SELECT
SELECT is a T-SQL command of the type Data Query Language (DQL). A SELECT query is used to retrieve rows from a table.
Prerequisite
- MS SQL Server database installed on Windows or Linux or on Mac OS.
- SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) or
sqlcmdutility.
Download sample database
Download the sample database here: AdventureWorks2019.bak.
Select the OLTP data that is used for most typical online transaction processing workloads.
Move the .bak file to your SQL Server backup location. The default location for a default instance of SQL Server 2019 is: C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL15.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Backup.
Restore to SQL Server
Next, you can use the .bak file to restore the sample database into your SQL Server.
Before you begin
- In the Object Explorer, click to expand AdventureWorks2019 > Tables.
- Select HumanResources.Employee and then click New Query from the top ribbon bar. where,
HumanResourcesis the schema name.Employeeis a table in the above schema.
- Run the below statement to use the 'AdventureWorks2019' sample database.
USE AdventureWorks2019;GO
SELECT T SQL statements
The statement is used to retrieve all of the columns or some columns based on certain clauses.
Syntax
SELECT [Arguments]FROM <table_name>WHERE <search_condition>GROUP BY <group_by_expression>HAVING <search_condition>ORDER BY <order_expression> [ASC|DESC]
The Arguments may be any of the following:
- ALL: The result set returns all the rows and columns and may include duplicate values. 'ALL' is the default.
- DISTINCT: Returns unique rows.
- column_list: A single column name or a list of comma-separated column names.
- *: The result set returns all columns and rows from a table/view, as specified in the 'FROM' clause.
Some of the common select query clauses are:
Select to retrieve all rows and columns
SELECT * FROM HumanResources.Employee;
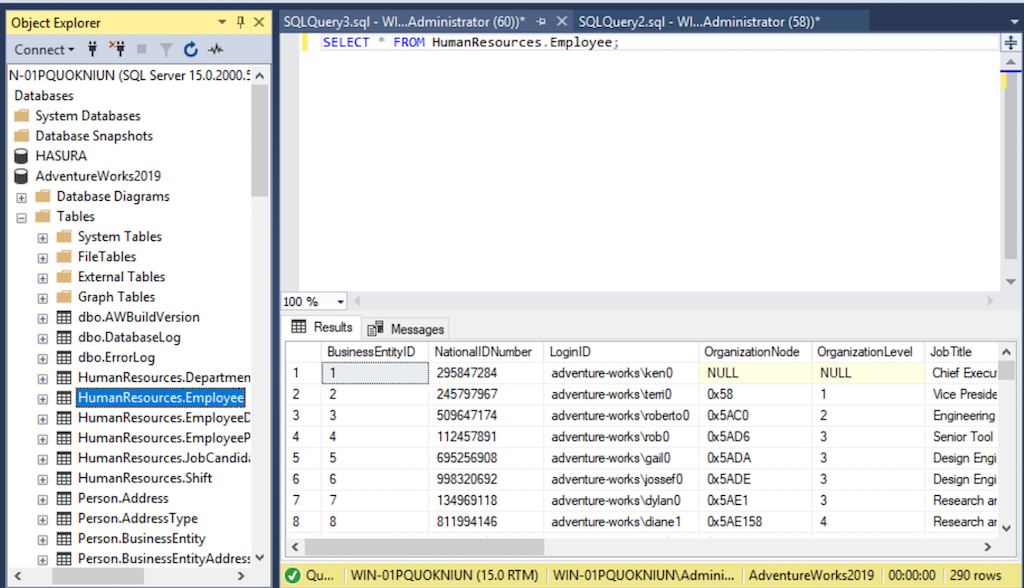
Get the count of all rows in a table
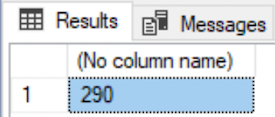
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM HumanResources.Employee;
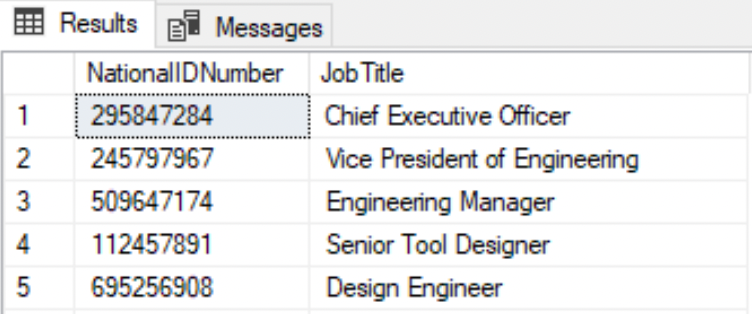
Select certain columns
SELECT NationalIDNumber, JobTitle FROM HumanResources.Employee;
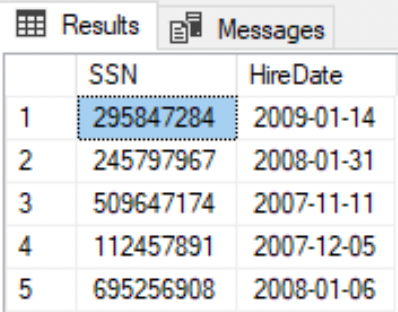
Select columns and print an alias column name
--First column is renamed as 'SSN'SELECT NationalIDNumber AS 'SSN', HireDateFROM HumanResources.Employee;
Derived column
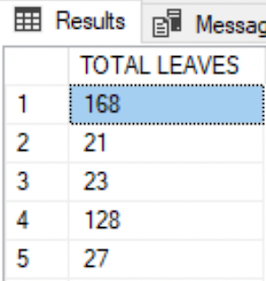
A derived column is based on the calculation results on another column(s).
