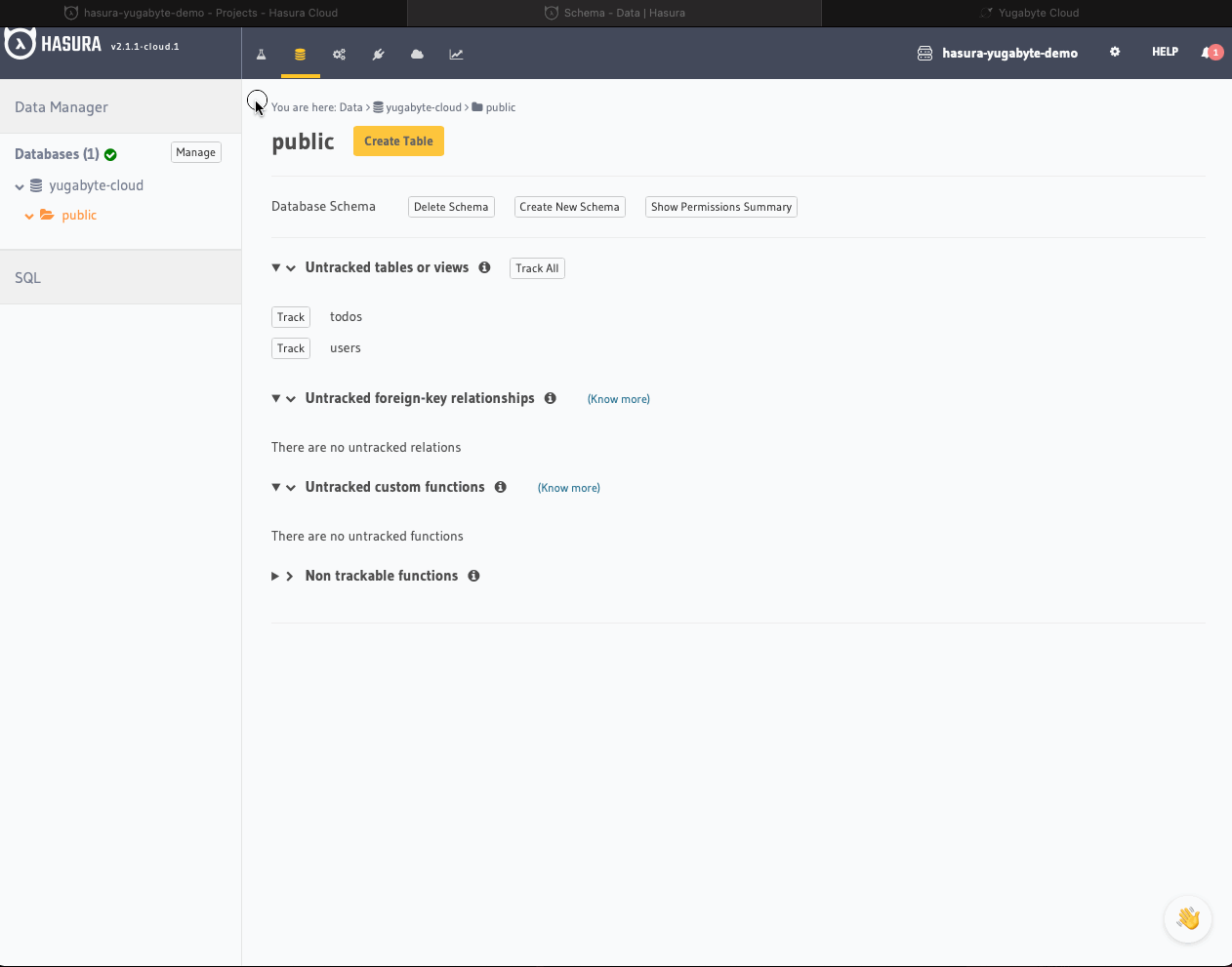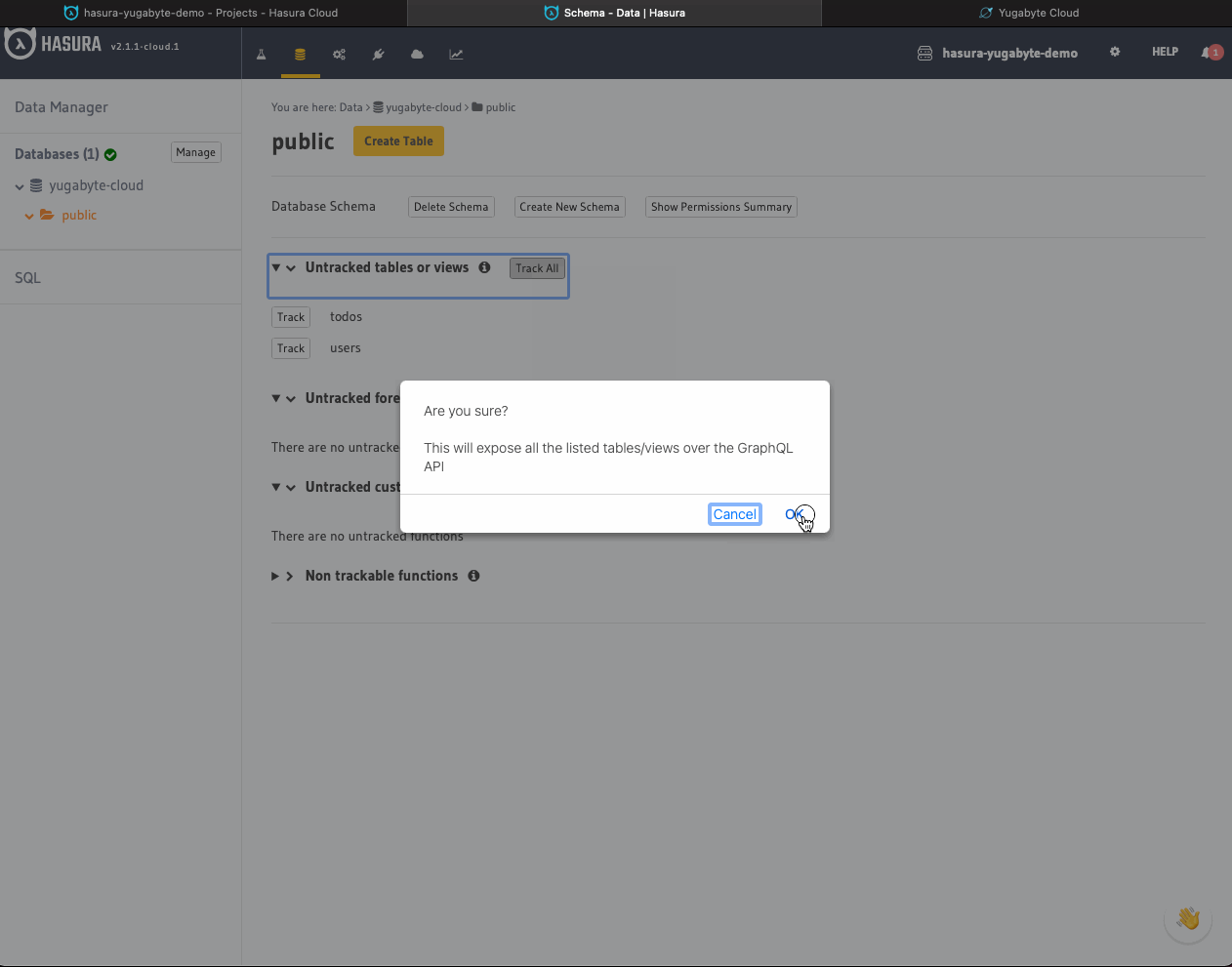