Create relationship
Create relationships across subgraphs
Finally, we'll create a relationship between entities in our different subgraphs. Our Chinook data source is a
music-based dataset that contains a type called Artist. We have a favorite_artist colum on our app_users table.
In /app/app_connector/models/Users.hml, let's add the following relationship:
---kind: Relationshipversion: v1definition:name: user_to_favorite_artistsource: Userstarget:model:subgraph: chinookname: ArtistrelationshipType: Objectmapping:- source:fieldPath:- fieldName: favoriteArtisttarget:modelField:- fieldName: artistId
Remember, you can use LSP to assist in authoring metadata.
While you can copy and paste the value above, don't forget that LSP is available to assist you when writing your own relationships, permissions, and any other metadata-authoring tasks you'll need to complete.
We can then run the following query and see that — rightly so — everyone's favorite artist is AC/DC 🤘
query MyQuery {app_users {nameuser_to_favorite_artist {name}}}
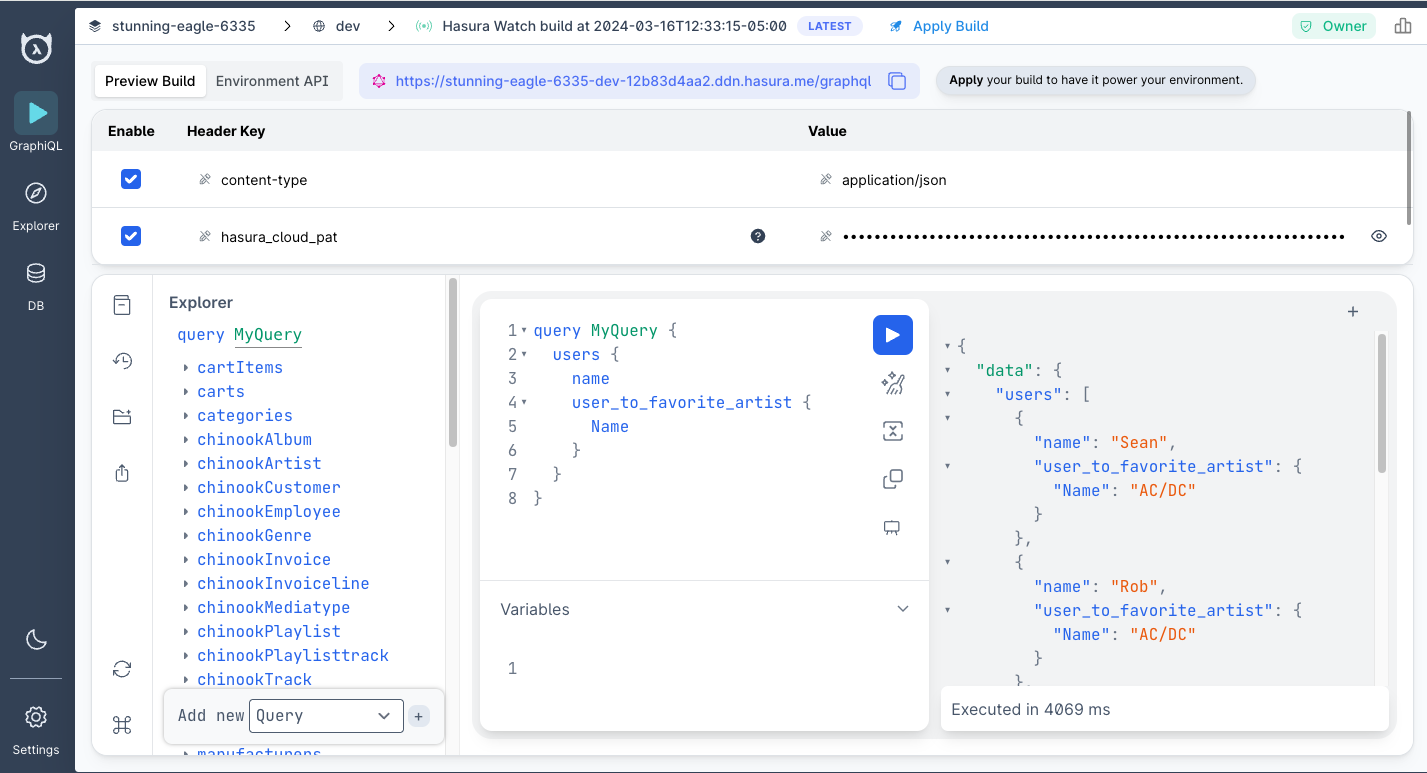
What just happened?
We created a second subgraph called chinook and added a completely separate data source using the chinook_connector.
We then created a relationship across these subgraphs to link disparate tables and make them available via a single
query. We can even visualize this using the console's explorer, available in the left-hand navigation.
Build apps and APIs 10x faster
Built-in authorization and caching
8x more performant than hand-rolled APIs