SELECT ( VacationHours + SickLeaveHours ) AS 'TOTAL LEAVES' FROM HumanResources.Employee;
Select distinct rows
DISTINCT keyword removes any duplicate row(s).
The query results in 290 rows
SELECT JobTitle FROM HumanResources.Employee;
The query results in 67 rows
SELECT DISTINCT JobTitle FROM HumanResources.Employee;
Limit the rows with the WHERE clause
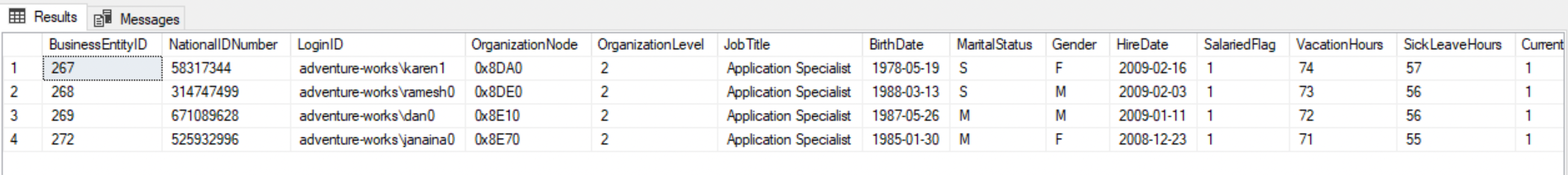
- Equal to
=operator
--List all the employees with a specific job titleSELECT * FROM HumanResources.EmployeeWHERE JobTitle='Application Specialist';
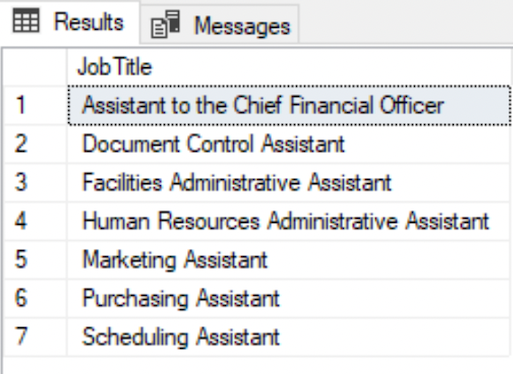
LIKE
The LIKE clause retrieves only the rows that match the search pattern (regular expression).
