Views
A View is a virtual table that is created by fetching data from one or more tables by a SQL query.
Just like a table, a view has data in the form of rows and columns. The content in a view is dynamically produced from the referencing table.
Views are generally used to:
- Simplify, customize, and filter data.
- Provide security by granting access to specific users on the views.
- Improve transaction performance
Syntax
CREATE VIEW <view_name> ASSELECT [* | <columns_list>]FROM <table_name>[LEFT | RIGHT | FULL] JOIN <another_table> --optionalWHERE <condition> --optional
<view_name>: A logical name for the view abiding to variables naming rules.[* | <columns_list>]:SELECTquery with select all (*) option, or a comma-separated list of column names.<table_name>: First table being referenced.<another_table>: Next table name being referenced by the join query.<condition>: TheWHEREclauses are applied to filter the result sets.
Limitations and Restrictions
- A view can be created only in the current database.
- A view can have a maximum of 1,024 columns.
Create views
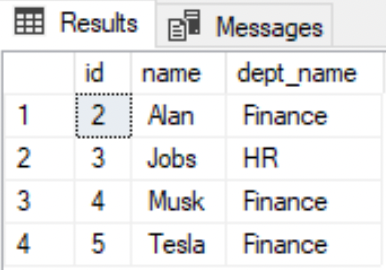
--Use the database that you createdUSE HASURA;GO--View that references 2 tables based on the join conditionCREATE VIEW vempDetails ASSELECT e.id, e.name, d.dept_nameFROM EMPLOYEE eINNER JOIN DEPARTMENT dON e.dept_id=d.id;--Retrieve data in a view as:SELECT * FROM vempDetails;
Modify data through views
A view is only updatable when it references a single table.
- Create a view referencing a single table
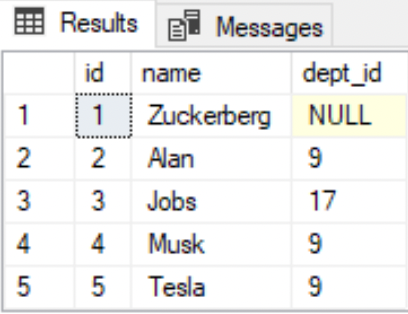
--View that references a single tableCREATE view v_employee ASSELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE;--Retrieve all the rows from the viewSELECT * FROM v_employee;
- Update the view
--Insert a new row. The dept_id (29) must already be present in the 'Department' tableINSERT INTO v_employee VALUES(6, 'Dell', 29);--Update valuesUPDATE v_employee SET name='Torvalds' where name='Dell';--Delete dataDELETE FROM v_employee WHERE id=6;
Alter views structure
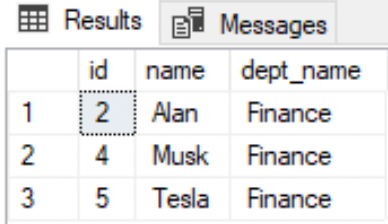
--Alter the view to filter the result set with a `WHERE` clauseALTER VIEW vempDetails ASSELECT e.id, e.name, d.dept_nameFROM EMPLOYEE eINNER JOIN DEPARTMENT dON e.dept_id=d.idWHERE d.dept_name='Finance';--Retrieve all the rows from the viewSELECT * FROM dbo.vempDetails;
Drop views
--Drop the view from the databaseDROP VIEW vempDetails;
Dropping a view does not affect the underlying referencing tables.
Display the views definition
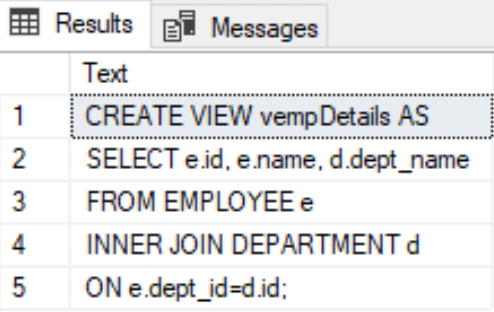
Use the system stored procedure sp_helptext to display the definition of the views (or any other user-defined objects).
--Pass the view name as an argument within single quotessp_helptext 'dbo.vempDetails';
Did you find this page helpful?
Start with GraphQL on Hasura for Free
Build apps and APIs 10x faster
Built-in authorization and caching
8x more performant than hand-rolled APIs






