Node.js
This guide is for you if any of the following satisfies:
- You want to accelerate your API creation journey
- You want to expose a GraphQL API (possibly with Node.js)
- You want a high-performance API, REST, or GraphQL
New to GraphQL? Check out the Introduction to GraphQL tutorial to learn the core concepts quickly.
- You will learn how to create a GraphQL server with Node.js and why you actually shouldn't.
- You will come across the performance implications of implementing a GraphQL server and how Hasura mitigates it with some benchmarks to showcase.
- If you have an existing GraphQL API with Node.js, you can integrate it with Hasura as a Remote Schema to get a unified GraphQL API or supergraph.
- If you have an existing REST API with Node.js, you can transform that declaratively to GraphQL without writing any code using Hasura REST Connectors.
- You can also re-use or custom write REST endpoints with Node.js and map the endpoint to a GraphQL schema in Hasura.
New to Hasura? The Hasura GraphQL Engine makes your data instantly accessible over a real-time GraphQL API to build and ship modern, performant apps and APIs 10x faster. Hasura connects to your databases, REST and GraphQL endpoints, and third-party APIs to provide a unified, connected, real-time, secured GraphQL API for all your data. Check out the documentation.
This guide covers common backend application tasks, such as creating REST endpoints using Express and TypeScript. This example works with Node version 18 or above. We also go over how to integrate your Node app with Hasura.
Building a custom GraphQL Server in Node.js
If you have ever built a GraphQL Server in any of the Node.js frameworks, you would have come across various steps before exposing the API endpoint in GraphQL. Some of them include:
- Setting up GraphQL dependencies and npm modules
- Defining GraphQL schema type definitions
- Writing GraphQL resolvers
- Setting up DataLoader / batching libraries for optimized performance
- Exposing a restricted list of queries to the clients with authorization
and many more during maintenance and updates.
Among all the repetitive steps above, writing resolvers in GraphQL is the most time-consuming, is a heavy lift, and is something you keep fiddling with as the API changes. Let us go over the steps outlined above.
Node.js project setup for GraphQL server
Initialize a Node app in a new folder.
npm init -y
In the created package.json replace "main": "index.js" with "type": "module"
Install the dependencies we will use.
npm install express graphql graphql-request graphql-yoga
Install the dev dependencies.
npm install -D @graphql-codegen/cli @graphql-codegen/client-preset @graphql-codegen/typescript @graphql-codegen/typescript-resolvers @tsconfig/node18-strictest @types/express @types/node @typescript-eslint/eslint-plugin @typescript-eslint/parser cross-env eslint ts-node ts-node-dev typescript
Create tsconfig.json
{"extends": "@tsconfig/node18-strictest/tsconfig.json","compilerOptions": {"importsNotUsedAsValues": "remove"}}
Create .eslintrc.cjs
module.exports = {extends: ["eslint:recommended", "plugin:@typescript-eslint/recommended"],parser: "@typescript-eslint/parser",plugins: ["@typescript-eslint"],root: true,};
Borrowing from the GraphQL Yoga quickstart we add two scripts to our package.json
{"scripts": {"dev": "cross-env NODE_ENV=development ts-node-dev --exit-child --respawn src/main.ts","start": "ts-node src/main.ts"}}
Create a Node.js GraphQL server with GraphQL Yoga
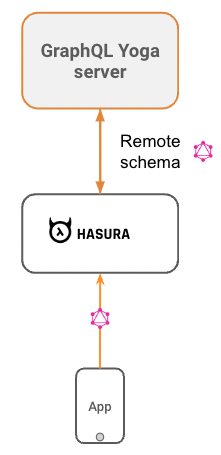
We can make a custom GraphQL server in Node using GraphQL Yoga and GraphQL Code Generator. Then we connect it to Hasura using a Remote Schema.
Create
server-codegen.tsimport type { CodegenConfig } from "@graphql-codegen/cli";const server: CodegenConfig = {schema: "schema.graphql",generates: {"./src/gql/server/resolvers-types.ts": {config: {useIndexSignature: true,},plugins: ["typescript", "typescript-resolvers"],},},};export default server;In
package.jsonadd a codgen script.{"scripts": {"codegen": "graphql-codegen --config server-codegen.ts"}}Define
schema.graphql, which will create the schema for our GraphQL server.type Post {id: Int!title: String!}type Query {posts: [Post]}Run the code generator
npm run codegen.Create the GraphQL Yoga server.
import { readFileSync } from "node:fs";import { createServer } from "@graphql-yoga/node";import { Resolvers } from "./gql/server/resolvers-types";const typeDefs = readFileSync("./schema.graphql", "utf8");const resolvers: Resolvers = {Query: {posts: async () => {return [{id: 1,title: "hi",},];},},};const graphQLServer = createServer({ schema: { typeDefs, resolvers } });Add it to Express.
app.use("/graphql", graphQLServer);Run the Express app and navigate to
<Express URL>/graphql, if everything works you should be able to queryposts.
