JOINS (MS SQL Server)
T-SQL statements use joins to retrieve data from two or more tables.
You can use joins in the FROM or WHERE clause.
Syntax
SELECT <arguments> FROM <first_table>[ LEFT | RIGHT | INNER ] JOIN <second_table>ON <join_condition>
<arguments>: use*to select all rows, or use column name(s) to retrieve selected columns.<first_table>: First table name<second_table>: Second table name<join_condition>: condition on which the two tables have a matching pair. This condition has to evaluate to be true.
Pre-requisite
- MSSQL Server
- SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS)
Prepare the tables
- Create the tables
--Use the 'HASURA' database that you createdUSE HASURA;GO--Create the first tableCREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE(id int PRIMARY KEY,name VARCHAR(10) not null,--A foreign key reference to 'id' column from the 'department'dept_id int FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES dbo.DEPARTMENT (id) NULL);--Create the second tableCREATE TABLE DEPARTMENT(id int PRIMARY KEY,dept_name VARCHAR(10),location VARCHAR(10));
- Insert data
--Begin by entering into the 'DEPARTMENT' table first respecting the foreign key referenceINSERT INTO DEPARTMENT VALUES (29, 'R&D', 'USA');INSERT INTO DEPARTMENT VALUES (17, 'HR', 'England');INSERT INTO DEPARTMENT VALUES (9, 'Finance', 'Germany');INSERT INTO DEPARTMENT VALUES (4, 'Product', 'India');--Insert into the 'EMPLOYEE' tableINSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (1, 'Zuckerberg', NULL);INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (3, 'Jobs', 17);INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (2, 'Turing', 9);INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (4, 'Musk', 9);INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (5, 'Tesla', 9);
- See the result sets of both tables.
SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE;SELECT * FROM DEPARTMENT;
LEFT JOIN
--All employees, including the ones that do not have a department assigned, are listed.SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE eLEFT JOIN DEPARTMENT dON e.dept_id=d.id;
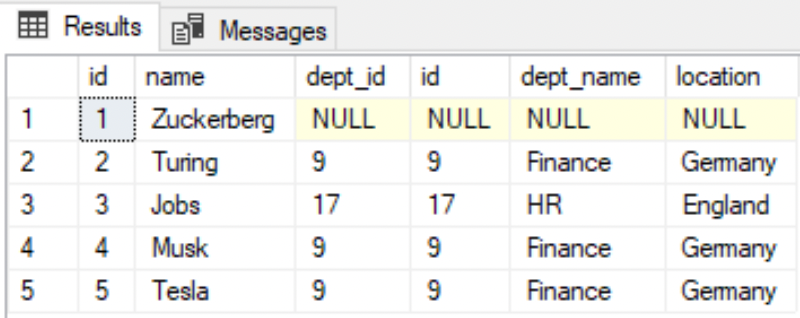
RIGHT JOIN
--All departments are listed, but only the employees that have a matching dept_id are shownSELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE eRIGHT JOIN DEPARTMENT dON e.dept_id=d.id;
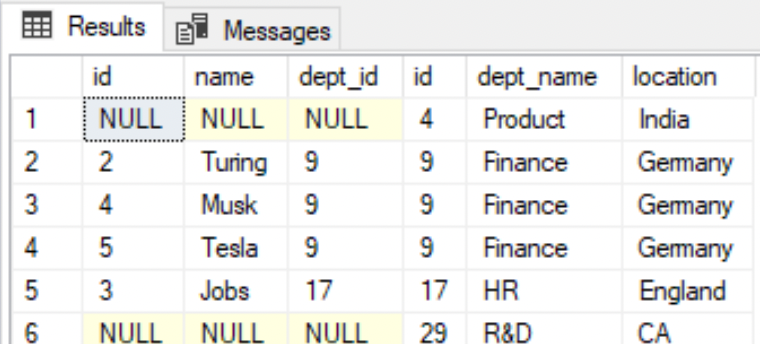
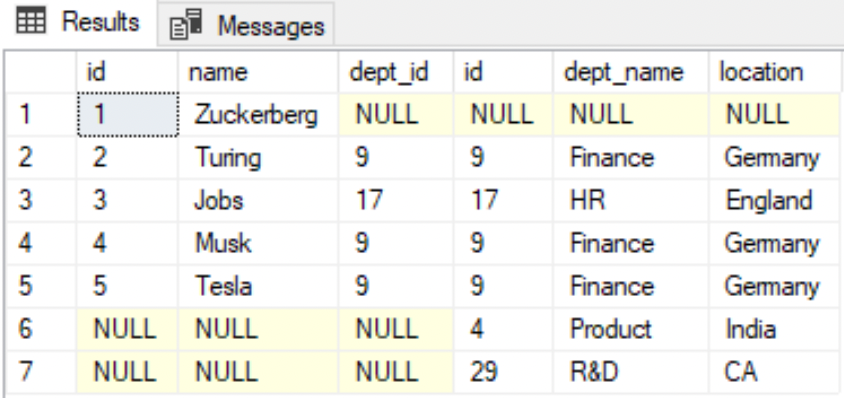
FULL JOIN
--All employee and department rows are listed including the ones with no matching recordsSELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE eFULL JOIN DEPARTMENT dON e.dept_id=d.id;
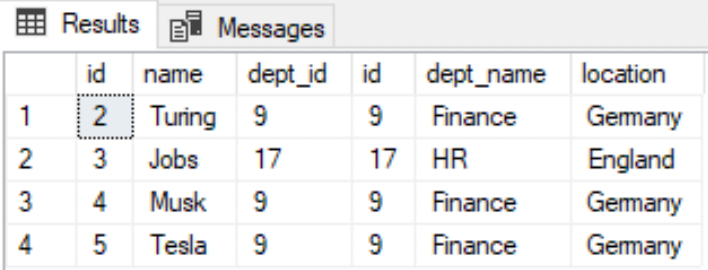
INNER JOIN
--Retrieve only the matching rows from both the tablesSELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE eINNER JOIN DEPARTMENT dON e.dept_id=d.id;
The keyword INNER is optional.
If you omit this and just use JOIN alone, the join defaults to the type INNER JOIN.
Did you find this page helpful?
Start with GraphQL on Hasura for Free
Build apps and APIs 10x faster
Built-in authorization and caching
8x more performant than hand-rolled APIs






