Access Control
In this part of the tutorial, we are going to define role based access control rules for each of the models that we created. Access control rules help in restricting querying on a table based on certain conditions.
Access control rules can be applied on
- Row level
- Column level
Row Level
With row level access control, users can access tables without having access to all rows on that table. This is particularly useful to protect sensitive personal data which is part of the table. This way, you can allow all users to access a table, but only a specific number of rows in that table.
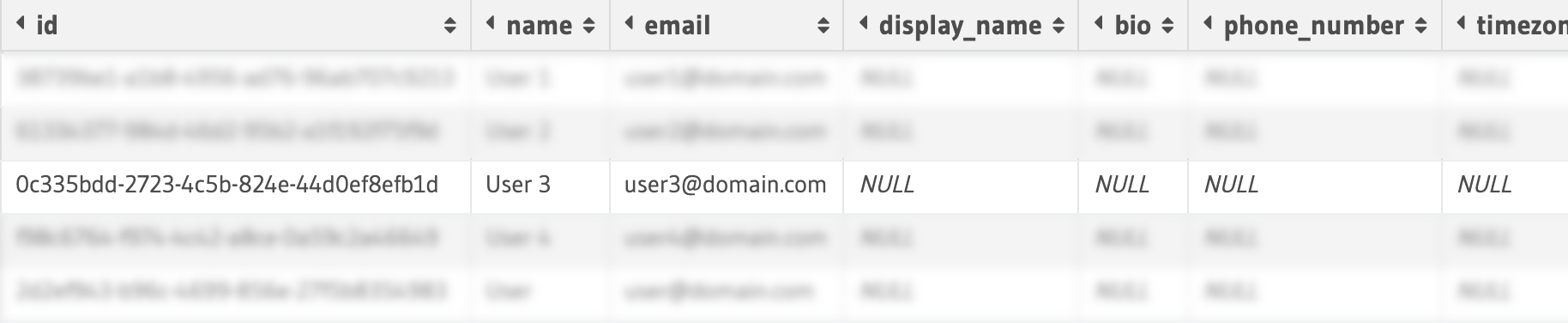
Column Level
Column level access control lets you restrict access to certain columns in the table. This is useful to hide data which are not relevant, sensitive or used for internal purposes. A typical representation of data looks like:
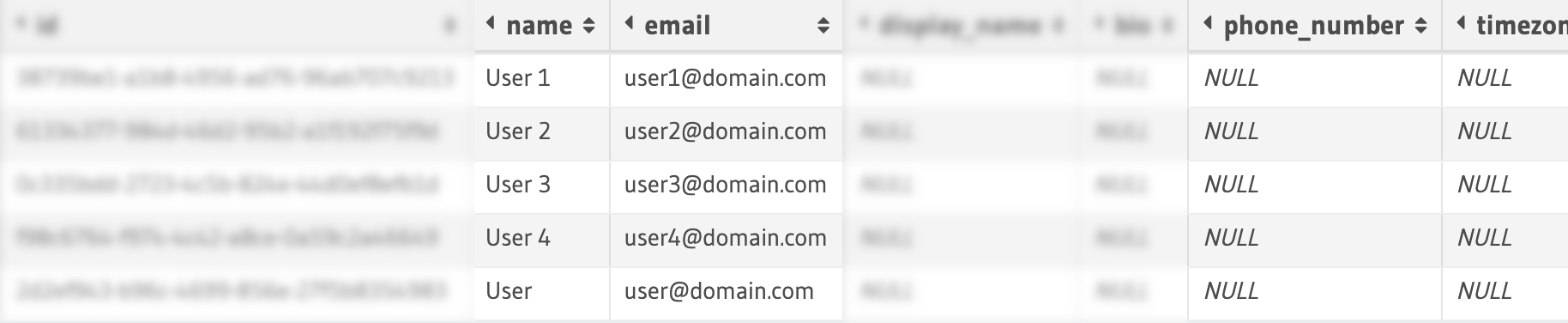
As you can imagine, combining both these rules gives a flexible and powerful way to control data access to different stakeholders involved.
Types of operations
Access control rules can be applied to all the CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update and Delete). Some operations can be completely restricted to not allow the user perform the operation.
In the previous section we learnt that the slack app requires a role called user. We will create permissions for this role in the next part.
Build apps and APIs 10x faster
Built-in authorization and caching
8x more performant than hand-rolled APIs