Here's the source code for the above GraphQL server.
This is the bare minimum boilerplate that you need to get your GraphQL API running for a simple query. Extrapolating this for an app like e-commerce or even a blog system, you might need to replicate schema type definitions and resolver code for as many models as your application has.
We looked at creating an API for simple CRUD. Extending this for real-time apps and use cases, you need an API layer that supports streaming data in real time. Interestingly, GraphQL spec provides a cleaner abstraction for consumers of real-time API through GraphQL Subscriptions.
Real-time Subscriptions
Let us break down the creation of a GraphQL Subscription API with a GraphQL Server in Node.js that you write yourself.
- You will need a pub-sub connection, exposed via WebSockets.
- Set up some directives (
@liveetc). This varies for server implementations and clients consuming them. - Optimize performance through multiplexing.
Hasura exposes a real-time GraphQL API on many databases. There are two forms of subscriptions that your clients can listen in:
- Live queries (Gives the entire result set of the query)
- Streaming Subscriptions (Gives only the newly added result set from the cursor)
The GraphQL Subscriptions API is out of the box with Hasura.
Read more about various types of GraphQL Subscriptions and the intricacies around the same.
High-performance GraphQL for Node.js
Building a high-performance GraphQL Server is tricky. Look at Ben Awad’s performance benchmarks for Node.js GraphQL Servers. Although these numbers are old, they throw light on why writing your own GraphQL Server in Node.js is not a great choice.
Let’s deep dive into how performance becomes a blocker at a high level.
- You start with one data source/database. Define schema. Write GraphQL sesolvers
- Find N+1 query problem 😭with naive implementations
- Optimize with DataLoader pattern and batching techniques
- Try to federate across multiple data sources
- Face more performance issues
And finally, give up on GraphQL.
Why is it hard to nail performance with a GraphQL API?
It is easy to implement a naive resolver that has N+1 problems. Resolvers typically overfetch data on the server side and return the same or a filtered object back to the client.
Compiler approach to GraphQL allows you to transform an incoming GraphQL query of any arbitrary depth, querying a single relational store to a highly optimized SQL query.
In a series of benchmarks with varying complexity of queries and data shapes, we measured query response times, query execution times, and memory usage and found that Hasura significantly outperformed a custom-written GraphQL resolver in Node.js. Some key takeaways include:
- Hasura was 3.6x faster in a benchmark against graphql-yoga on PostgreSQL.
- Apollo server requires 9x more nodes to have similar performance that Hasura was able to accomplish for 1k concurrent users on Oracle.
Benchmarks for Hasura vs. GraphQL Yoga on PostgreSQL Read more on the benchmark setup
Node.js GraphQL API federation using Hasura Remote Schema
We can connect our custom GraphQL server to Hasura using Remote Schemas.
In the Hasura Console Remote Schema tab, add your Node server
<Express URL>/graphqlIn the API Explorer tab, try querying the sample shows.
{posts {title}}
Convert a Node.js REST API endpoint to GraphQL
In this section, we will write a REST endpoint in Node.js using Express and see how to transform that to GraphQL. We will create a login POST endpoint that takes a username and password and returns an access code.
In our src/main.ts, we use Express to create an HTTP server:
import express from "express";import { actionRouter } from "./action/action";export interface ActionPayload<T> {action: {name: string;};input: T;request_query: string;session_variables: Record<string, string>;}const app = express();app.use(express.json());const port = 3000;app.use("/action", actionRouter);app.listen(port, () => {console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}`);});
In action/action.ts, we generate the handler:
import express, { Router, Request, Response } from "express";import { ActionPayload } from "../main";const actionRouter: Router = express.Router();interface loginArgs {username: string;password: string;}interface LoginResponse {AccessToken: string;}actionRouter.post("",async (req: Request<object, object, ActionPayload<loginArgs>>,res: Response<LoginResponse>) => {console.log(req.body);res.send({ AccessToken: "test" });});export { actionRouter };
Run the app.
npm run dev
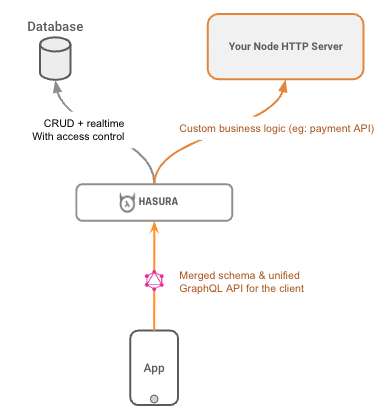
Add Node REST endpoint to GraphQL schema using Hasura Actions
When writing a backend we usually have to write around 80% of our code doing boilerplate CRUD operations. Hasura helps us by autogenerating this part.