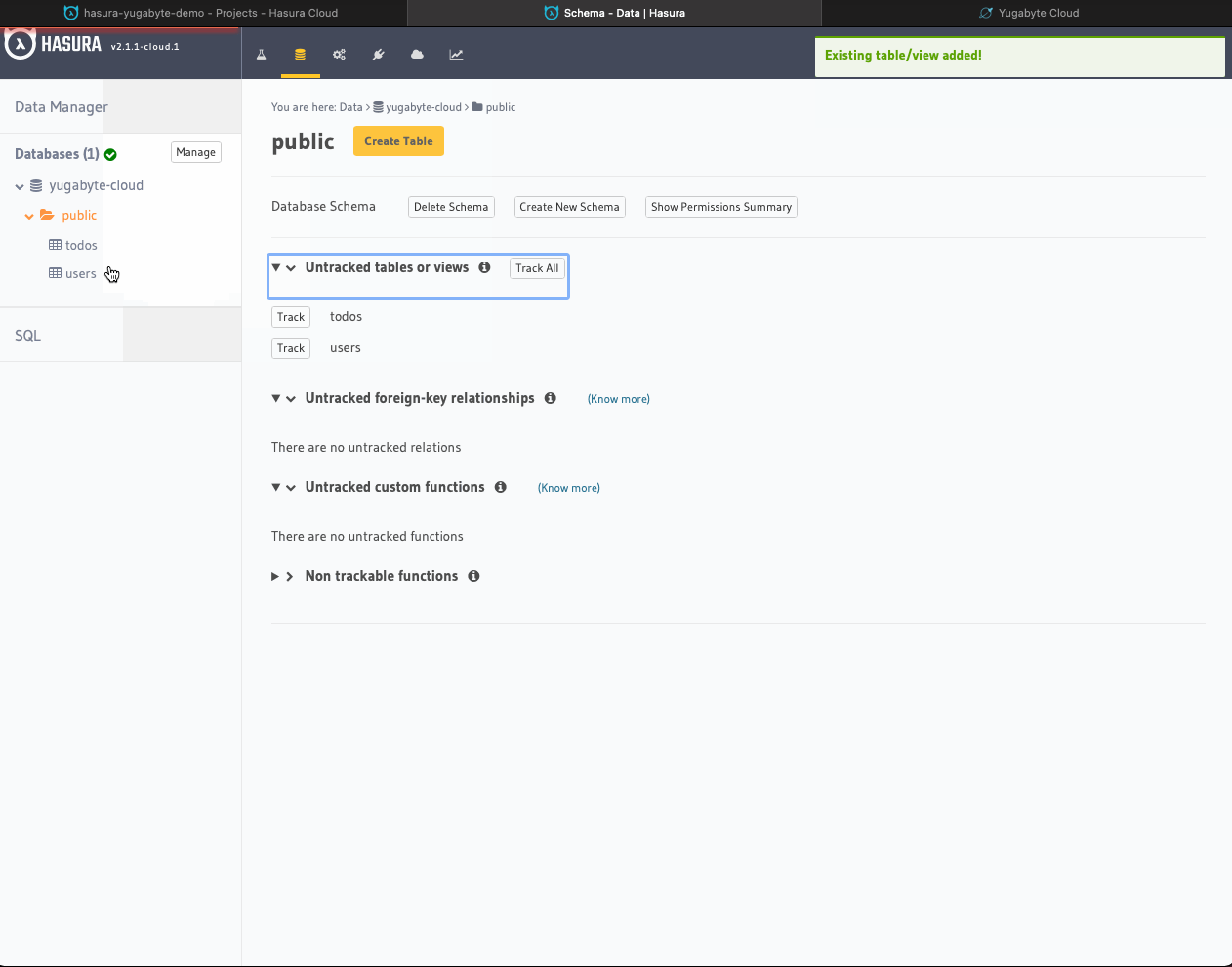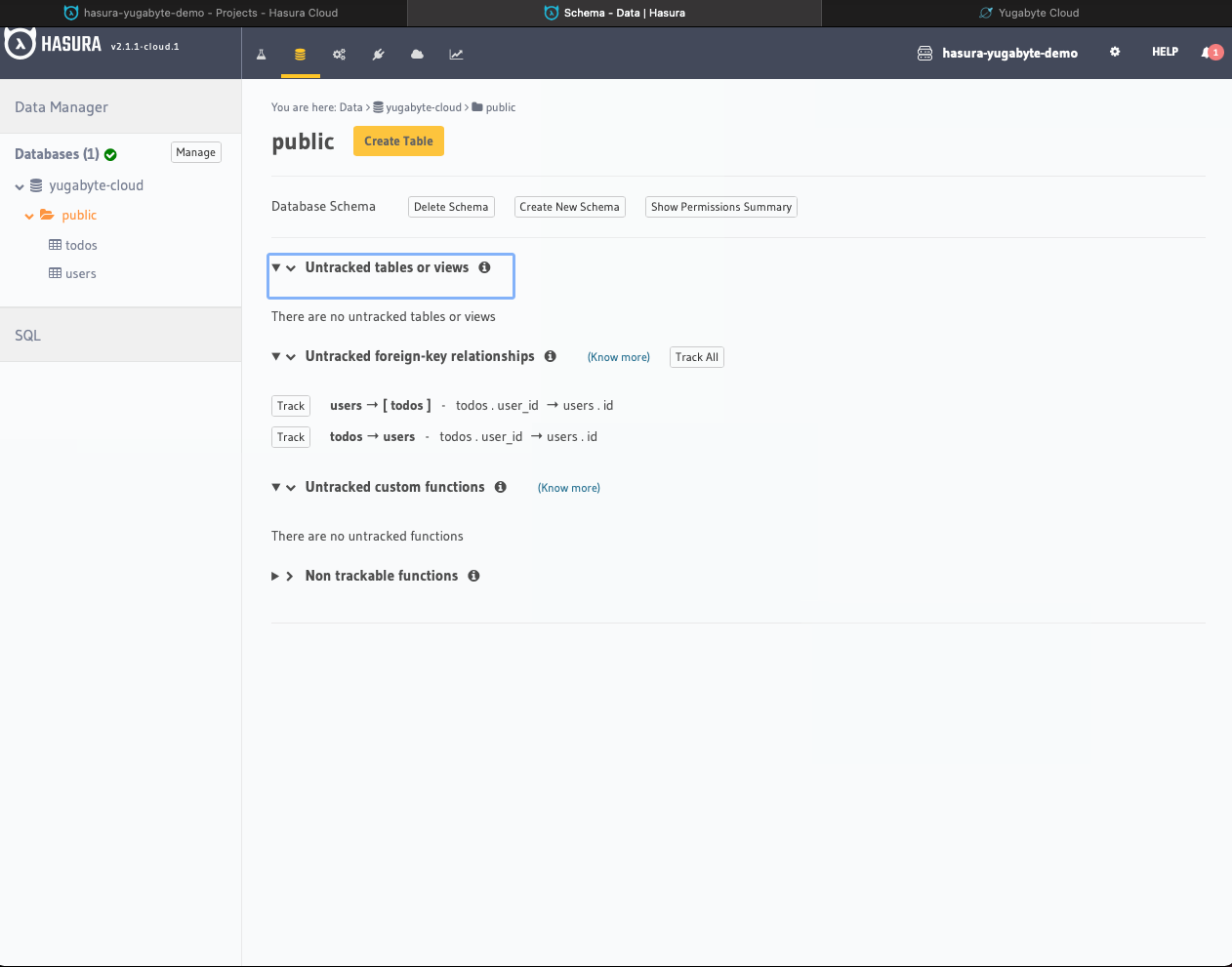
- Open the Data & Schema Management tab of the Hasura Console.
- Click the Track All button to be able to work with both Users and Todos via GraphQL APIs.