--Search with a regular expression - 'Assistant' anywhere in the textSELECT DISTINCT JobTitle FROM HumanResources.EmployeeWHERE JobTitle LIKE '%Assistant%';
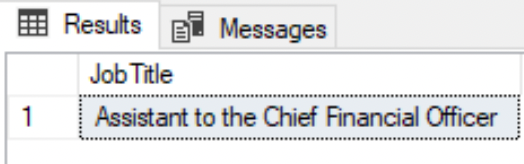
--Job Title that begins with 'Assistant' followed by any textSELECT DISTINCT JobTitle FROM HumanResources.EmployeeWHERE JobTitle LIKE 'Assistant%';
--Job Title that ends with 'Assistant'SELECT DISTINCT JobTitle FROM HumanResources.EmployeeWHERE JobTitle LIKE '%Assistant';
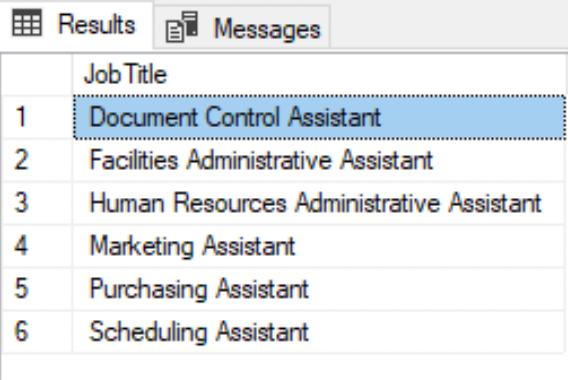
--Job Title that begins with 'Human' and ends with 'Assistant'SELECT DISTINCT JobTitle FROM HumanResources.EmployeeWHERE JobTitle LIKE 'Human%Assistant';
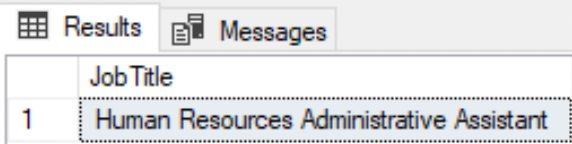
NOT LIKE
-- Retrieve all the roles, where 'Job Title' is not like the given string.SELECT DISTINCT JobTitle FROM HumanResources.EmployeeWHERE JobTitle NOT LIKE '%Supervisor%';
- LOGICAL
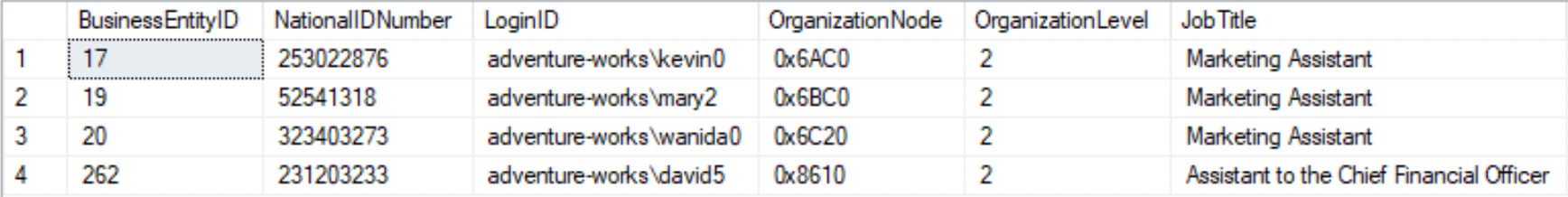
AND
--Select the rows where both the `Where` conditions are trueSELECT * FROM HumanResources.EmployeeWHERE OrganizationLevel=2 AND JobTitle LIKE '%Assistant%';
- LOGICAL
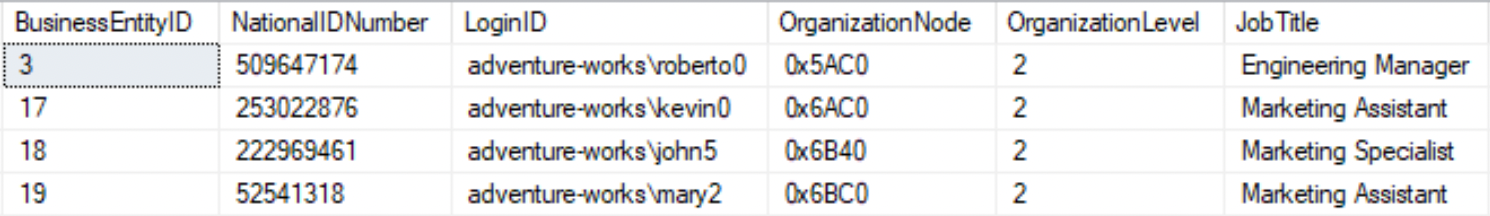
OR
--Show the rows where any one of the conditions is trueSELECT * FROM HumanResources.EmployeeWHERE OrganizationLevel=2 OR JobTitle LIKE '%Assistant%';
IN
SELECT * FROM HumanResources.EmployeeWHERE OrganizationLevel IN (1,3);
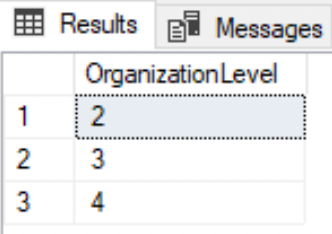
BETWEEN
--Rows with OrganizationLevel that include 2,3, AND 4.SELECT DISTINCT OrganizationLevel FROM HumanResources.EmployeeWHERE OrganizationLevel BETWEEN 2 and 4;
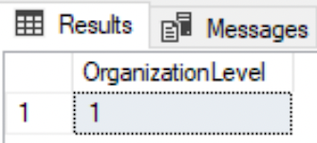
NOT
--Rows with OrganizationLevel that do not include 2,3, AND 4.SELECT DISTINCT OrganizationLevel FROM HumanResources.EmployeeWHERE OrganizationLevel NOT BETWEEN 2 and 4;
Group BY
The GROUP BY clause is used to categorize the result set based on a single or multiple columns.