When we need to write custom business logic, we can integrate our Node REST endpoint using Hasura Actions, giving us the best of both worlds.
In the Actions tab on the Hasura Console, we will set up a custom login function that calls the REST endpoint we created:
type Mutation {login(username: String!, password: String!): LoginResponse}
New types definition:
type LoginResponse {AccessToken: String!}
Create the action, click the Codegen tab, and select typescript-express.
Copy the files and run the Express application:
npm run dev
In the Hasura API explorer tab you should now be able to test it.
mutation {login(password: "password", username: "username") {AccessToken}}
Result:
{"data": {"login": {"AccessToken": "test"}}}
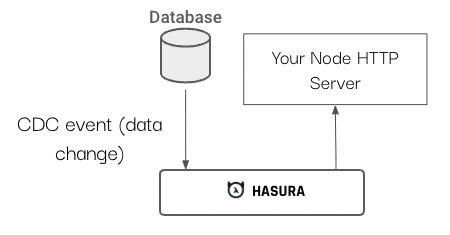
Run async scheduled events using a Node REST API and Hasura GraphQL
Databases like PostgreSQL can run triggers when data changes, with Hasura Event Triggers we can easily call an HTTP endpoint whenever we have one of these events.
Let's send a webhook when a new user is created and print out their name.
In the Hasura Console add a
usertable with aTextcolumnnameand the frequently usedUUIDcolumn id.In the Event Trigger tab, on the
usertable, check the insert via console trigger operations.The Event Trigger payload schema can be found in the docs. We make an interface in TypeScript to represent this:
interface EventPayload<New, Old> {created_at: string;delivery_info: {current_retry: number;max_retries: number;};event: {data: {new: New;old: Old;};op: "INSERT" | "UPDATE" | "DELETE" | "MANUAL";session_variables: Record<string, string>;trace_context: {span_id: string;trace_id: string;};};id: string;table: {name: string;schema: string;};trigger: {name: string;};}Now we make a REST controller that handles the event.
interface UserTable {id: string;name: string;}const eventRouter: Router = express.Router();eventRouter.post("",async (req: Request<object, object, EventPayload<UserTable, null>>,res: Response) => {console.log(req.body);res.sendStatus(200);});export { eventRouter };Add the route to
src/main.ts.app.use("/event", eventRouter);
When you add a user in Hasura your Express server should receive the event.
Example: Querying GraphQL with Node Client graphql-request
To query a GraphQL endpoint from Node we use graphql-request.
Create
client-codegen.ts.import type { CodegenConfig } from "@graphql-codegen/cli";const client: CodegenConfig = {overwrite: true,schema: "<GraphQL URL>",documents: "src/**/*.ts",generates: {"./src/gql/client/": {preset: "client",plugins: [],},},};export default client;Modify the
package.jsoncodegen script.{"scripts": {"codegen": "graphql-codegen --config server-codegen.ts && graphql-codegen --config client-codegen.ts"}}In
src/action/action.tswe add our query. We are going to fetch all users.import { GraphQLClient } from "graphql-request";import { graphql } from "../gql/client/index";const userQuery = graphql(`query AllUsers {users: user {id}}`);Run codegen
npm run codegen.In our action handler query all users.
actionRouter.post("",async (req: Request<object, object, ActionPayload<loginArgs>>,res: Response<LoginResponse>) => {const { users } = await request("http://localhost:8080/v1/graphql",userQuery);console.log(users, req.body);res.send({ AccessToken: "test" });});Call your action REST endpoint and you should see all users printed out!
Summary
When developing backend applications, we may need to write custom business logic. When we use Hasura, it autogenerates most of our API but gives us nice hooks for this custom logic.
We've gone over a few ways you can use the power of Node and TypeScript. This is also improving a lot more with Hasura v3, which lets you write TypeScript functions that get mapped to a GraphQL API. We will update this guide once that becomes GA.
See the server source code on GitHub.
If you use Hasura and are ready to go to production, check out Hasura Cloud for a fully managed Hasura deployment.

Build apps and APIs 10x faster
Built-in authorization and caching
8x more performant than hand-rolled APIs