Query Users
Next, read records of the Users table with GraphQL:
- Open the API Explorer tab of the Hasura Console:
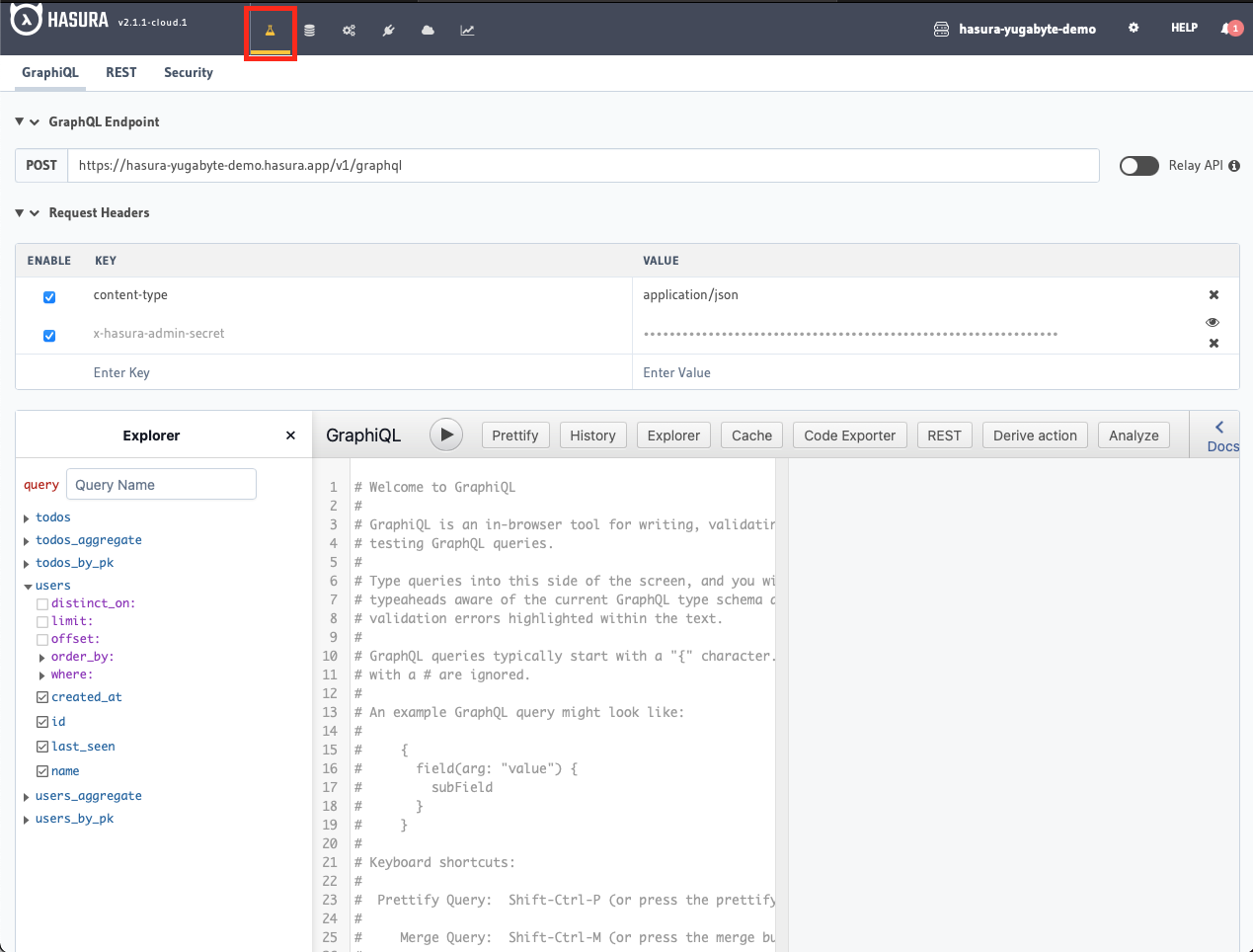
- Execute the GraphQL query below:
query {users {idnamecreated_atlast_seen}}
- Confirm the output is as follows:
{"data": {"users": [{"id": 1,"name": "Mark","created_at": "2022-02-02T18:49:45.092247","last_seen": null},{"id": 2,"name": "Jenny","created_at": "2022-02-02T18:49:45.092247","last_seen": null}]}}
As you see, your Hasura instance successfully receives the query, translates it to a Postgres-compliant SQL request, and executes over YugabyteDB data.
Build apps and APIs 10x faster
Built-in authorization and caching
8x more performant than hand-rolled APIs






