GraphQL Response Caching
Hasura GraphQL Engine (OSS) supports Query Response Caching, where the internal representation of the fully qualified GraphQL AST is cached. When a GraphQL query is made, the generated SQL is a prepared statement with the right session variables hitting the database. These prepared statements help in making queries fast. Read more about Query Response Caching
Now, some queries are more frequently accessed than others. Typically, there could be latency and slow response times due to the following:
- Size of the response
- Location of the server
- Number of concurrent API calls etc
Hasura Cloud provides support for caching query responses. When queried with the cache configuration, Hasura Cloud ensures that the response data is cached to improve response time.
Note: The Standard tier comes with GraphQL Response Caching enabled by default and a cache size of up to 100 MB.
How does caching work?
Hasura has metadata about the data models across data sources and the authorization rules at the application level. This helps Hasura to provide end-to-end application caching.
A GraphQL query’s response can be cached only if the following conditions hold:
- The query does not make use of remote schemas or remote joins
- The query and any related user permissions do not make use of session variables
- The response JSON is under 100KB in size
Cached responses are stored for a period of time in an LRU (least recently used) cache and removed from the cache as needed based on usage.
For example, the users records in the slack model will be frequently accessed. We can cache this through the following query:
query slackUsersCached @cached {users {idnamedisplay_namebio}}
Note that in the above query, we have included the @cached directive to specify that this query needs to be cached. By default the response for this is cached for 60 seconds.
Now let's verify if the response was cached successfully. Ideally, the HTTP response will include a Cache-Control header that indicates the maximum number of seconds for the returned response to remain in the cache. After that time, it will be removed from the LRU.
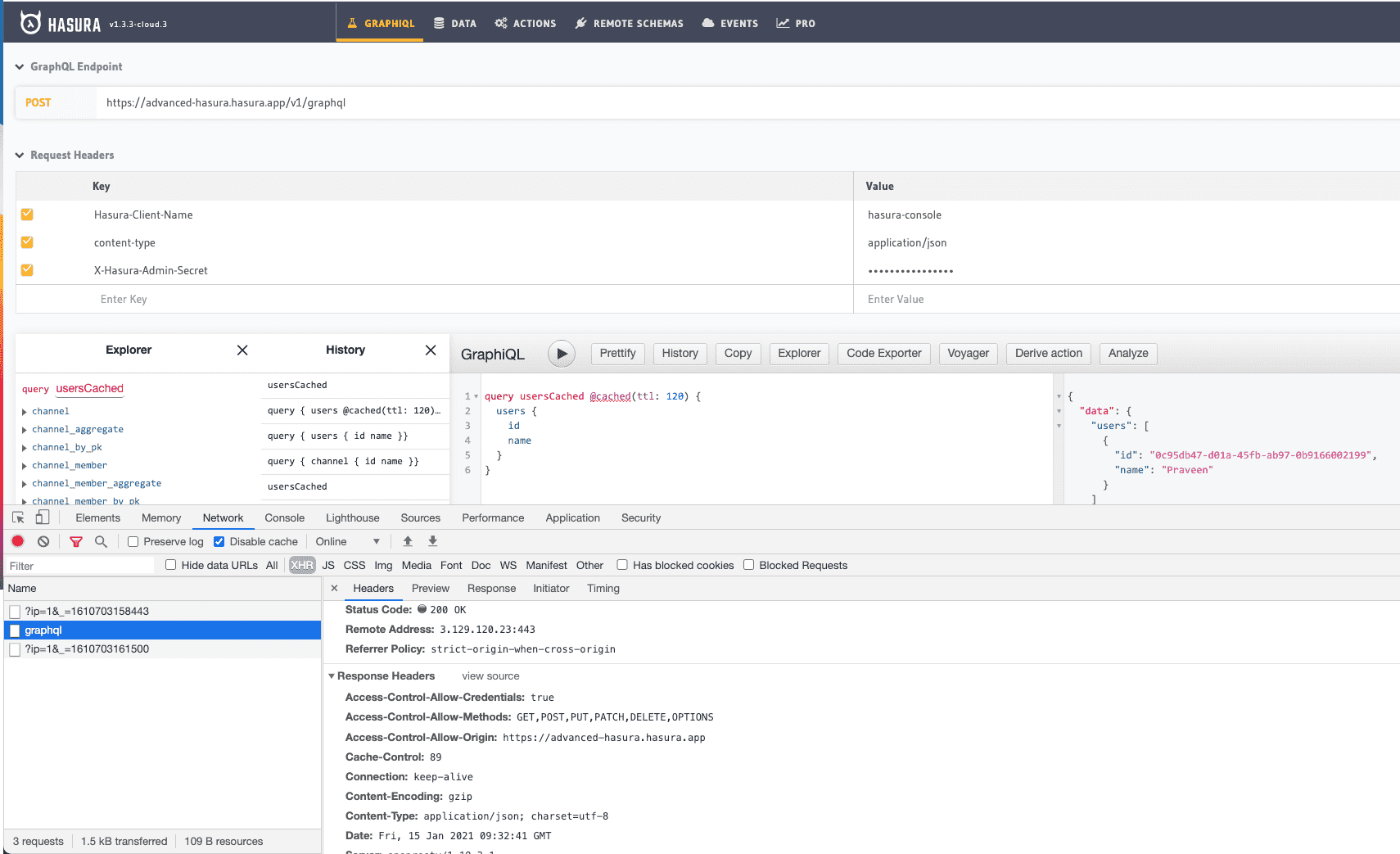
You can see the value of the Cache-Control response header indicating how much more time in seconds this response would be cached.
Cache Lifetime
The maximum lifetime of an entry in the cache can be controlled using the TTL argument to the @cached query directive. The value is an integer number of seconds:
query usersCached @cached(ttl: 300) {users {idnamedisplay_namebio}}
We have included a ttl argument for the @cached directive in the above query. This is used to specify how long the cache needs to be in place.
The maximum allowed value is 300 seconds (5 minutes), which we have used in the above query.
Now reading the Cache-Control header, you will know how long the query will be in the cache. The clients can typically use this header to keep track of cached responses.
Build apps and APIs 10x faster
Built-in authorization and caching
8x more performant than hand-rolled APIs