- The clause can be applied only on the column(s) that are listed in the
SELECTquery - All non-aggregate columns listed in the
SELECTquery must be included in theGROUP BYclause. Or, the column on which you apply theGROUP BYclause must be a non-aggregate column.
--Get the count of employees in each department.SELECT COUNT(NationalIDNumber) AS 'Count of employees', JobTitleFROM HumanResources.EmployeeGROUP BY JobTitle;
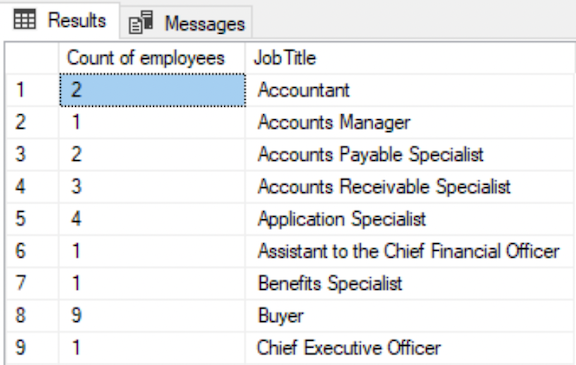
HAVING
Is used along with the GROUP BY clause to limit the result set obtained by the Group by clause.
It specifies a search condition on the Groups.
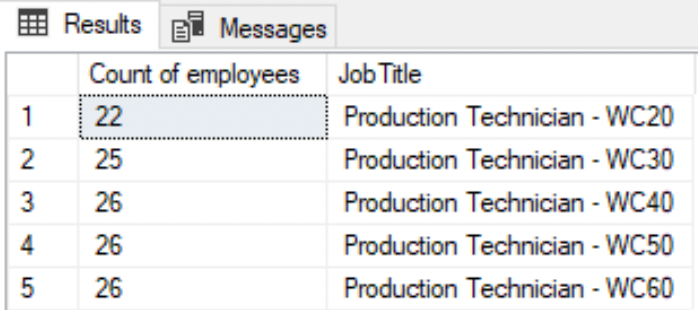
--List the department that has more than 25 employeesSELECT COUNT(NationalIDNumber) AS 'Count of employees', JobTitleFROM HumanResources.EmployeeGROUP BY JobTitleHAVING COUNT(NationalIDNumber) > 20;
ORDER BY
The result set can be sorted by any column's value in ascending (ASC) or descending (DESC) order.
By default, the rows are sorted in ascending order. To change the order in descending order run the following statement:
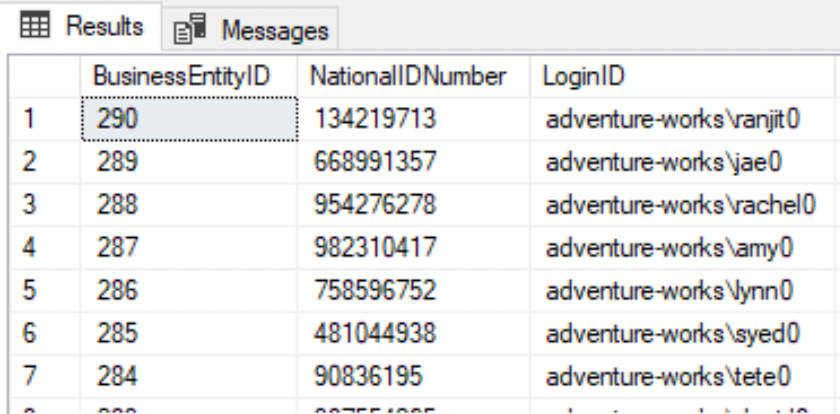
--Rows ordered in descending order of BusinessEntityIDSELECT * FROM HumanResources.EmployeeORDER BY BusinessEntityID DESC;
SELECT INTO
Use the SELECT INTO statement to create another (backup) table from an existing table.
USE AdventureWorks2019;GOSELECT *INTO PRODUCTION.PRODUCT_BACKUPFROM PRODUCTION.PRODUCT;
Build apps and APIs 10x faster
Built-in authorization and caching
8x more performant than hand-rolled APIs






